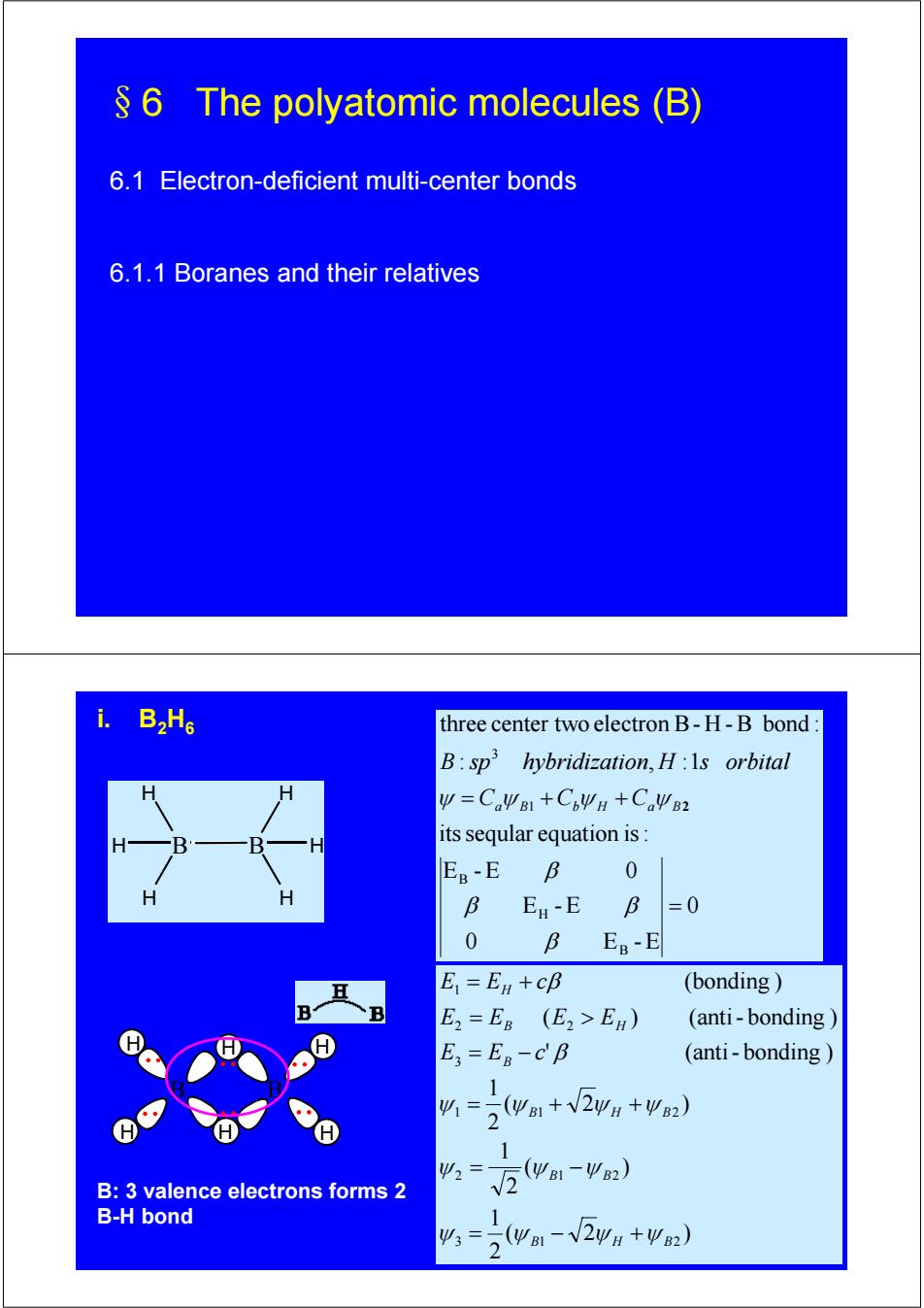
6 The polyatomic molecules (B) 6.1 Electron-deficient multi-center bonds 6.1.1 Boranes and their relatives i. B2H6 three center two electron B-H-B bond: B:sp hybridization,H:Is orbital y=CaWB1+C6ΨH+CaW2 its seqular equation is: B EB-E B 0 H B E-E B =0 0 B EB-E E=En +cB (bonding E2=ER (E2>EB) (anti-bonding E=ER-CB (anti-bonding 1 41=。(wB1+√2ΨH+ΨB2) 2 1 Ψ2 B:3 valence electrons forms 2 V2wa1-2) B-H bond 1 43=5(yB1-√2wH+Ψ2) 2
§6 The polyatomic molecules (B) 6.1 Electron-deficient multi-center bonds 6.1.1 Boranes and their relatives B H H H B H H H 0 0 E -E E -E E -E 0 itsseqular equation is: : , :1 three center two electron B- H -B bond : B H B 1 3 = = + + β β β β ψ Ca ψ B Cb ψ H Ca ψ B2 B sp hybridization H s orbital i. B2H6 B H H H H H H B B: 3 valence electrons forms 2 B-H bond ( 2 ) 2 1 ( ) 2 1 ( 2 ) 2 1 ' (anti- bonding ) ( ) (anti- bonding ) (bonding ) 3 1 2 2 1 2 1 1 2 3 2 2 1 B H B B B B H B B B H H E E c E E E E E E c ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ β β = − + = − = + + = − = > = +
