正在加载图片...
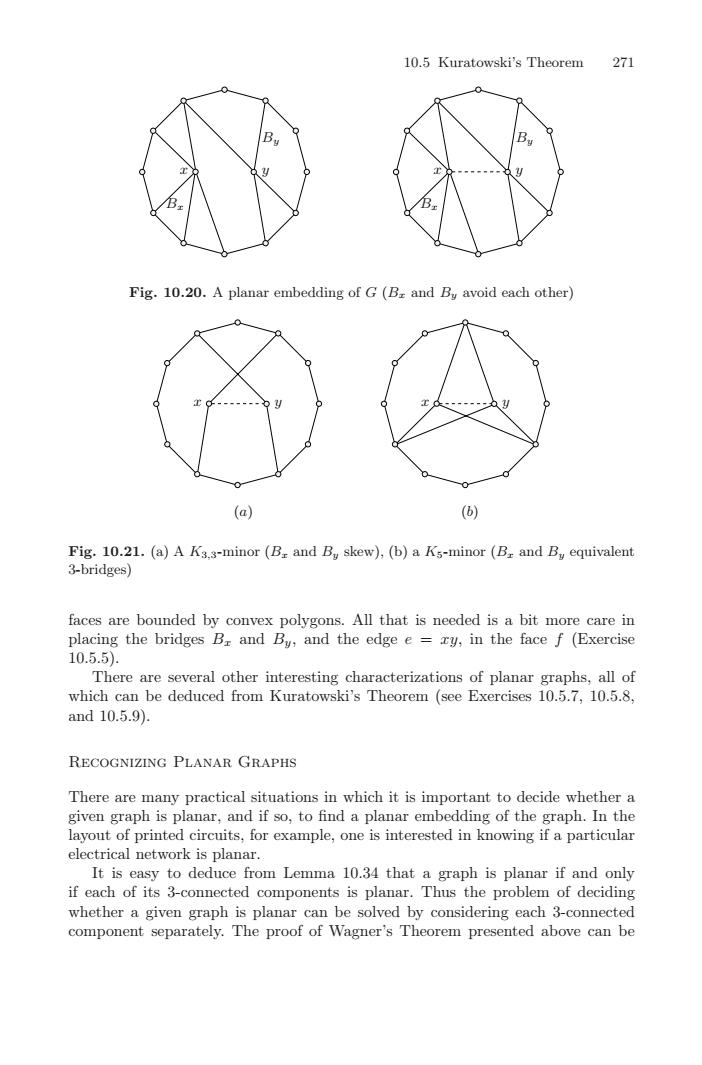
27103Fig.10.20.Aplanar embedding of G (Br and Byavoid each other)Edb-(a)(6)Fig. 10.21. (a)A Ka.s-minor (Br and B, skew), (b)a Ks-minor (Br and B equivalent3-bridges)faces are bounded by convex polygons. All that is needed is a bit more care inplacing the bridges Br and By, and the edge e = ry, in the face f (Exercise10.5.5).There are several other interesting characterizations of planar graphs, all ofwhich can be deduced from Kuratowski's Theorem (see Exercises 10.5.7, 10.5.8,and 10.5.9).RECOGNNGPLANARGRAPHS in which it is important to decide whetherThegiven graph is planar, and ifso, tofind a planarembedding of thegraph.In thelayout of printed circuits,for example, one is interested in knowing if a particularelectrical networkisplanarIt is easy to deduce from Lemma 10.34 that a graph is planar if and onlyif each of its 3-connected components is planar.Thus the problem of decidingwhether a given graph is planar can be solved by considering each 3-connectedcomponent separately.The proof of Wagner's Theorem presented above can be10.5 Kuratowski’s Theorem 271 x y y x Bx Bx By By Fig. 10.20. A planar embedding of G (Bx and By avoid each other) x y y x (a) (b) Fig. 10.21. (a) A K3,3-minor (Bx and By skew), (b) a K5-minor (Bx and By equivalent 3-bridges) faces are bounded by convex polygons. All that is needed is a bit more care in placing the bridges Bx and By, and the edge e = xy, in the face f (Exercise 10.5.5). There are several other interesting characterizations of planar graphs, all of which can be deduced from Kuratowski’s Theorem (see Exercises 10.5.7, 10.5.8, and 10.5.9). Recognizing Planar Graphs There are many practical situations in which it is important to decide whether a given graph is planar, and if so, to find a planar embedding of the graph. In the layout of printed circuits, for example, one is interested in knowing if a particular electrical network is planar. It is easy to deduce from Lemma 10.34 that a graph is planar if and only if each of its 3-connected components is planar. Thus the problem of deciding whether a given graph is planar can be solved by considering each 3-connected component separately. The proof of Wagner’s Theorem presented above can be