正在加载图片...
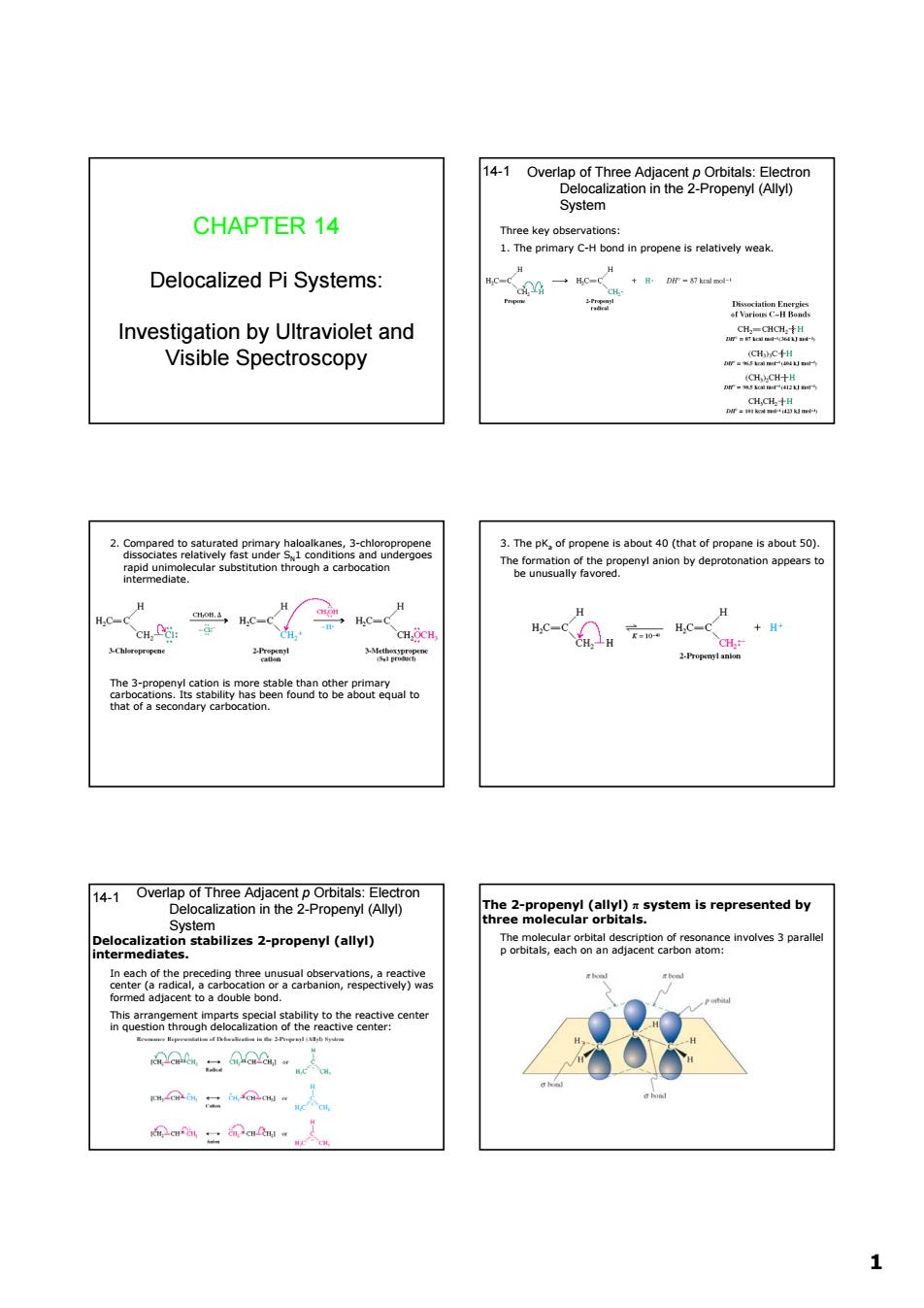
CHAPTER 14 Delocalized Pi Systems: Investigation by Ultraviolet and mkaqt Visible Spectroscopy reermaenyterceen a学 -c H eao 14-1 he2pcaeenrl(ay5ystemisrepresentedby d时 R09g3977e6me 8 1 1 CHAPTER 14 Delocalized Pi Systems: Investigation by Ultraviolet and Visible Spectroscopy Overlap of Three Adjacent p Orbitals: Electron Delocalization in the 2-Propenyl (Allyl) System 14-1 Three key observations: 1. The primary C-H bond in propene is relatively weak. 2. Compared to saturated primary haloalkanes, 3-chloropropene dissociates relatively fast under SN1 conditions and undergoes rapid unimolecular substitution through a carbocation intermediate. The 3-propenyl cation is more stable than other primary carbocations. Its stability has been found to be about equal to that of a secondary carbocation. 3. The pKa of propene is about 40 (that of propane is about 50). The formation of the propenyl anion by deprotonation appears to be unusually favored. Overlap of Three Adjacent p Orbitals: Electron Delocalization in the 2-Propenyl (Allyl) System 14-1 Delocalization stabilizes 2-propenyl (allyl) intermediates. In each of the preceding three unusual observations, a reactive center (a radical, a carbocation or a carbanion, respectively) was formed adjacent to a double bond. This arrangement imparts special stability to the reactive center in question through delocalization of the reactive center: The 2-propenyl (allyl) π system is represented by three molecular orbitals. The molecular orbital description of resonance involves 3 parallel p orbitals, each on an adjacent carbon atom: