正在加载图片...
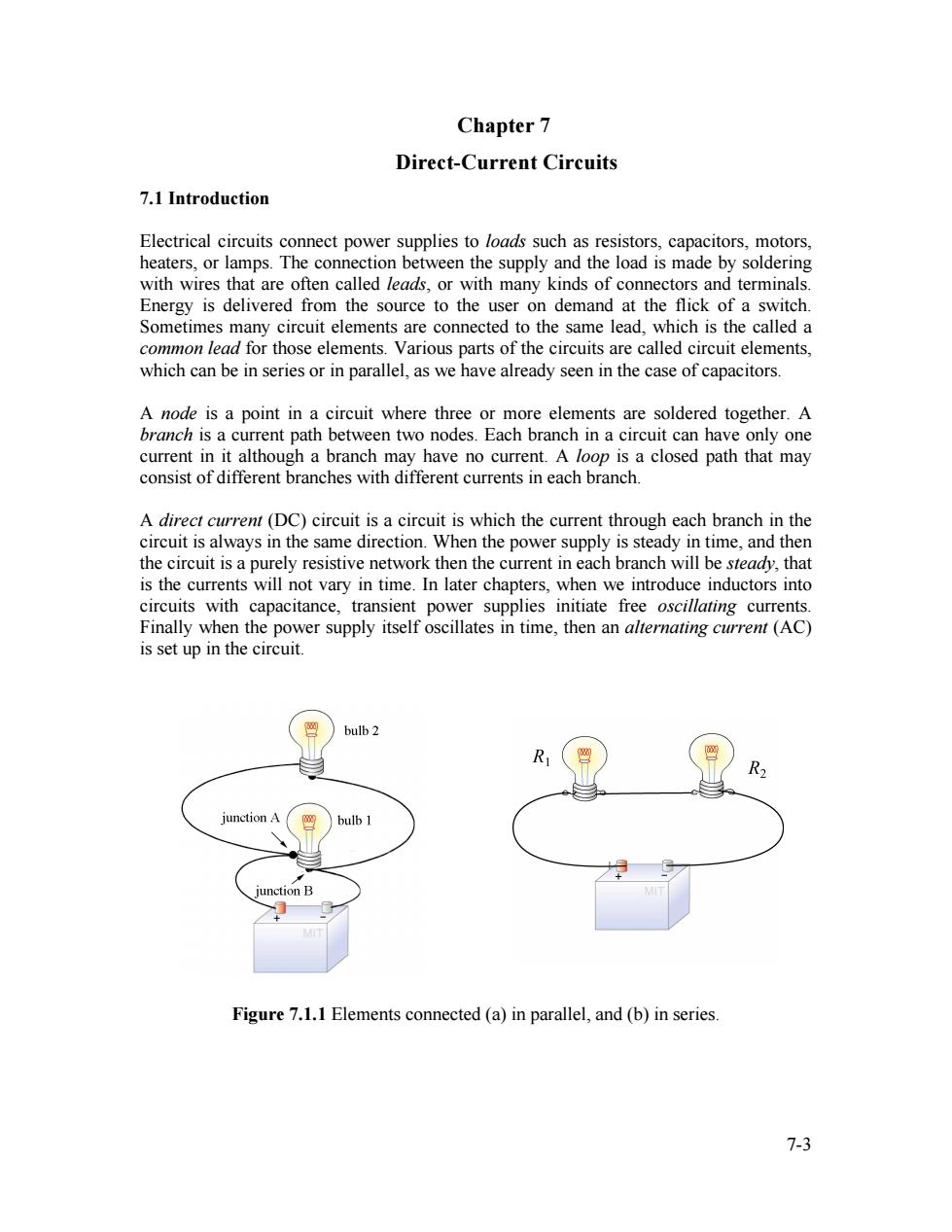
Chapter 7 Direct-Current Circuits 7.1 Introduction Electrical circuits connect power supplies to loads such as resistors,capacitors,motors, heaters,or lamps.The connection between the supply and the load is made by soldering with wires that are often called leads,or with many kinds of connectors and terminals. Energy is delivered from the source to the user on demand at the flick of a switch Sometimes many circuit elements are connected to the same lead,which is the called a common lead for those elements.Various parts of the circuits are called circuit elements, which can be in series or in parallel,as we have already seen in the case of capacitors. A node is a point in a circuit where three or more elements are soldered together.A branch is a current path between two nodes.Each branch in a circuit can have only one current in it although a branch may have no current.A loop is a closed path that may consist of different branches with different currents in each branch. A direct current (DC)circuit is a circuit is which the current through each branch in the circuit is always in the same direction.When the power supply is steady in time,and then the circuit is a purely resistive network then the current in each branch will be steady,that is the currents will not vary in time.In later chapters,when we introduce inductors into circuits with capacitance,transient power supplies initiate free oscillating currents. Finally when the power supply itself oscillates in time,then an alternating current(AC) is set up in the circuit. bulb 2 R2 junction A bulb 1 Junction B Figure 7.1.1 Elements connected (a)in parallel,and (b)in series. 7-37-3 Chapter 7 Direct-Current Circuits 7.1 Introduction Electrical circuits connect power supplies to loads such as resistors, capacitors, motors, heaters, or lamps. The connection between the supply and the load is made by soldering with wires that are often called leads, or with many kinds of connectors and terminals. Energy is delivered from the source to the user on demand at the flick of a switch. Sometimes many circuit elements are connected to the same lead, which is the called a common lead for those elements. Various parts of the circuits are called circuit elements, which can be in series or in parallel, as we have already seen in the case of capacitors. A node is a point in a circuit where three or more elements are soldered together. A branch is a current path between two nodes. Each branch in a circuit can have only one current in it although a branch may have no current. A loop is a closed path that may consist of different branches with different currents in each branch. A direct current (DC) circuit is a circuit is which the current through each branch in the circuit is always in the same direction. When the power supply is steady in time, and then the circuit is a purely resistive network then the current in each branch will be steady, that is the currents will not vary in time. In later chapters, when we introduce inductors into circuits with capacitance, transient power supplies initiate free oscillating currents. Finally when the power supply itself oscillates in time, then an alternating current (AC) is set up in the circuit. Figure 7.1.1 Elements connected (a) in parallel, and (b) in series