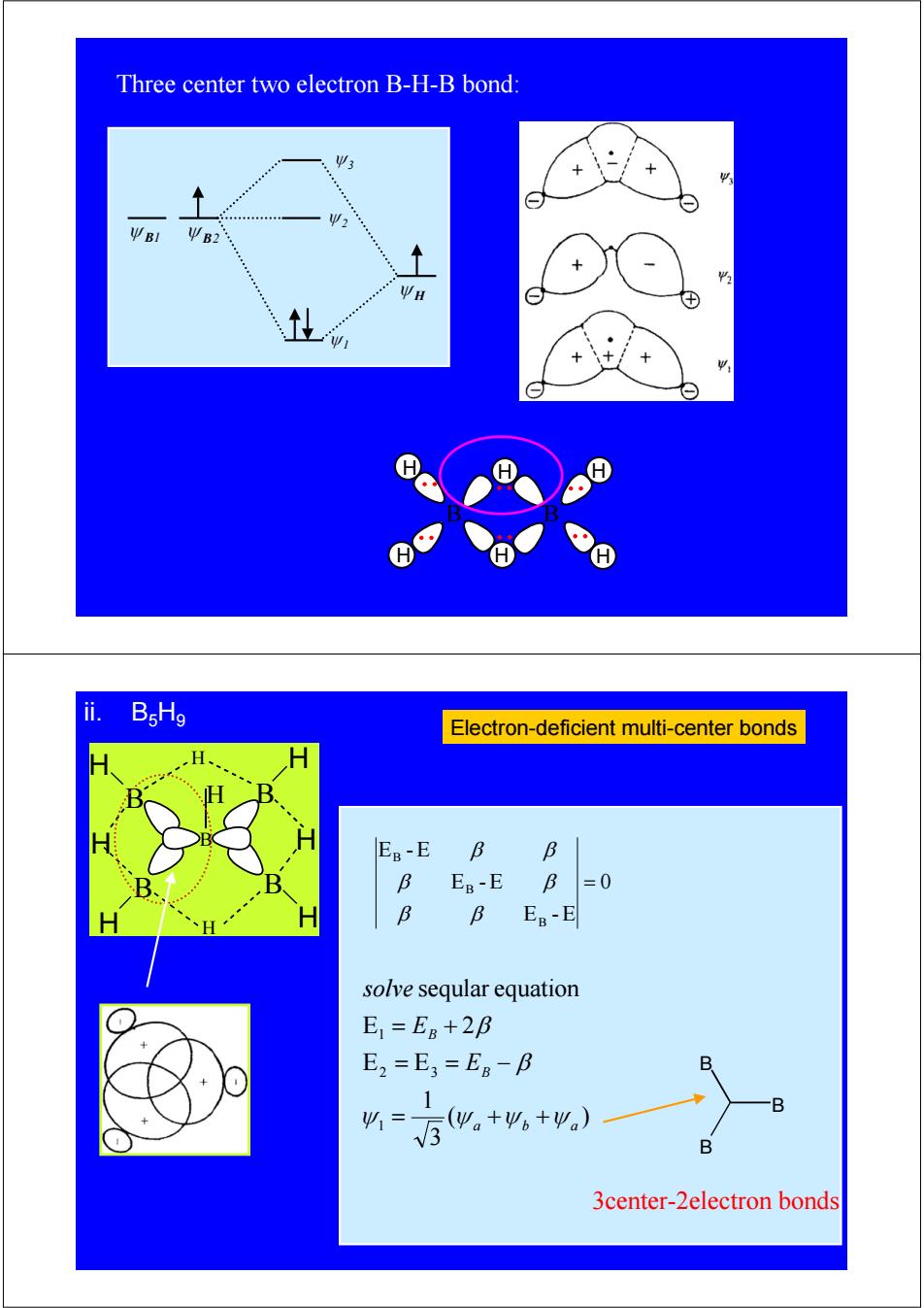
Three center two electron B-H-B bond: Ψ3 Ψ2 ΨBl U B2 H H ii. BsHg Electron-deficient multi-center bonds E8-E B B B EB-E B=0 B B EB-E solve seqular equation E=E8+28 E2=E3=EB-B B 5。+4。+,) 4= → B B 3center-2electron bonds
ψ B1 ψ B2 ψ H ψ 1 ψ 2 ψ 3 B H H H H H H B Three center two electron B-H-B bond: ii. B5H9 Electron-deficient multi-center bonds 0 E - E E -E E -E B B B = β β β β β β ( ) 3 1 E E E 2 seqular equation 1 2 3 1 a b a B B E E solve ψ ψ ψ ψ β β = + + = = − = + B B B 3center-2electron bonds B H H B H H B H B H B H H H
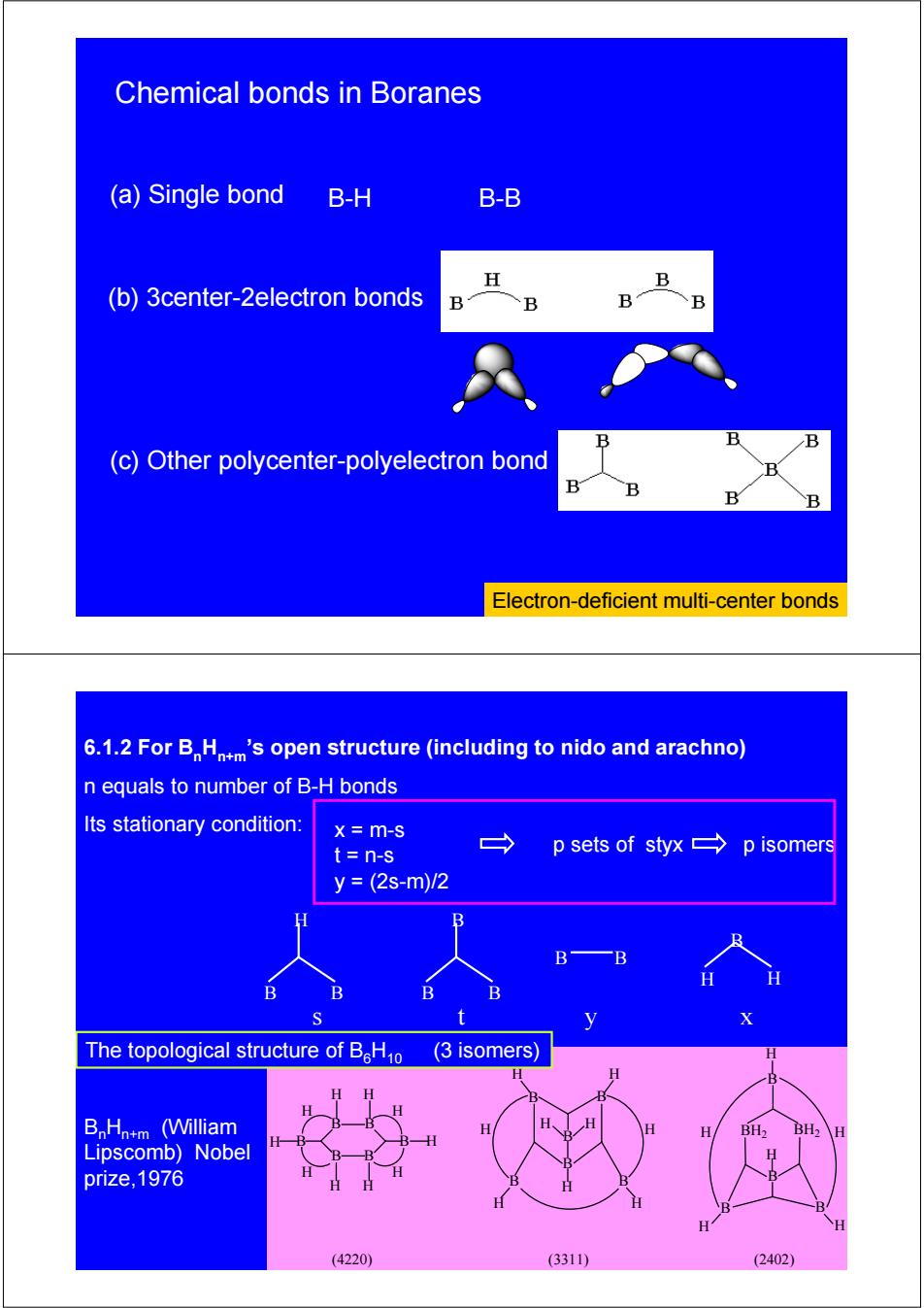
Chemical bonds in Boranes (a)Single bond B-H B-B H (b)3center-2electron bonds B B B (c)Other polycenter-polyelectron bond B B Electron-deficient multi-center bonds 6.1.2 For BHntm's open structure(including to nido and arachno) n equals to number of B-H bonds Its stationary condition: x=m-S t=n-s → p sets of styx p isomers y=(2s-m)/2 H B B H The topological structure of BHo (3 isomers) BnHn+m (William H BH2 BH2\H Lipscomb)Nobel H prize,1976 (4220) (3311) (2402)
