正在加载图片...
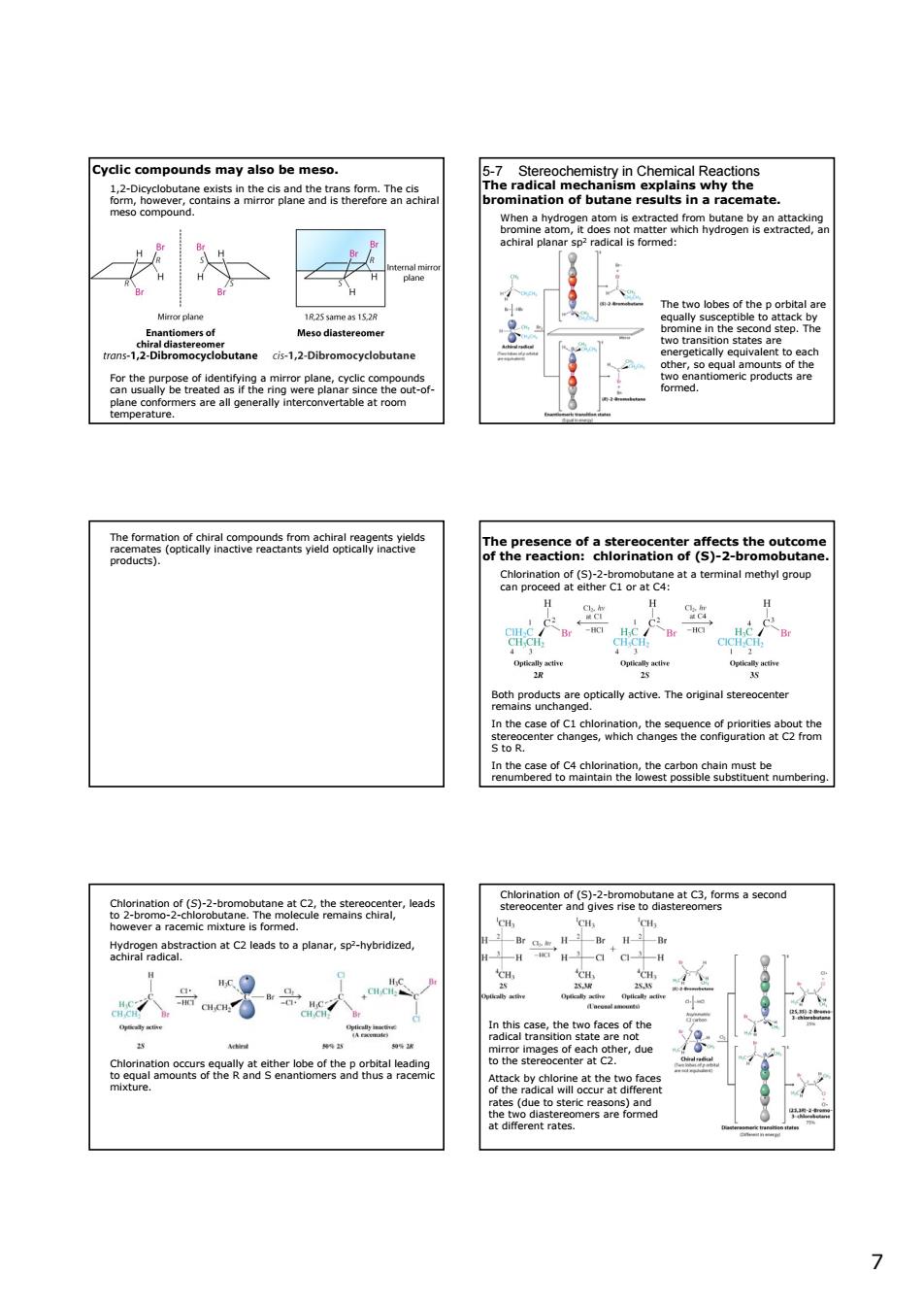
Cycic compounds may also be meso. ce89g y89aa82 Chpoegth2-taoeaatatomnalmethngroup 人等】 w n the c 6292sert品e6e t9rg7eabtndonata1essoapanar,sp-hybridzed 人号人 88然2 77 Cyclic compounds may also be meso. 1,2-Dicyclobutane exists in the cis and the trans form. The cis form, however, contains a mirror plane and is therefore an achiral meso compound. For the purpose of identifying a mirror plane, cyclic compounds can usually be treated as if the ring were planar since the out-ofplane conformers are all generally interconvertable at room temperature. 5-7 Stereochemistry in Chemical Reactions The radical mechanism explains why the bromination of butane results in a racemate. When a hydrogen atom is extracted from butane by an attacking bromine atom, it does not matter which hydrogen is extracted, an achiral planar sp2 radical is formed: The two lobes of the p orbital are equally susceptible to attack by bromine in the second step. The two transition states are energetically equivalent to each other, so equal amounts of the two enantiomeric products are formed. The formation of chiral compounds from achiral reagents yields racemates (optically inactive reactants yield optically inactive products). The presence of a stereocenter affects the outcome of the reaction: chlorination of (S)-2-bromobutane. Chlorination of (S)-2-bromobutane at a terminal methyl group can proceed at either C1 or at C4: Both products are optically active. The original stereocenter remains unchanged. In the case of C1 chlorination, the sequence of priorities about the stereocenter changes, which changes the configuration at C2 from S to R. In the case of C4 chlorination, the carbon chain must be renumbered to maintain the lowest possible substituent numbering. Chlorination of (S)-2-bromobutane at C2, the stereocenter, leads to 2-bromo-2-chlorobutane. The molecule remains chiral, however a racemic mixture is formed. Hydrogen abstraction at C2 leads to a planar, sp2-hybridized, achiral radical. Chlorination occurs equally at either lobe of the p orbital leading to equal amounts of the R and S enantiomers and thus a racemic mixture. Chlorination of (S)-2-bromobutane at C3, forms a second stereocenter and gives rise to diastereomers In this case, the two faces of the radical transition state are not mirror images of each other, due to the stereocenter at C2. Attack by chlorine at the two faces of the radical will occur at different rates (due to steric reasons) and the two diastereomers are formed at different rates