正在加载图片...
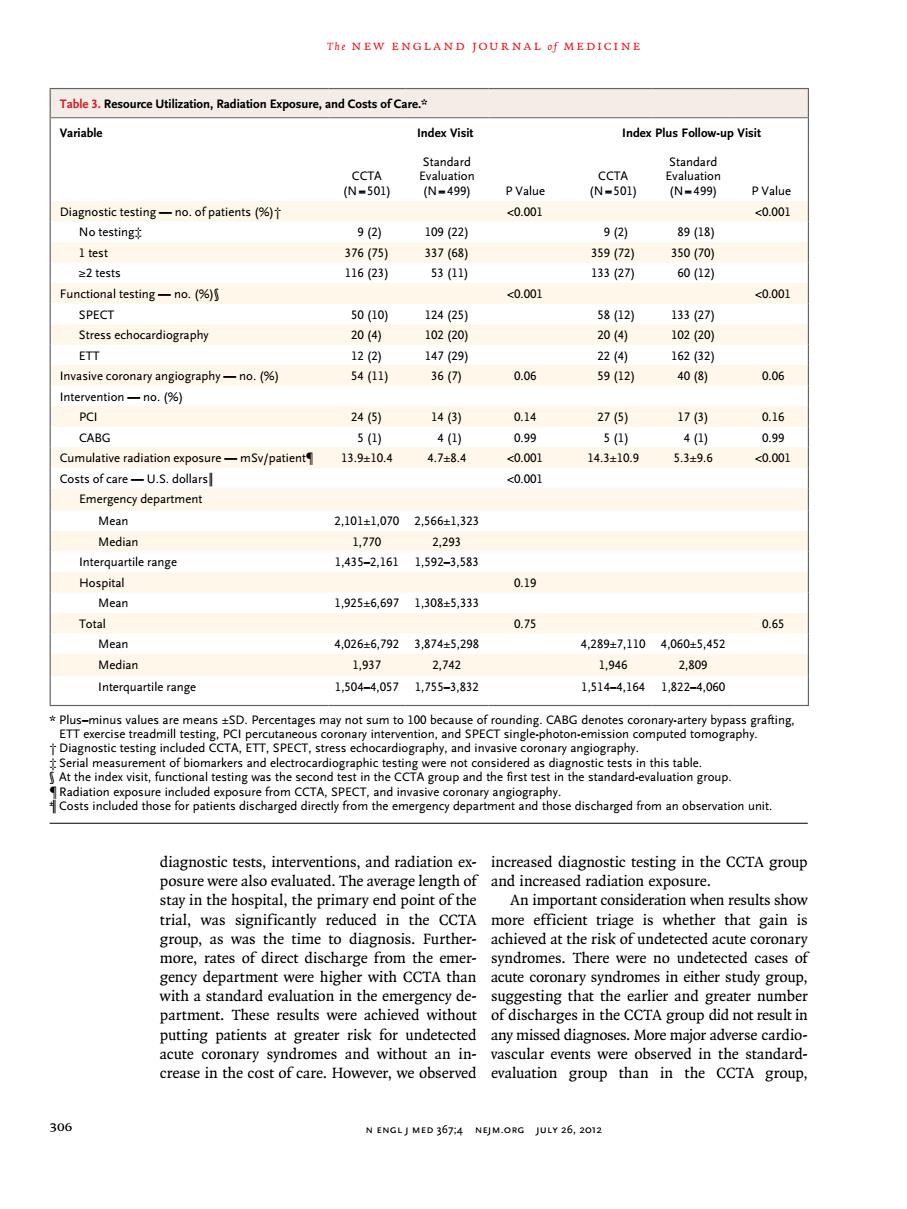
The NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL f MEDICINE Table 3.Resource Utilization,Radiation Exposure,and Costs of Care. Variable Index Visit Index Plus Follow-up Visit S06 Standard P Valu iagnostic testing-no.of patients( 0.00 No testing Functional testing-no.( 0.001 0.00 SPECT vecoronary angiography-no.(%) 0c1 17 86 Cumulative radiation -mSv/patient 1390 143109 0001 000 ency depar men 2,101±1,0702,566±1,323 Median tile range 1,435-2,161 Hos 0.19 1,9256,6971,30345,333 0.75 0.65 4,026±6,7923,8745,298 4,289±7,10406045,452 Median 9 2,742 1,946 2809 Interquartile range 1,504-4,0571,755-3,832 1,5144,1641,822-4,060 Serial measu t of biomarkers and fro CTA, sedischarged from an observation unit. eests interventions,and radiation ex-increased diagnostic testing in the CCrA The average lengt and rad posure ital the Phe CCTA as the time to diagnosis.Further. syndromes.There were no undetected cases of gency department were higher with CCTA than acute coronary syndromes in either study group with a standard evaluation in the partment.Ines resuits were d not res any m diagnoses.More m and with ved aluatonentt n group th group N ENGLJ MED 367:4 NEJM.ORG JULY 26,2012 T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e 306 n engl j med 367;4 nejm.org july 26, 2012 diagnostic tests, interventions, and radiation exposure were also evaluated. The average length of stay in the hospital, the primary end point of the trial, was significantly reduced in the CCTA group, as was the time to diagnosis. Furthermore, rates of direct discharge from the emergency department were higher with CCTA than with a standard evaluation in the emergency department. These results were achieved without putting patients at greater risk for undetected acute coronary syndromes and without an increase in the cost of care. However, we observed increased diagnostic testing in the CCTA group and increased radiation exposure. An important consideration when results show more efficient triage is whether that gain is achieved at the risk of undetected acute coronary syndromes. There were no undetected cases of acute coronary syndromes in either study group, suggesting that the earlier and greater number of discharges in the CCTA group did not result in any missed diagnoses. More major adverse cardiovascular events were observed in the standardevaluation group than in the CCTA group, Table 3. Resource Utilization, Radiation Exposure, and Costs of Care.