B-H B-B (c) Other polycenter-polyelectron bond (b) 3center-2electron bonds (a) Single bond Electron-deficient multi-center bonds Chemical bonds in Boranes B H B H H H B B B B H H H H H H B B B B B B H H H H H H H H H H H H H B B BH2 BH2 B B H (4220) (3311) (2402) H The topological structure of B6H10 (3 isomers) BnHn+m (William Lipscomb) Nobel prize,1976 n equals to number of B-H bonds 6.1.2 For BnHn+m’s open structure (including to nido and arachno) B B H B B B B H H B B s ty x Its stationary condition: x = m-s t = n-s y = (2s-m)/2 p sets of styx p isomers
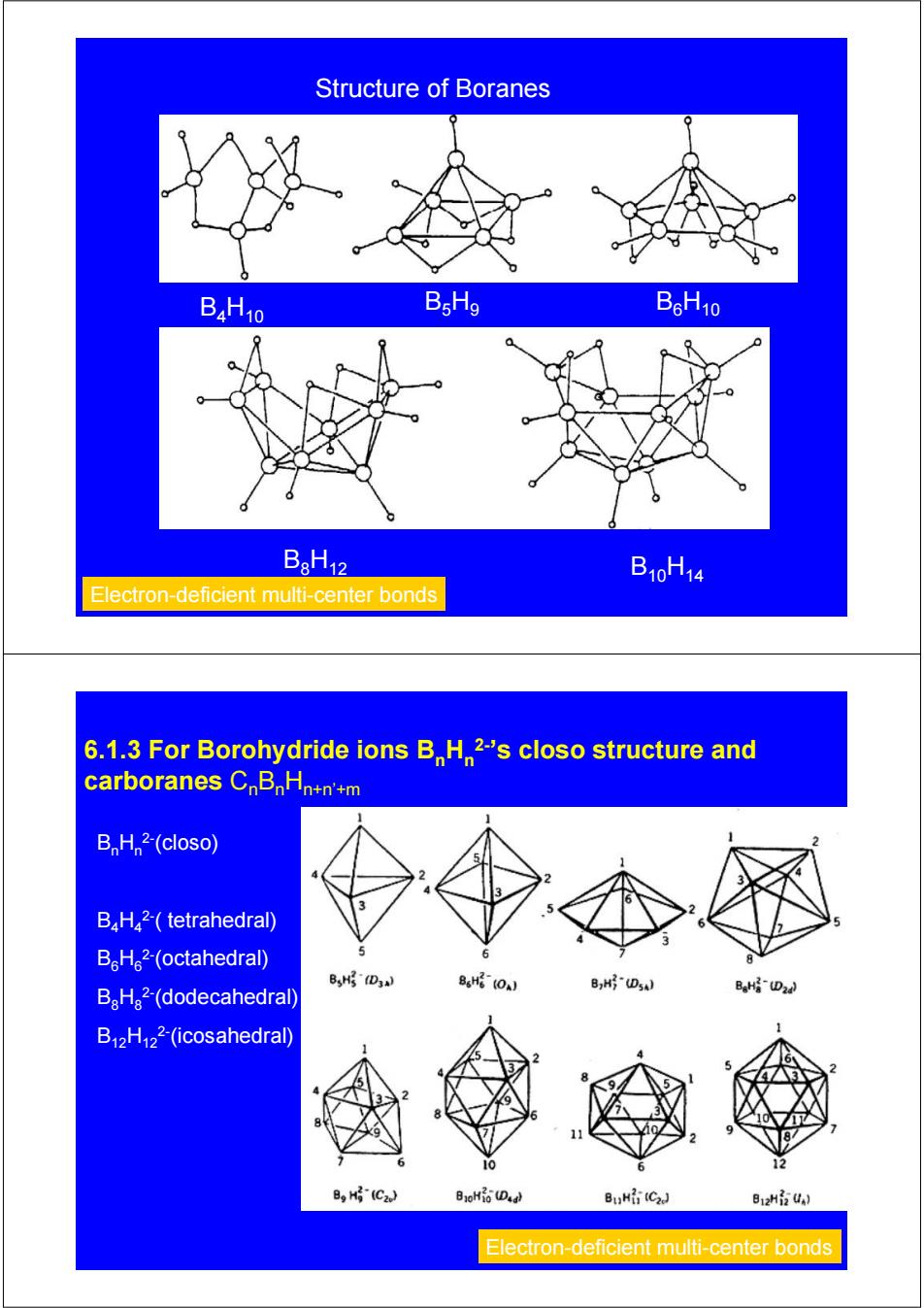
Structure of Boranes B4H10 BsHo BoH10 B8H12 B10H14 Electron-deficient multi-center bonds 6.1.3 For Borohydride ions BH2-'s closo structure and carboranes CnBnHn+n'+m B,H 2-(closo) BH2-(tetrahedral) B。H。2-(octahedral) 6 8 B,州D3 BaH2-(dodecahedral) 86H(0J B,H(DsA) BaH(D24 B12H122-(icosahedral) 10 BH(C2.) B3oHi Da) BuH(C2J B12Hi UA) Electron-deficient multi-center bonds
