正在加载图片...
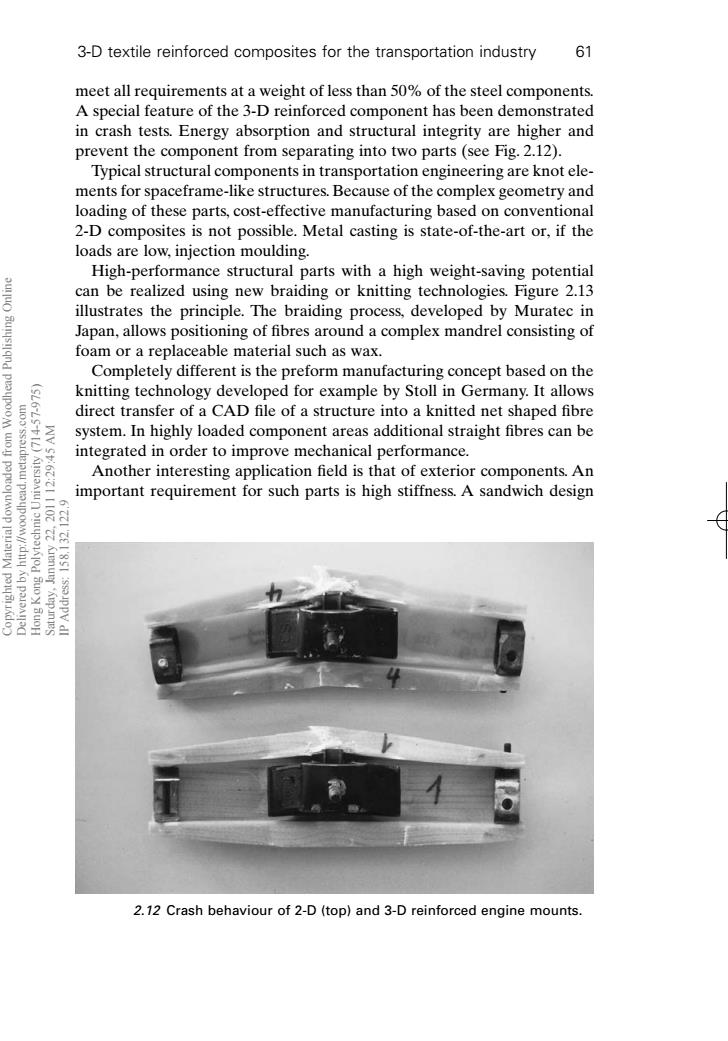
3-D textile reinforced composites for the transportation industry 61 meet all requirements at a weight of less than 50%of the steel components. A special feature of the 3-D reinforced component has been demonstrated in crash tests.Energy absorption and structural integrity are higher and prevent the component from separating into two parts (see Fig.2.12). Typical structural components in transportation engineering are knot ele- ments for spaceframe-like structures.Because of the complex geometry and loading of these parts,cost-effective manufacturing based on conventional 2-D composites is not possible.Metal casting is state-of-the-art or,if the loads are low,injection moulding. High-performance structural parts with a high weight-saving potential can be realized using new braiding or knitting technologies.Figure 2.13 illustrates the principle.The braiding process,developed by Muratec in Japan,allows positioning of fibres around a complex mandrel consisting of foam or a replaceable material such as wax. Completely different is the preform manufacturing concept based on the knitting technology developed for example by Stoll in Germany.It allows direct transfer of a CAD file of a structure into a knitted net shaped fibre system.In highly loaded component areas additional straight fibres can be integrated in order to improve mechanical performance. Another interesting application field is that of exterior components.An important requirement for such parts is high stiffness.A sandwich design 10E I'8SI 2.12 Crash behaviour of 2-D(top)and 3-D reinforced engine mounts.meet all requirements at a weight of less than 50% of the steel components. A special feature of the 3-D reinforced component has been demonstrated in crash tests. Energy absorption and structural integrity are higher and prevent the component from separating into two parts (see Fig. 2.12). Typical structural components in transportation engineering are knot elements for spaceframe-like structures. Because of the complex geometry and loading of these parts, cost-effective manufacturing based on conventional 2-D composites is not possible. Metal casting is state-of-the-art or, if the loads are low, injection moulding. High-performance structural parts with a high weight-saving potential can be realized using new braiding or knitting technologies. Figure 2.13 illustrates the principle. The braiding process, developed by Muratec in Japan, allows positioning of fibres around a complex mandrel consisting of foam or a replaceable material such as wax. Completely different is the preform manufacturing concept based on the knitting technology developed for example by Stoll in Germany. It allows direct transfer of a CAD file of a structure into a knitted net shaped fibre system. In highly loaded component areas additional straight fibres can be integrated in order to improve mechanical performance. Another interesting application field is that of exterior components. An important requirement for such parts is high stiffness. A sandwich design 3-D textile reinforced composites for the transportation industry 61 2.12 Crash behaviour of 2-D (top) and 3-D reinforced engine mounts. RIC2 7/10/99 7:26 PM Page 61 Copyrighted Material downloaded from Woodhead Publishing Online Delivered by http://woodhead.metapress.com Hong Kong Polytechnic University (714-57-975) Saturday, January 22, 2011 12:29:45 AM IP Address: 158.132.122.9