* Variable Index Visit Index Plus Follow-up Visit CCTA (N=501) Standard Evaluation (N=499) P Value CCTA (N=501) Standard Evaluation (N=499) P Value Diagnostic testing — no. of patients (%)† <0.001 <0.001 No testing‡ 9 (2) 109 (22) 9 (2) 89 (18) 1 test 376 (75) 337 (68) 359 (72) 350 (70) ≥2 tests 116 (23) 53 (11) 133 (27) 60 (12) Functional testing — no. (%)§ <0.001 <0.001 SPECT 50 (10) 124 (25) 58 (12) 133 (27) Stress echocardiography 20 (4) 102 (20) 20 (4) 102 (20) ETT 12 (2) 147 (29) 22 (4) 162 (32) Invasive coronary angiography — no. (%) 54 (11) 36 (7) 0.06 59 (12) 40 (8) 0.06 Intervention — no. (%) PCI 24 (5) 14 (3) 0.14 27 (5) 17 (3) 0.16 CABG 5 (1) 4 (1) 0.99 5 (1) 4 (1) 0.99 Cumulative radiation exposure — mSv/patient¶ 13.9±10.4 4.7±8.4 <0.001 14.3±10.9 5.3±9.6 <0.001 Costs of care — U.S. dollars‖ <0.001 Emergency department Mean 2,101±1,070 2,566±1,323 Median 1,770 2,293 Interquartile range 1,435–2,161 1,592–3,583 Hospital 0.19 Mean 1,925±6,697 1,308±5,333 Total 0.75 0.65 Mean 4,026±6,792 3,874±5,298 4,289±7,110 4,060±5,452 Median 1,937 2,742 1,946 2,809 Interquartile range 1,504–4,057 1,755–3,832 1,514–4,164 1,822–4,060 * Plus–minus values are means ±SD. Percentages may not sum to 100 because of rounding. CABG denotes coronary-artery bypass grafting, ETT exercise treadmill testing, PCI percutaneous coronary intervention, and SPECT single-photon-emission computed tomography. † Diagnostic testing included CCTA, ETT, SPECT, stress echocardiography, and invasive coronary angiography. ‡ Serial measurement of biomarkers and electrocardiographic testing were not considered as diagnostic tests in this table. § At the index visit, functional testing was the second test in the CCTA group and the first test in the standard-evaluation group. ¶Radiation exposure included exposure from CCTA, SPECT, and invasive coronary angiography. ‖ Costs included those for patients discharged directly from the emergency department and those discharged from an observation unit