Structure of Boranes B4H10 B5H9 B6H10 B8H12 B10H14 Electron-deficient multi-center bonds 6.1.3 For Borohydride ions BnHn 2-’s closo structure and carboranes CnBnHn+n’+m BnHn 2-(closo) B4H4 2-( tetrahedral) B6H6 2-(octahedral) B8H8 2-(dodecahedral) B12H12 2-(icosahedral) Electron-deficient multi-center bonds

polyhedra with n vertices trigonal bipyramid octahedron pentagonal bipyramid N=5 N=6 N=7 dodecahedron tricapped trigonal prism N=8 N=9 bicapped square antiprism N=10 icosahedron N=12 octadecahedron 16.8 N=11 "Closo"series -formula BH2- Total valence electrons(CVE)=3n(from B)+n(from H) +2 (negative charge)=4n+2 Each BH unit uses 2 electrons.Hence skeletal or framework electrons (NFE=4n+2-2n=2n+2) There is little tendency to add H+and form neutral species. The closo species are,in effect,the anions of quite strong acids. Structures are those of the appropriate polyhedra with n vertices
polyhedra with n vertices “Closo” series -formula BnHn 2- Total valence electrons (CVE) = 3n (from B) +n (from H) +2 (negative charge) = 4n+2 • Each BH unit uses 2 electrons. Hence skeletal or framework electrons (NFE=4n+2-2n=2n+2) • There is little tendency to add H+ and form neutral species. The closo species are , in effect, the anions of quite strong acids. • Structures are those of the appropriate polyhedra with n vertices
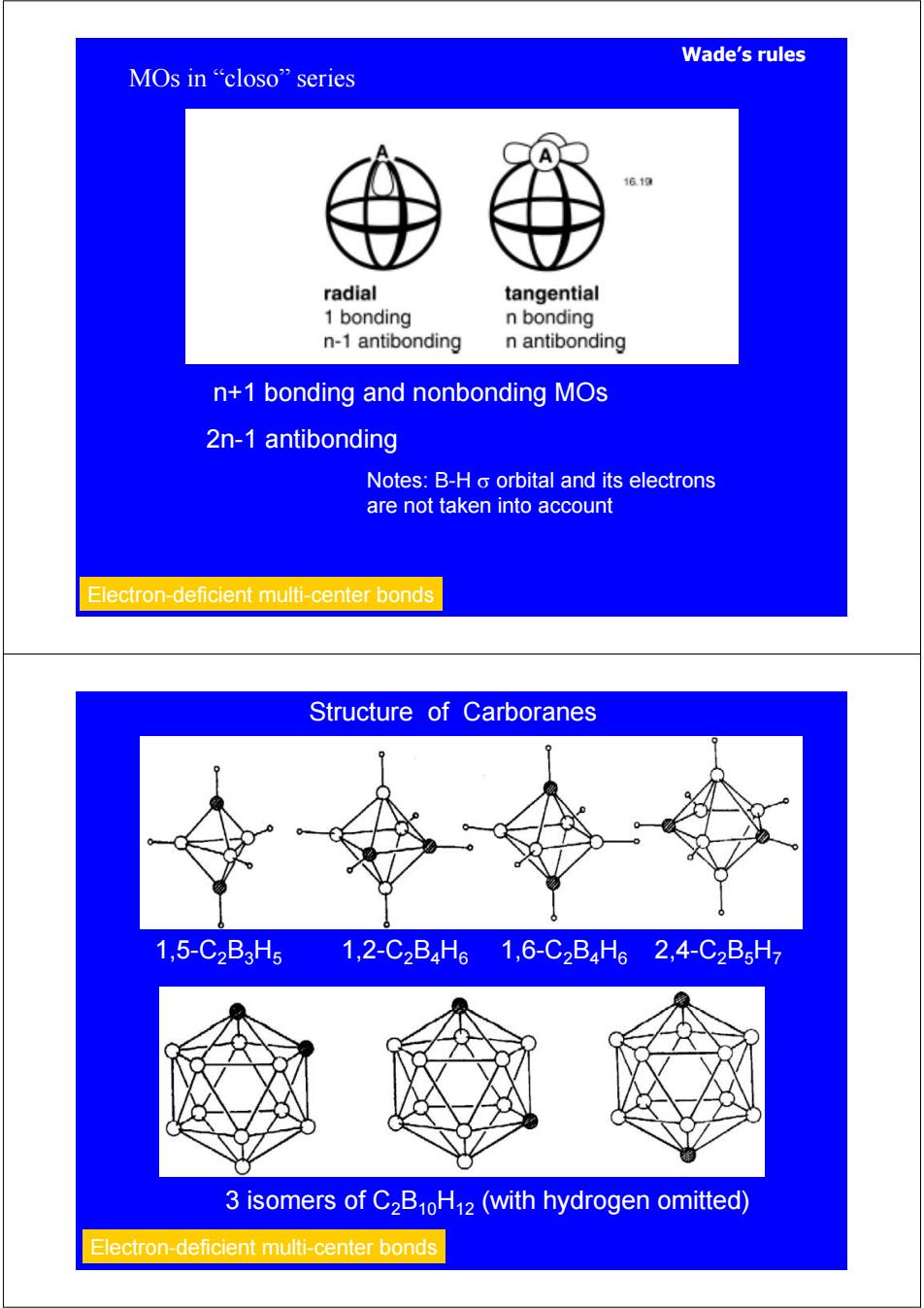
Wade's rules MOs in "closo”series 16.1a radial tangential 1 bonding n bonding n-1 antibonding n antibonding n+1 bonding and nonbonding MOs 2n-1 antibonding Notes:B-H o orbital and its electrons are not taken into account Electron-deficient multi-center bonds Structure of Carboranes 1,5-C2B3H5 1,2-C2B4H61,6-C2B4H62,4-C2B5H7 3 isomers of C2B10H12 (with hydrogen omitted) Electron-deficient multi-center bonds
Wade’s rules n+1 bonding and nonbonding MOs 2n-1 antibonding Notes: B-H σ orbital and its electrons are not taken into account Electron-deficient multi-center bonds MOs in “closo” series Structure of Carboranes 1,5-C2B3H5 1,2-C2B4H6 1,6-C2B4H6 2,4-C2B5H7 3 isomers of C2B10H12 (with hydrogen omitted) Electron-deficient multi-center bonds
