正在加载图片...
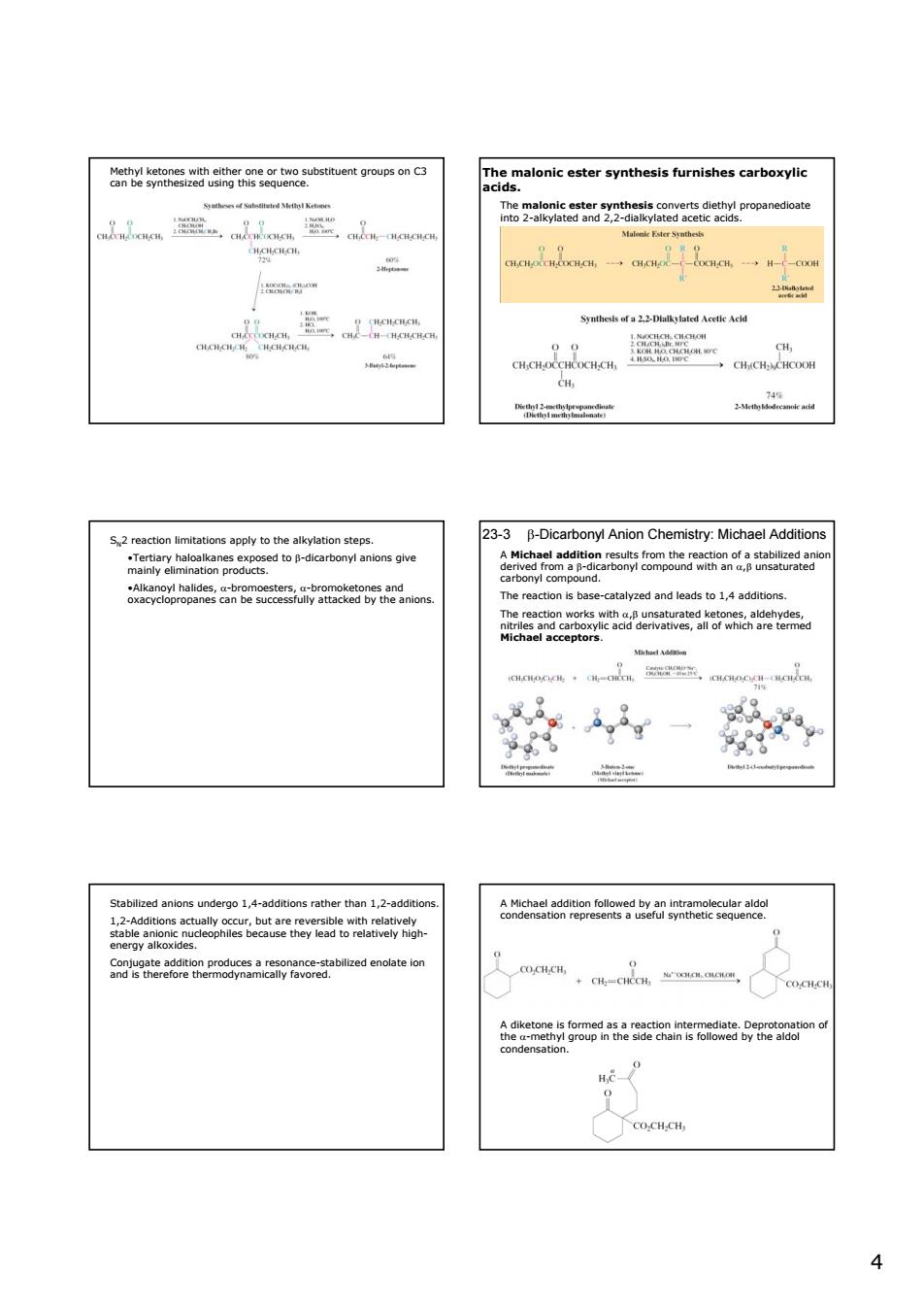
alonic ester synthesis furnishes carboxylic Ts2anY2heoaneco CH →CH./CH. CH 23-3 B-Dicarbonyl Anion Chemistry:Michael Additions he reaction is base-catah d and leads to 1,4 additions. thetnce Ca2aen6aenepmcaao6etablaedenoateon 合8ae62e5o8Ee5a CO.CHCH 44 Methyl ketones with either one or two substituent groups on C3 can be synthesized using this sequence. The malonic ester synthesis furnishes carboxylic acids. The malonic ester synthesis converts diethyl propanedioate into 2-alkylated and 2,2-dialkylated acetic acids. SN2 reaction limitations apply to the alkylation steps. •Tertiary haloalkanes exposed to β-dicarbonyl anions give mainly elimination products. •Alkanoyl halides, α-bromoesters, α-bromoketones and oxacyclopropanes can be successfully attacked by the anions. 23-3 β-Dicarbonyl Anion Chemistry: Michael Additions A Michael addition results from the reaction of a stabilized anion derived from a β-dicarbonyl compound with an α,β unsaturated carbonyl compound. The reaction is base-catalyzed and leads to 1,4 additions. The reaction works with α,β unsaturated ketones, aldehydes, nitriles and carboxylic acid derivatives, all of which are termed Michael acceptors. Stabilized anions undergo 1,4-additions rather than 1,2-additions. 1,2-Additions actually occur, but are reversible with relatively stable anionic nucleophiles because they lead to relatively highenergy alkoxides. Conjugate addition produces a resonance-stabilized enolate ion and is therefore thermodynamically favored. A Michael addition followed by an intramolecular aldol condensation represents a useful synthetic sequence. A diketone is formed as a reaction intermediate. Deprotonation of the α-methyl group in the side chain is followed by the aldol condensation