正在加载图片...
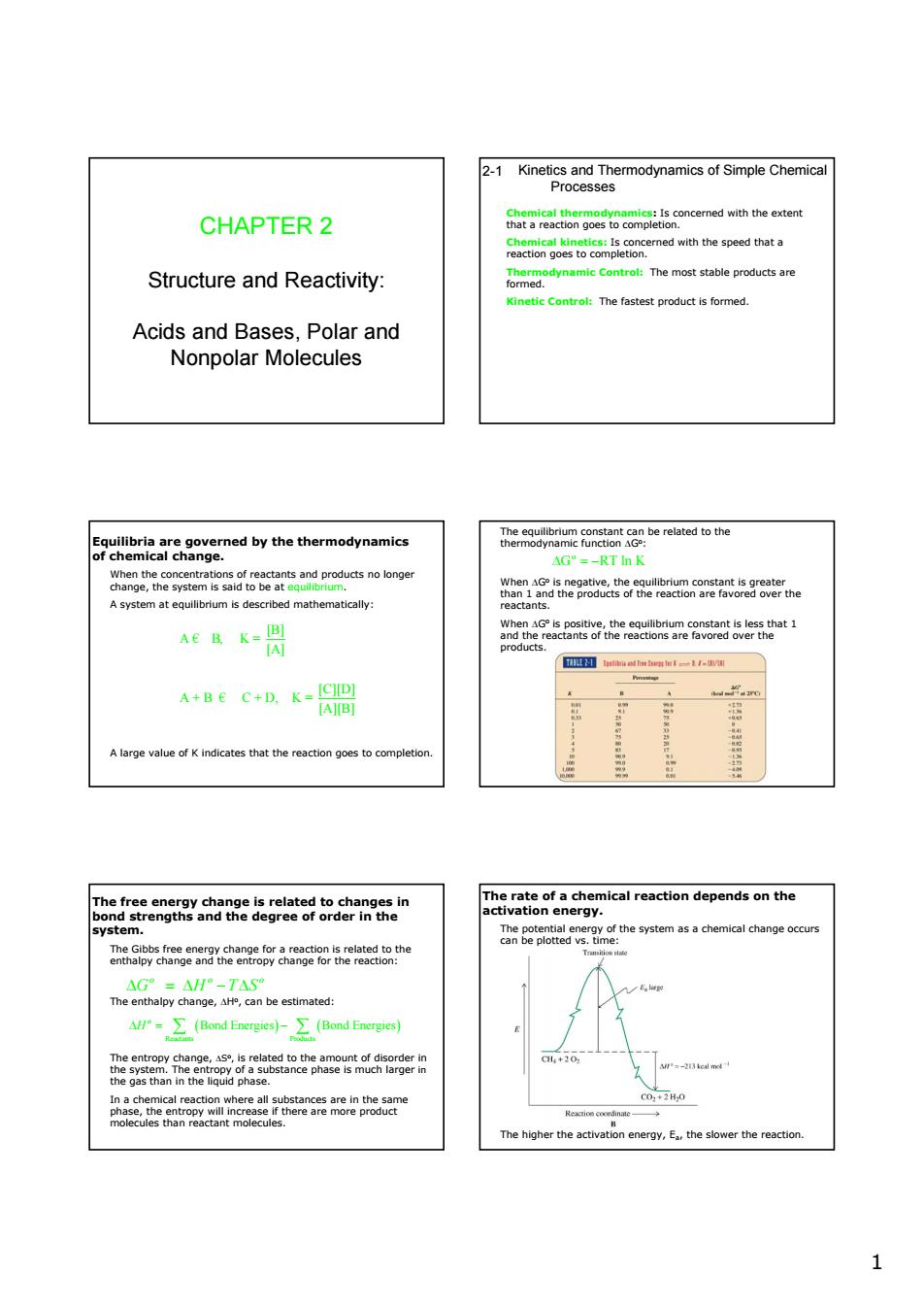
2-1 Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Simple Chemical Processes CHAPTER 2 atarectongoeocome5 that Structure and Reactivity: The products The ormed. Acids and Bases,Polar and Nonpolar Molecules heuwhancf8netantentereatedothe cagen8gno5gocarindpmotsnoonge agaeag6an AEBK-周 s1 ABec+Bk-器 Alarge value K indicates that ga8gch aivtsaevmlcalreactondependsonthe chemical change enhanehe AFr-∑(Bond-)∑(Bond) We-ici nd n energy.E..the slower the rea 1 1 CHAPTER 2 Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Simple Chemical Processes 2-1 Chemical thermodynamics: Is concerned with the extent that a reaction goes to completion. Chemical kinetics: Is concerned with the speed that a reaction goes to completion. Thermodynamic Control: The most stable products are formed. Kinetic Control: The fastest product is formed. Equilibria are governed by the thermodynamics of chemical change. When the concentrations of reactants and products no longer change, the system is said to be at equilibrium. A system at equilibrium is described mathematically: [B] A B, K = [A] [C][D] A + B C + D, K = [A][B] or € € A large value of K indicates that the reaction goes to completion. The equilibrium constant can be related to the thermodynamic function ΔGo: o Δ =− G RT ln K When ΔGo is negative, the equilibrium constant is greater than 1 and the products of the reaction are favored over the reactants. When ΔGo is positive, the equilibrium constant is less that 1 and the reactants of the reactions are favored over the products. The free energy change is related to changes in bond strengths and the degree of order in the system. The Gibbs free energy change for a reaction is related to the enthalpy change and the entropy change for the reaction: o oo Δ =Δ − Δ G H TS The enthalpy change, ΔHo, can be estimated: ( )( ) Reactants Products Bond Energies Bond Energies o Δ= − H ∑ ∑ The entropy change, ΔSo, is related to the amount of disorder in the system. The entropy of a substance phase is much larger in the gas than in the liquid phase. In a chemical reaction where all substances are in the same phase, the entropy will increase if there are more product molecules than reactant molecules. The rate of a chemical reaction depends on the activation energy. The potential energy of the system as a chemical change occurs can be plotted vs. time: The higher the activation energy, Ea, the slower the reaction