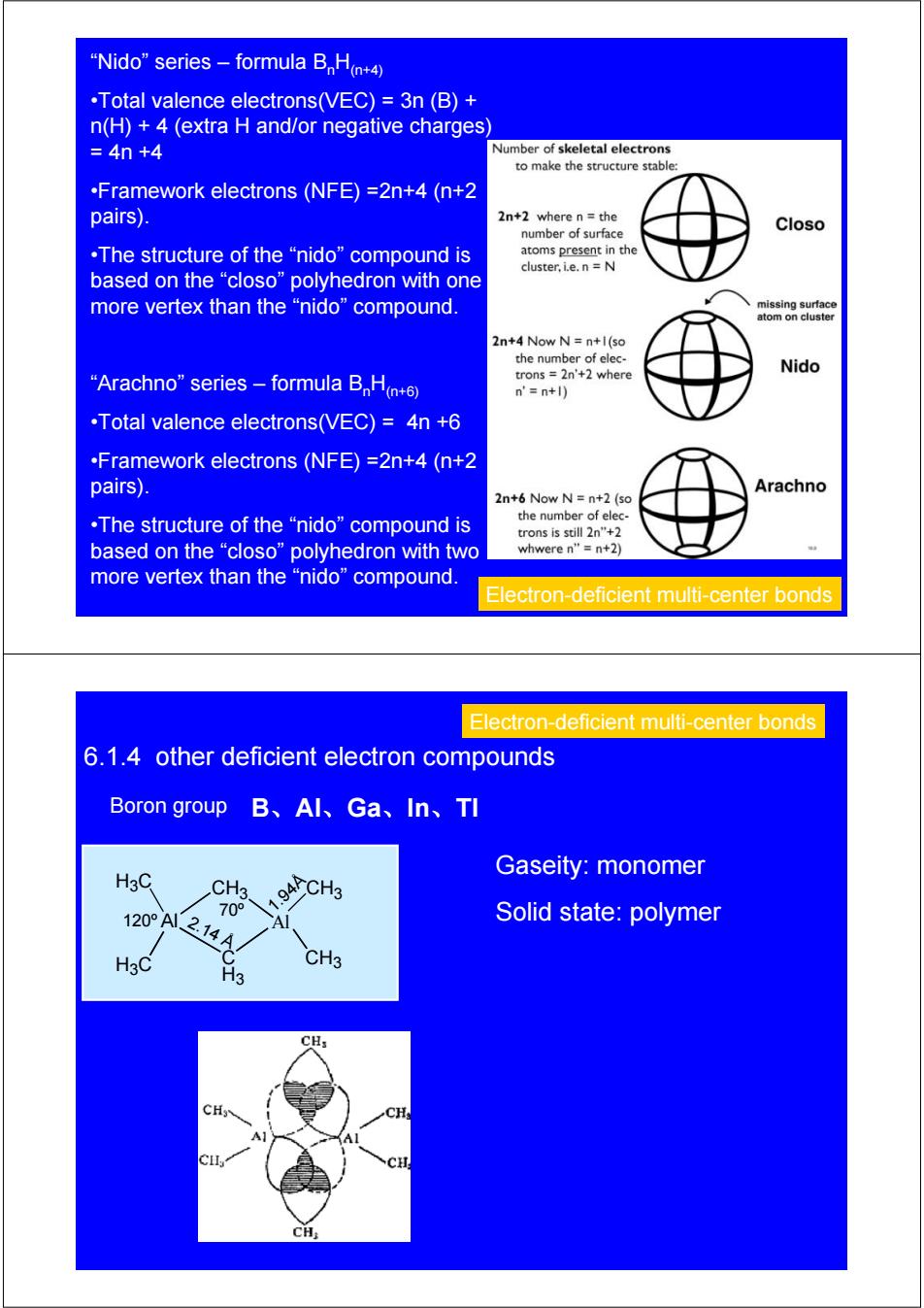
"Nido"series -formula BH+4) .Total valence electrons(VEC)=3n (B)+ n(H)+4 (extra H and/or negative charges) =4n+4 Number of skeletal electrons to make the structure stable: .Framework electrons (NFE)=2n+4(n+2 pairs). 2n+2 where n=the number of surface Closo ,The structure of the“nido”compound is atoms present in the cluster,i.e.n =N based on the“closo”polyhedron with one more vertex than the“nido”compound, missing surface atom on cluster 2n+4 Now N=n+l(so the number of elec- trons 2n'+2 where Nido “Arachno”series-formula B,Ha+6 n'=n+) .Total valence electrons(VEC)=4n +6 .Framework electrons(NFE)=2n+4(n+2 pairs) Arachno 2n+6 Now N=n+2 (so ,The structure of the“nido”compound is the number of elec- trons is still 2n"+2 based on the“closo”polyhedron with two whwere n"=n+2) more vertex than the“nido”compound. Electron-deficient multi-center bonds Electron-deficient multi-center bonds 6.1.4 other deficient electron compounds Boron group B、AI、Ga、In、TI Gaseity:monomer H3C CH3. 120A214A 70° A Solid state:polymer H3C CH3 H3 CH: CHy CH;
