正在加载图片...
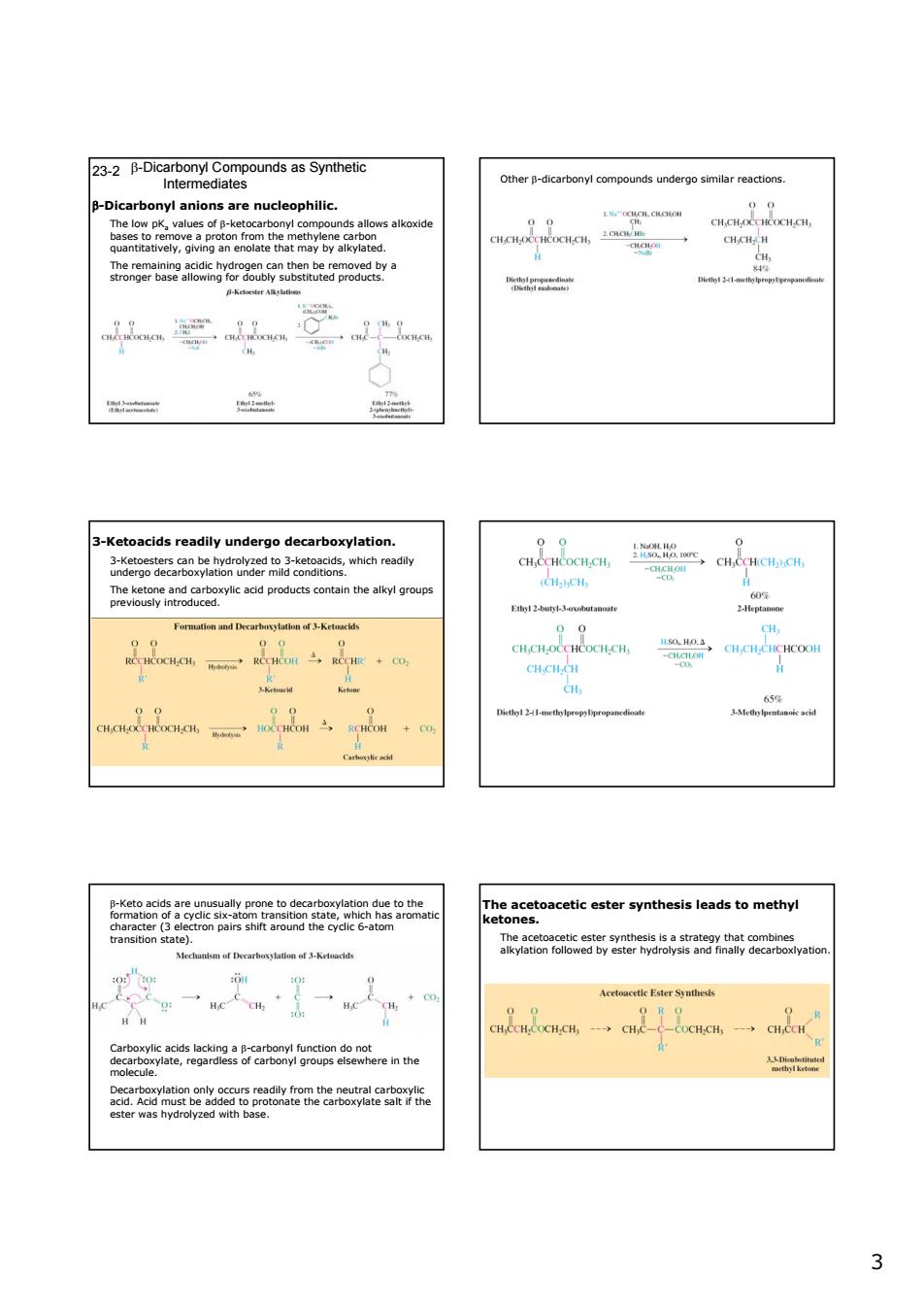
23-2 B-Dicarbony Compounds as Synthetic thecrbnyl comounds undergosmreacts p-olcartbonyanionsarenueieophile alkoxid acids re dily undergo decarboxylation. vlic add products contain the alkyl group CHCH.CH CH f af 3-Ketaadids e。 3 3 β-Dicarbonyl Compounds as Synthetic Intermediates 23-2 β-Dicarbonyl anions are nucleophilic. The low pKa values of β-ketocarbonyl compounds allows alkoxide bases to remove a proton from the methylene carbon quantitatively, giving an enolate that may by alkylated. The remaining acidic hydrogen can then be removed by a stronger base allowing for doubly substituted products. Other β-dicarbonyl compounds undergo similar reactions. 3-Ketoacids readily undergo decarboxylation. 3-Ketoesters can be hydrolyzed to 3-ketoacids, which readily undergo decarboxylation under mild conditions. The ketone and carboxylic acid products contain the alkyl groups previously introduced. β-Keto acids are unusually prone to decarboxylation due to the formation of a cyclic six-atom transition state, which has aromatic character (3 electron pairs shift around the cyclic 6-atom transition state). Carboxylic acids lacking a β-carbonyl function do not decarboxylate, regardless of carbonyl groups elsewhere in the molecule. Decarboxylation only occurs readily from the neutral carboxylic acid. Acid must be added to protonate the carboxylate salt if the ester was hydrolyzed with base. The acetoacetic ester synthesis leads to methyl ketones. The acetoacetic ester synthesis is a strategy that combines alkylation followed by ester hydrolysis and finally decarboxlyation