正在加载图片...
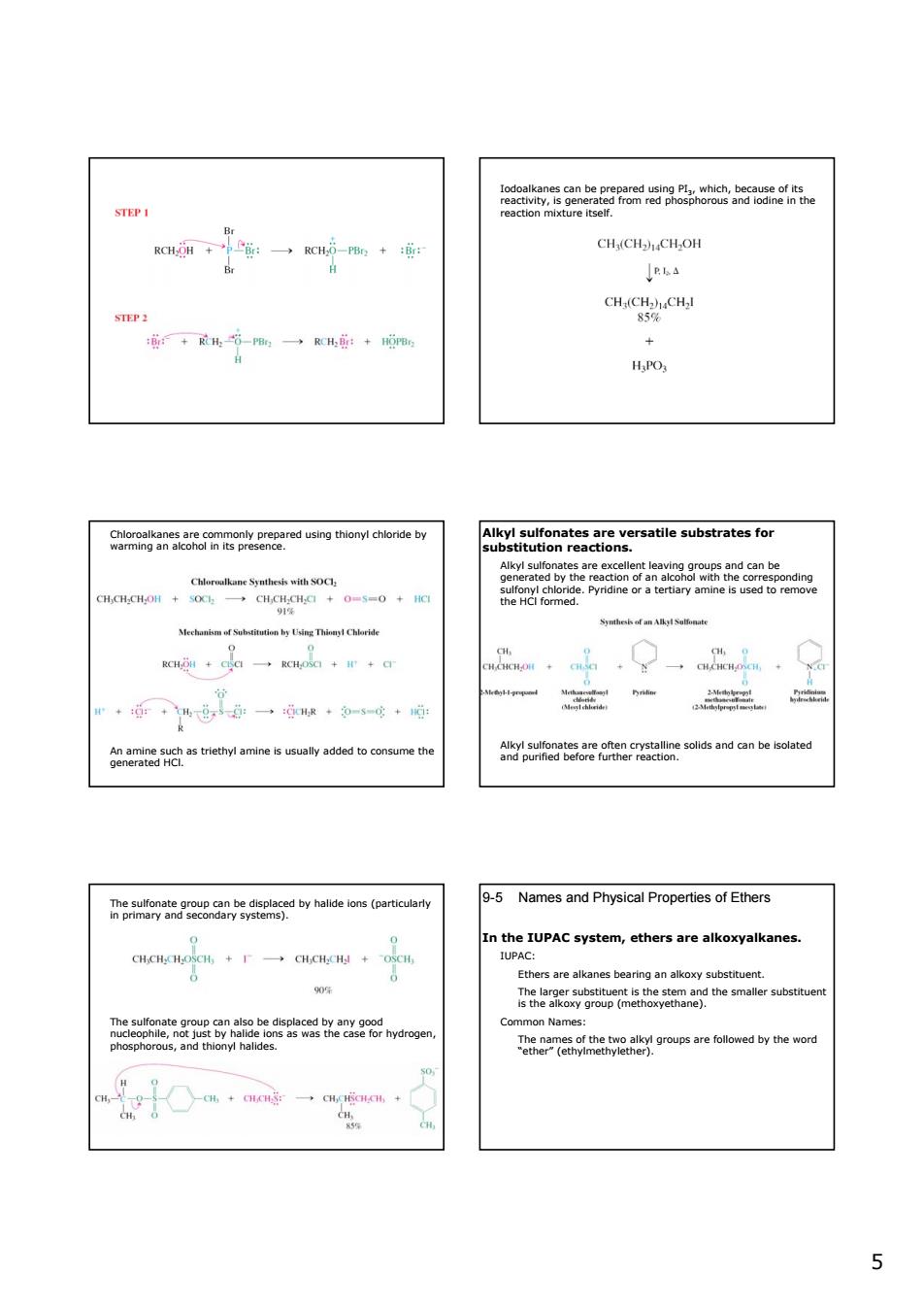
STEPI CH/CH2.CH.OH : ouU HPOs Ceogans8sBagrcausngthomndhenae7 substrates for haan与nI Cre +道r4,0一0·多-g+心 的,d 9-5 Names and Physical Properties of Ethers in the IUPAC system,ethers are alkoxyalkanes m 55 Iodoalkanes can be prepared using PI3, which, because of its reactivity, is generated from red phosphorous and iodine in the reaction mixture itself. Chloroalkanes are commonly prepared using thionyl chloride by warming an alcohol in its presence. An amine such as triethyl amine is usually added to consume the generated HCl. Alkyl sulfonates are versatile substrates for substitution reactions. Alkyl sulfonates are excellent leaving groups and can be generated by the reaction of an alcohol with the corresponding sulfonyl chloride. Pyridine or a tertiary amine is used to remove the HCl formed. Alkyl sulfonates are often crystalline solids and can be isolated and purified before further reaction. The sulfonate group can be displaced by halide ions (particularly in primary and secondary systems). The sulfonate group can also be displaced by any good nucleophile, not just by halide ions as was the case for hydrogen, phosphorous, and thionyl halides. 9-5 Names and Physical Properties of Ethers In the IUPAC system, ethers are alkoxyalkanes. IUPAC: Ethers are alkanes bearing an alkoxy substituent. The larger substituent is the stem and the smaller substituent is the alkoxy group (methoxyethane). Common Names: The names of the two alkyl groups are followed by the word “ether” (ethylmethylether)