正在加载图片...
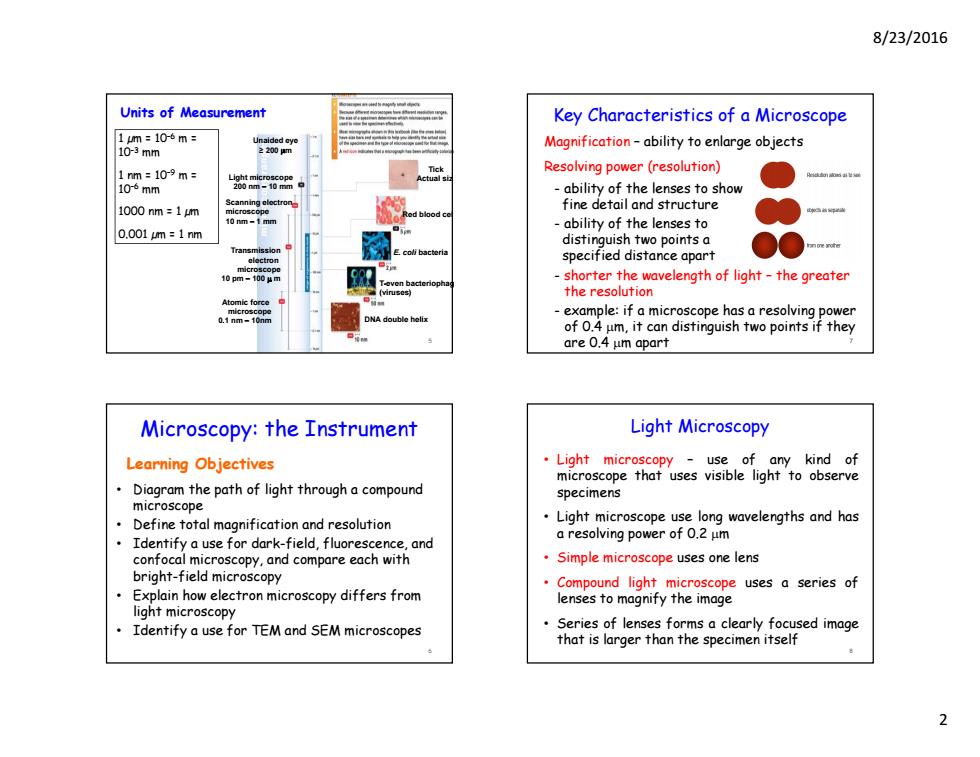
8/23/2016 Units of Measurement Key Characteristics of a Microscope 1m=106m= Magnification-ability to enlarge objects 103mm 1nm=109m= Resolving power (resolution) 106mm ability of the lenses to show 1000nm-1m fine detail and structure 10 nm t m -ability of the lenses to 0.001m:1nm distinguish two points a specified distance apart -shorter the wavelength of light-the greater the resolution NA double helix -example:if a microscope has a resolving power of 0.4 um,it can distinguish two points if they are 0.4 um apart Microscopy:the Instrument Light Microscopy Learning Objectives Light microscopy use of any kind of microscope that uses visible light to observe Diagram the path of light through a compound specimens microscope Define total magnification and resolution Light microscope use long wavelengths and has Identify a use for dark-field,fluorescence,and a resolving power of 0.2 um confocal microscopy,and compare each with Simple microscope uses one lens bright-field microscopy Compound light microscope uses a series of Explain how electron microscopy differs from lenses to magnify the image light microscopy Identify a use for TEM and SEM microscopes Series of lenses forms a clearly focused image that is larger than the specimen itself8/23/2016 2 Tick Actual siz Red blood cel E. coli bacteria T-even bacteriophag (viruses) DNA double helix 1 µm = 10–6 m = 10–3 mm 1 nm = 10–9 m = 10–6 mm 1000 nm = 1 µm 0.001 µm = 1 nm Units of Measurement Unaided eye ≥ 200 m Light microscope 200 nm – 10 mm Scanning electron microscope 10 nm – 1 mm Transmission electron microscope 10 pm – 100 m Atomic force microscope 0.1 nm – 10nm 5 Learning Objectives • Diagram the path of light through a compound microscope • Define total magnification and resolution • Identify a use for dark-field, fluorescence, and confocal microscopy, and compare each with bright-field microscopy • Explain how electron microscopy differs from light microscopy • Identify a use for TEM and SEM microscopes Microscopy: the Instrument 6 Magnification – ability to enlarge objects Resolving power (resolution) - ability of the lenses to show fine detail and structure - ability of the lenses to distinguish two points a specified distance apart - shorter the wavelength of light – the greater the resolution - example: if a microscope has a resolving power of 0.4 m, it can distinguish two points if they are 0.4 m apart Key Characteristics of a Microscope 7 Light Microscopy • Light microscopy – use of any kind of microscope that uses visible light to observe specimens • Light microscope use long wavelengths and has a resolving power of 0.2 m • Simple microscope uses one lens • Compound light microscope uses a series of lenses to magnify the image • Series of lenses forms a clearly focused image that is larger than the specimen itself 8