正在加载图片...
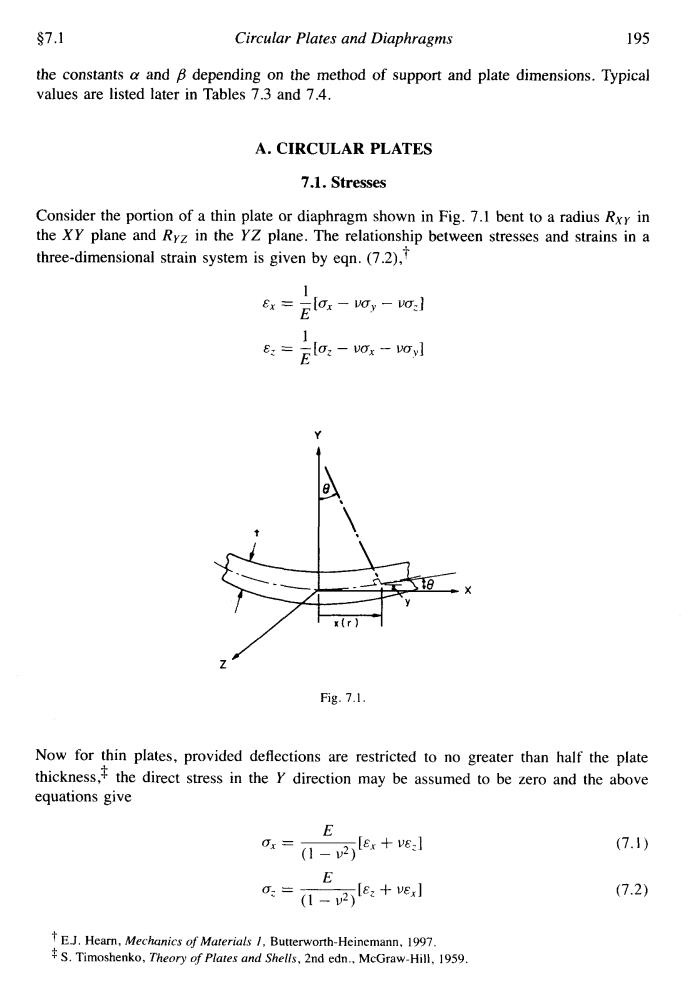
$7.1 Circular Plates and Diaphragms 195 the constants a and B depending on the method of support and plate dimensions.Typical values are listed later in Tables 7.3 and 7.4. A.CIRCULAR PLATES 7.1.Stresses Consider the portion of a thin plate or diaphragm shown in Fig.7.1 bent to a radius Rxy in the XY plane and Ryz in the YZ plane.The relationship between stresses and strains in a three-dimensional strain system is given by eqn.(7.2), 6=glo,-w 1 1 lo:-vox-voyl Fig.7.1. Now for thin plates,provided deflections are restricted to no greater than half the plate thickness,the direct stress in the y direction may be assumed to be zero and the above equations give E 0x≠ 0-2e:+e] (7.1) E 0-2吗8,+e (7.2) EJ.Hearn,Mechanics of Materials /Butterworth-Heinemann,1997. S.Timoshenko,Theory of Plates and Shells,2nd edn.McGraw-Hill.1959.$7.1 Circular Plates and Diaphragms 195 the constants a and ,~9 depending on the method of support and plate dimensions. Typical values are listed later in Tables 7.3 and 7.4. A. CIRCULAR PLATES 7.1. Stresses Consider the portion of a thin plate or diaphragm shown in Fig. 7.1 bent to a radius RxU in the XY plane and RYZ in the YZ plane. The relationship between stresses and strains in a three-dimensional strain system is given by eqn. (7.2): 1 E - -[a, - uay - ua,] ,-E 1 E E? = -[a, - ua, - !Jay] Y Z / Fig. 7.1. Now for thin plates, provided deflections are restricted to no greater than half the plate thickness3 the direct stress in the Y direction may be assumed to be zero and the above equations give E a, = [E, + UE,] ~ (1 - u2) E.J. Hearn, Mechanics of Materials I, Butterworth-Heinemann, 1997. S. Timoshenko, Theory of Plates and Shells, 2nd edn., McGraw-Hill, 1959