正在加载图片...
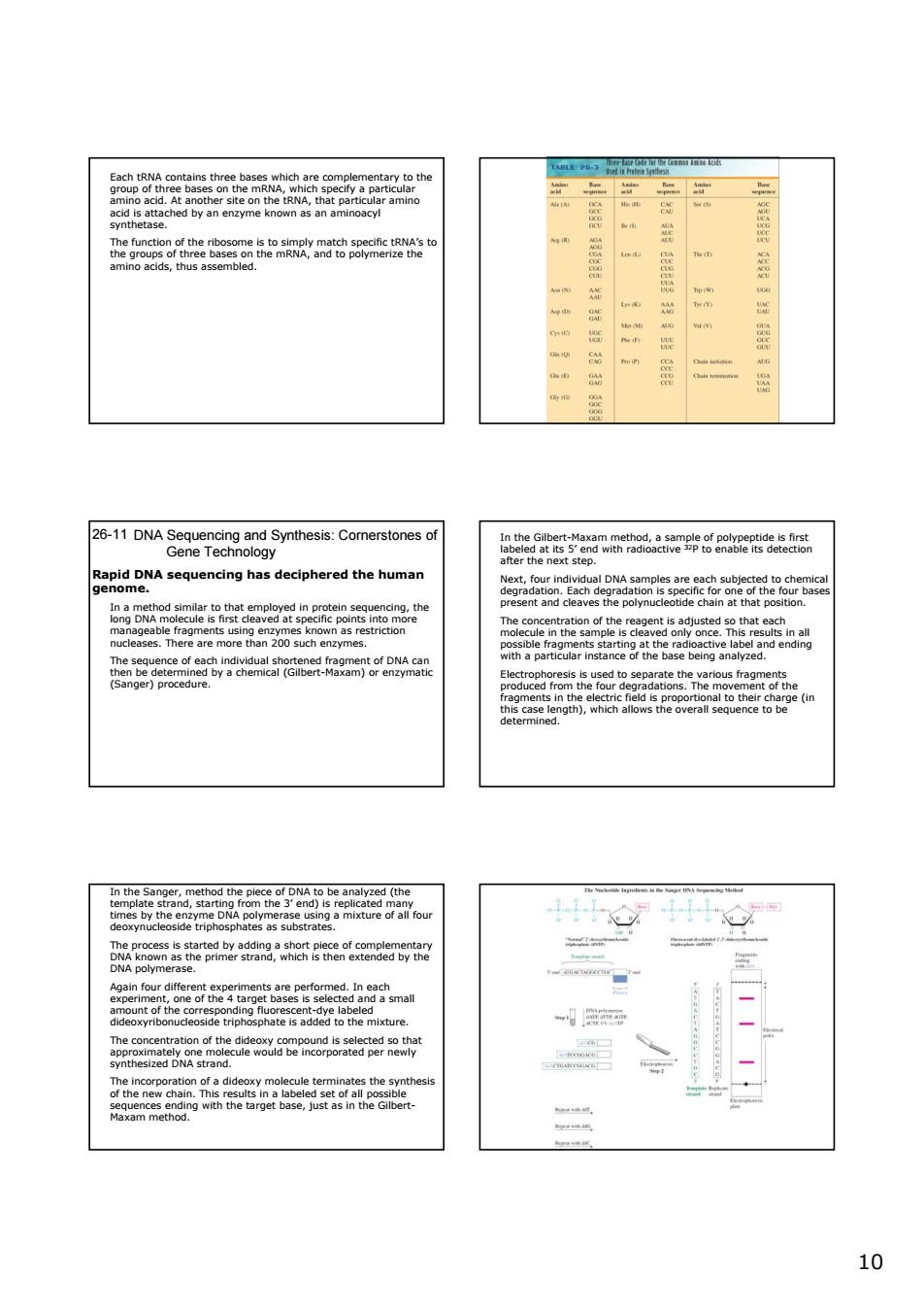
ogy ae$828a has deciphered the human E586 1010 Each tRNA contains three bases which are complementary to the group of three bases on the mRNA, which specify a particular amino acid. At another site on the tRNA, that particular amino acid is attached by an enzyme known as an aminoacyl synthetase. The function of the ribosome is to simply match specific tRNA’s to the groups of three bases on the mRNA, and to polymerize the amino acids, thus assembled. DNA Sequencing and Synthesis: Cornerstones of Gene Technology 26-11 Rapid DNA sequencing has deciphered the human genome. In a method similar to that employed in protein sequencing, the long DNA molecule is first cleaved at specific points into more manageable fragments using enzymes known as restriction nucleases. There are more than 200 such enzymes. The sequence of each individual shortened fragment of DNA can then be determined by a chemical (Gilbert-Maxam) or enzymatic (Sanger) procedure. In the Gilbert-Maxam method, a sample of polypeptide is first labeled at its 5’ end with radioactive 32P to enable its detection after the next step. Next, four individual DNA samples are each subjected to chemical degradation. Each degradation is specific for one of the four bases present and cleaves the polynucleotide chain at that position. The concentration of the reagent is adjusted so that each molecule in the sample is cleaved only once. This results in all possible fragments starting at the radioactive label and ending with a particular instance of the base being analyzed. Electrophoresis is used to separate the various fragments produced from the four degradations. The movement of the fragments in the electric field is proportional to their charge (in this case length), which allows the overall sequence to be determined. In the Sanger, method the piece of DNA to be analyzed (the template strand, starting from the 3’ end) is replicated many times by the enzyme DNA polymerase using a mixture of all four deoxynucleoside triphosphates as substrates. The process is started by adding a short piece of complementary DNA known as the primer strand, which is then extended by the DNA polymerase. Again four different experiments are performed. In each experiment, one of the 4 target bases is selected and a small amount of the corresponding fluorescent-dye labeled dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphate is added to the mixture. The concentration of the dideoxy compound is selected so that approximately one molecule would be incorporated per newly synthesized DNA strand. The incorporation of a dideoxy molecule terminates the synthesis of the new chain. This results in a labeled set of all possible sequences ending with the target base, just as in the GilbertMaxam method