正在加载图片...
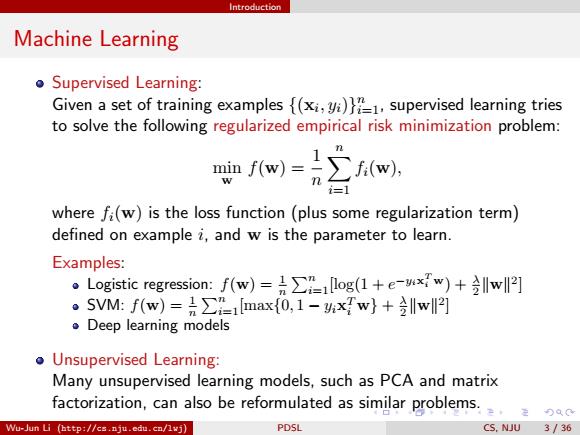
Introduction Machine Learning o Supervised Learning: Given a set of training examples {(xi,yi)1,supervised learning tries to solve the following regularized empirical risk minimization problem: where fi(w)is the loss function(plus some regularization term) defined on example i,and w is the parameter to learn. Examples: ·Logistic regression:f(w)=员∑1log(l+e-xw)+lw鬥] 。SVM:f(w)=是∑1Imax{0,1-xTw}+lw鬥] Deep learning models o Unsupervised Learning: Many unsupervised learning models,such as PCA and matrix factorization,can also be reformulated as similar problems. Wu-Jun Li (http://cs.nju.edu.cn/lvj) PDSL CS,NJU 3/36Introduction Machine Learning Supervised Learning: Given a set of training examples {(xi , yi)} n i=1, supervised learning tries to solve the following regularized empirical risk minimization problem: min w f(w) = 1 n Xn i=1 fi(w), where fi(w) is the loss function (plus some regularization term) defined on example i, and w is the parameter to learn. Examples: Logistic regression: f(w) = 1 n Pn i=1[log(1 + e −yix T i w) + λ 2 kwk 2 ] SVM: f(w) = 1 n Pn i=1[max{0, 1 − yix T i w} + λ 2 kwk 2 ] Deep learning models Unsupervised Learning: Many unsupervised learning models, such as PCA and matrix factorization, can also be reformulated as similar problems. Wu-Jun Li (http://cs.nju.edu.cn/lwj) PDSL CS, NJU 3 / 36