正在加载图片...
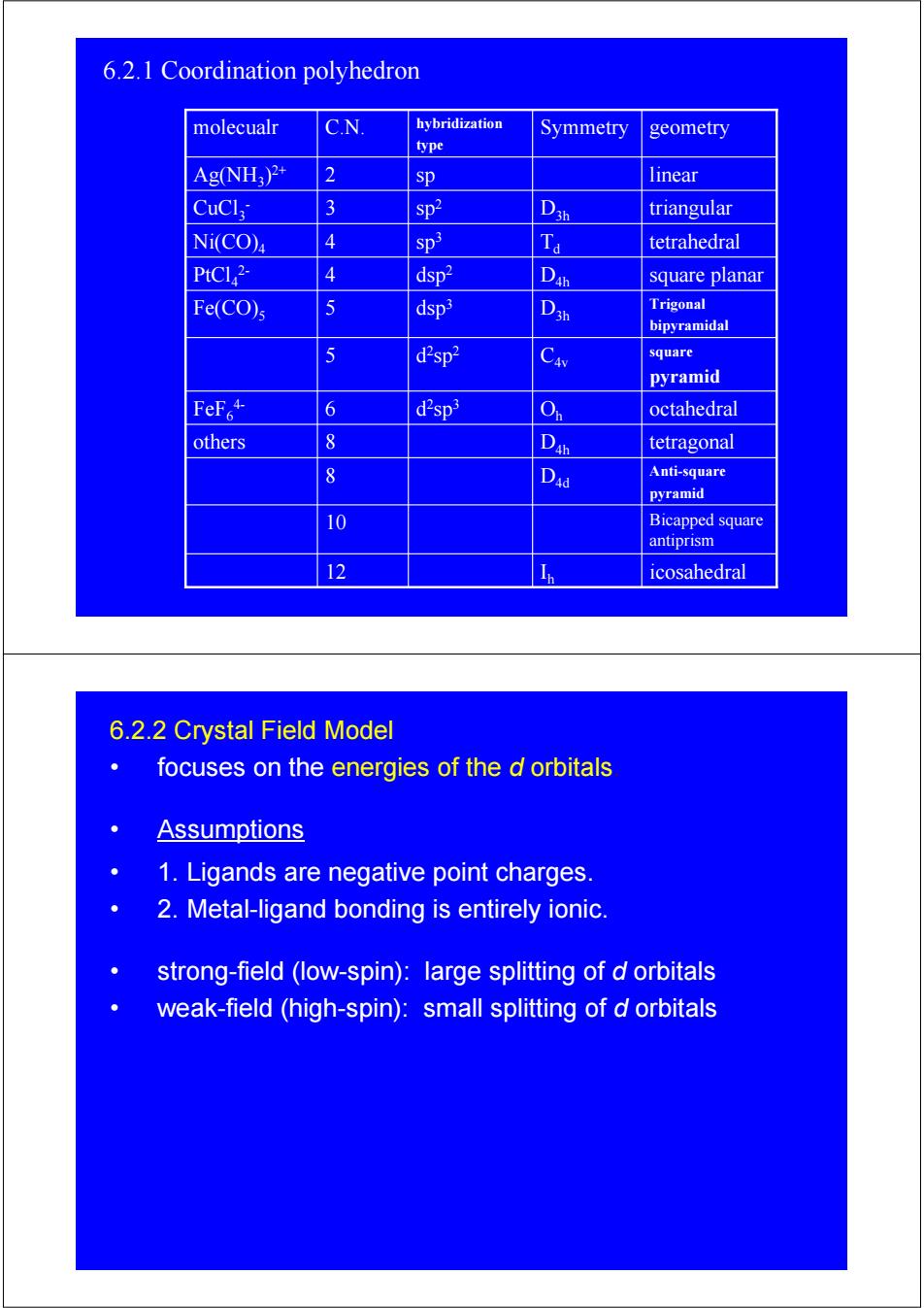
6.2.1 Coordination polyhedron molecualr C.N. hybridization Symmetry geometry type Ag(NH:)2+ 2 sp linear CuCl 3 sp2 triangular Ni(CO)4 4 Sp3 tetrahedral PtCl2- 4 dsp2 D square planar Fe(CO)s 5 dsp3 Trigonal bipyramidal 5 d2sp2 Cav square pyramid FeF+ 6 d2sp3 octahedral others 8 D tetragonal 8 Dad Anti-square pyramid 10 Bicapped square antiprism 12 Icosahedral 6.2.2 Crystal Field Model focuses on the energies of the d orbitals Assumptions 1.Ligands are negative point charges. 2.Metal-ligand bonding is entirely ionic. strong-field (low-spin):large splitting of d orbitals weak-field (high-spin):small splitting of d orbitalsI icosahedral 12 h Bicapped square antiprism 10 Anti-square pyramid 8 D4d D tetragonal others 8 4h O octahedral d h 2sp3 FeF6 6 4- square pyramid d C4v 2sp2 5 Trigonal bipyramidal dsp D3h 3 Fe(CO)5 5 D square planar dsp 4h 2 PtCl4 4 2- T tetrahedral d sp3 Ni(CO)4 4 D triangular 3h sp2 CuCl3 3 - Ag(NH 2 sp linear 3)2+ Symmetry geometry hybridization type molecualr C.N. 6.2.1 Coordination polyhedron 6.2.2 Crystal Field Model • focuses on the energies of the d orbitals. • Assumptions • 1. Ligands are negative point charges. • 2. Metal-ligand bonding is entirely ionic. • strong-field (low-spin): large splitting of d orbitals • weak-field (high-spin): small splitting of d orbitals