正在加载图片...
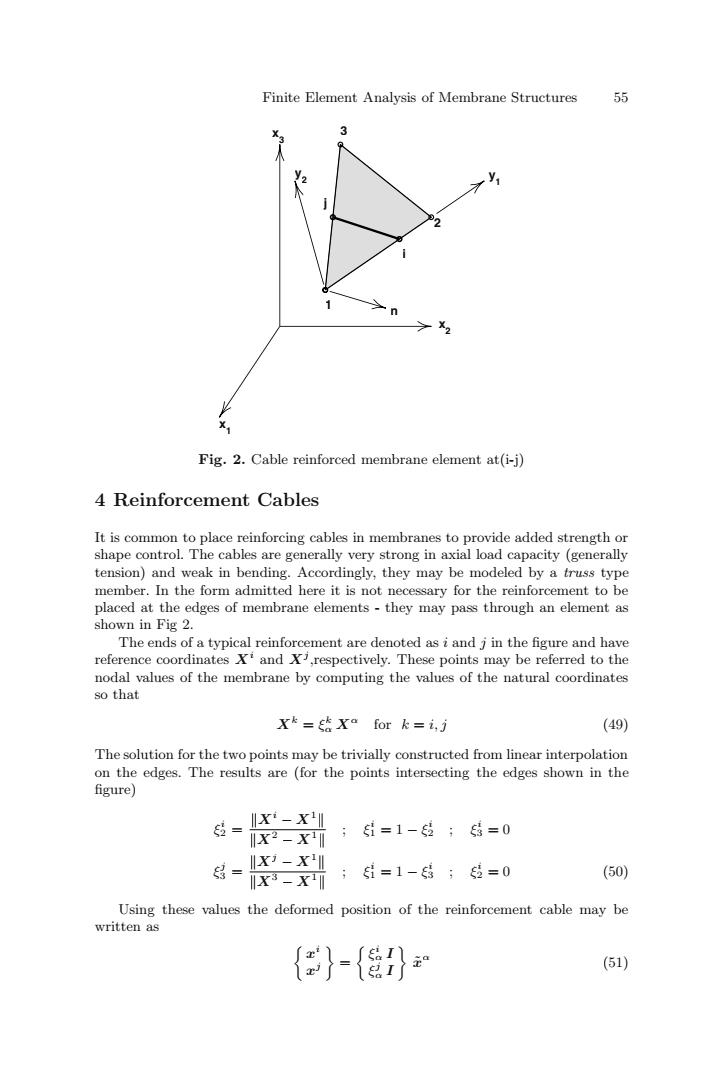
Finite Element Analysis of Membrane Structures 55 3 Fig.2.Cable reinforced membrane element at(i-j) 4 Reinforcement Cables It is common to place reinforcing cables in membranes to provide added strength or shape control.The cables are generally very strong in axial load capacity (generally tension)and weak in bending.Accordingly,they may be modeled by a truss type member.In the form admitted here it is not necessary for the reinforcement to be placed at the edges of membrane elements-they may pass through an element as shown in Fig 2. The ends of a typical reinforcement are denoted as i and j in the figure and have reference coordinates Xi and X,respectively.These points may be referred to the nodal values of the membrane by computing the values of the natural coordinates so that Xko for k=i,j (49) The solution for the two points may be trivially constructed from linear interpolation on the edges.The results are (for the points intersecting the edges shown in the figure) 货=IK-x X2-X ;i=1-;结=0 X3-X川 X3-X i=1-结;经=0 (50) Using these values the deformed position of the reinforcement cable may be written as {}-{升” (51)Finite Element Analysis of Membrane Structures 55 Fig. 2. Cable reinforced membrane element at(i-j) 4 Reinforcement Cables It is common to place reinforcing cables in membranes to provide added strength or shape control. The cables are generally very strong in axial load capacity (generally tension) and weak in bending. Accordingly, they may be modeled by a truss type member. In the form admitted here it is not necessary for the reinforcement to be placed at the edges of membrane elements - they may pass through an element as shown in Fig 2. The ends of a typical reinforcement are denoted as i and j in the figure and have reference coordinates Xi and Xj ,respectively. These points may be referred to the nodal values of the membrane by computing the values of the natural coordinates so that Xk = ξk α Xα for k = i, j (49) The solution for the two points may be trivially constructed from linear interpolation on the edges. The results are (for the points intersecting the edges shown in the figure) ξi 2 = Xi − X1 X2 − X1 ; ξi 1 = 1 − ξi 2 ; ξi 3 = 0 ξj 3 = Xj − X1 X3 − X1 ; ξi 1 = 1 − ξi 3 ; ξi 2 = 0 (50) Using these values the deformed position of the reinforcement cable may be written as % xi xj & = % ξi α I ξj α I & x˜α (51) x2 x3 x1 1 2 3 i j y1 y2 n