正在加载图片...
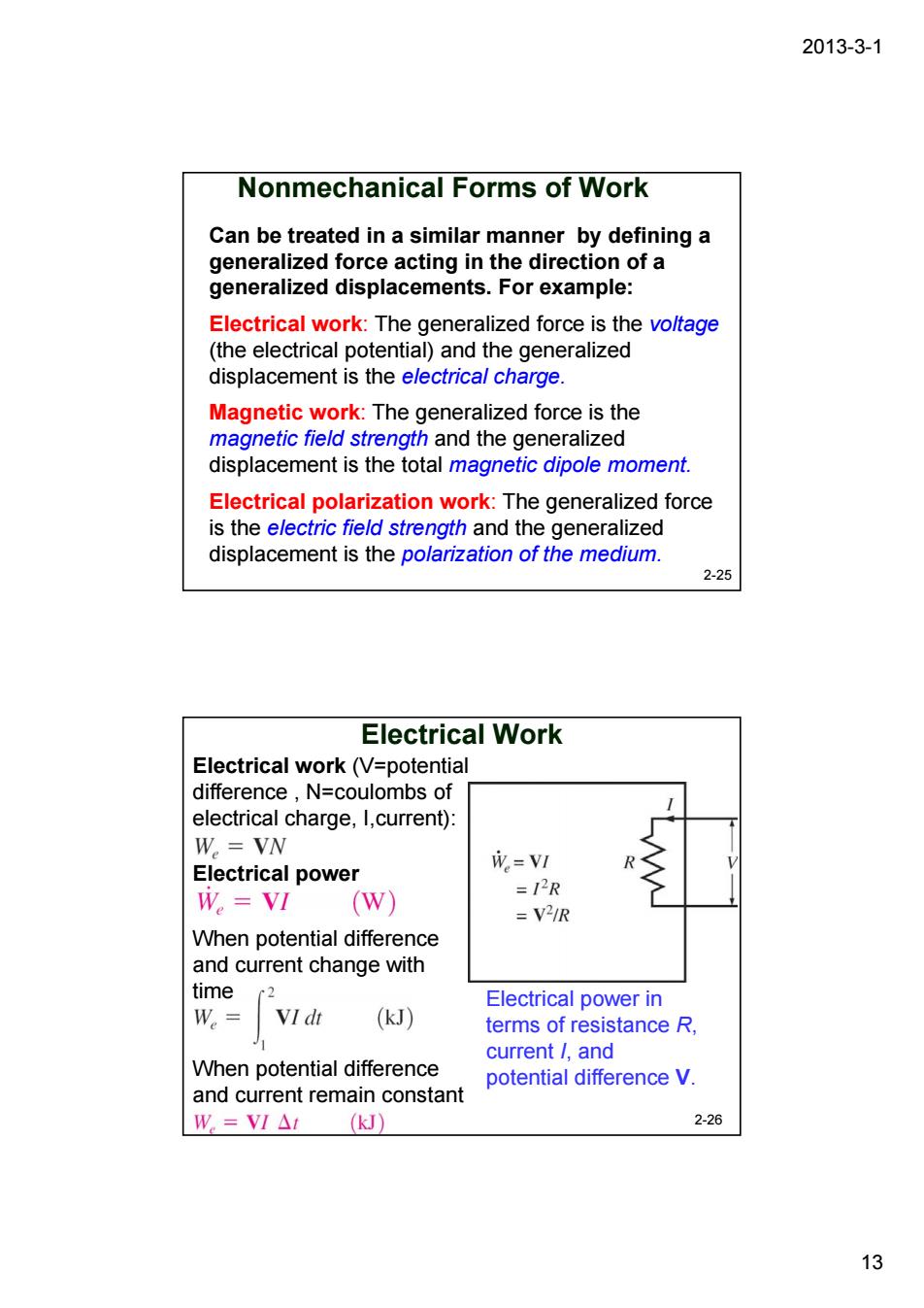
2013-3-1 Nonmechanical Forms of Work Can be treated in a similar manner by defining a generalized force acting in the direction of a generalized displacements.For example: Electrical work:The generalized force is the vo/tage (the electrical potential)and the generalized displacement is the electrical charge. Magnetic work:The generalized force is the magnetic field strength and the generalized displacement is the total magnetic dipole moment. Electrical polarization work:The generalized force is the electric field strength and the generalized displacement is the polarization of the medium. 2-25 Electrical Work Electrical work(V=potential difference,N=coulombs of electrical charge,I,current): W.=VN Electrical power 成=VI W。=V (W) =12R =V21R When potential difference and current change with time Electrical power in W.= (kJ) terms of resistance R, When potential difference current /and potential difference V. and current remain constant W=VI△(kJ) 2-26 132013-3-1 13 Can be treated in a similar manner by defining a generalized force acting in the direction of a generalized displacements. For example: Electrical work: The generalized force is the voltage (the electrical potential) and the generalized displacement is the electrical charge. Magnetic work: The generalized force is the magnetic field strength and the generalized displacement is the total magnetic dipole moment. Electrical polarization work: The generalized force is the electric field strength and the generalized displacement is the polarization of the medium. 2-25 Nonmechanical Forms of Work 2-26 Electrical Work Electrical power in terms of resistance R, current I, and potential difference V. Electrical work (V=potential difference , N=coulombs of electrical charge, I,current): Electrical power When potential difference and current change with time When potential difference and current remain constant