“Nido” series – formula BnH(n+4) •Total valence electrons(VEC) = 3n (B) + n(H) + 4 (extra H and/or negative charges) = 4n +4 •Framework electrons (NFE) =2n+4 (n+2 pairs). •The structure of the “nido” compound is based on the “closo” polyhedron with one more vertex than the “nido” compound. “Arachno” series – formula BnH(n+6) •Total valence electrons(VEC) = 4n +6 •Framework electrons (NFE) =2n+4 (n+2 pairs). •The structure of the “nido” compound is based on the “closo” polyhedron with two more vertex than the “nido” compound. Electron-deficient multi-center bonds 6.1.4 other deficient electron compounds Electron-deficient multi-center bonds 1.94Å 2.14 Å 120º 70º B、Al、Ga、In、Tl Gaseity: monomer Solid state: polymer Boron group H3C Al H3C Al C CH3 H3 CH3 CH3
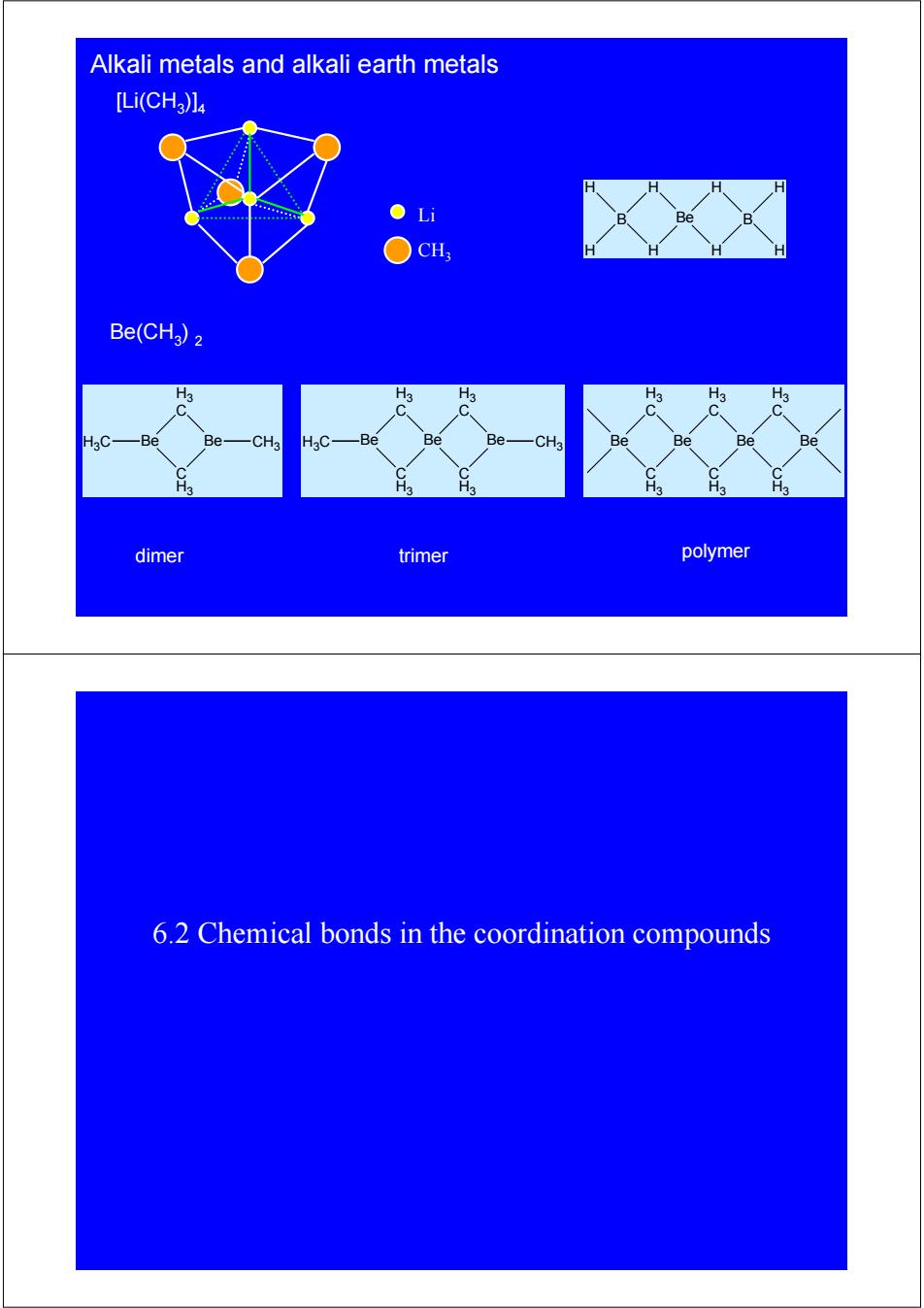
Alkali metals and alkali earth metals [Li(CHa)l : ●Li Be ○CH Be(CHa)2 H3 H3 H3 C -Be Be- -CH3 H3C -Be Be Be- CH3 Be Be Be Be H3 H3 H3 dimer trimer polymer 6.2 Chemical bonds in the coordination compounds
Alkali metals and alkali earth metals Li CH3 polymer [Li(CH3)]4 Be(CH3) 2 dimer trimer Be H3 C C H3 Be C H3 H3 C Be H3 C C H3 Be Be H3 C H3C C H3 Be C H3 H3 C Be Be CH3 H3 C H3C C H3 Be CH3 B H H H H Be H H B H H 6.2 Chemical bonds in the coordination compounds

Coordination compounds compounds composed of a metal atom or ion and one or more ligands. Ligands usually donate electrons to the metal Includes organometallic compounds New theories arose to describe bonding. -Valence bond,crystal field,and ligand field Co H.c ethylenediaminetetraacetate(EDTA4-) (hexadentate) CoEDTA
Coordination compounds Coordination compounds compounds composed of a metal atom or ion and one or more ligands. – Ligands usually donate electrons to the metal – Includes organometallic compounds New theories arose to describe bonding. –Valence bond, crystal field, and ligand field. N CH2 CH2 N CH2 C O O CH2 C O O C H2C O O C H2C O O ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA4–) (hexadentate)
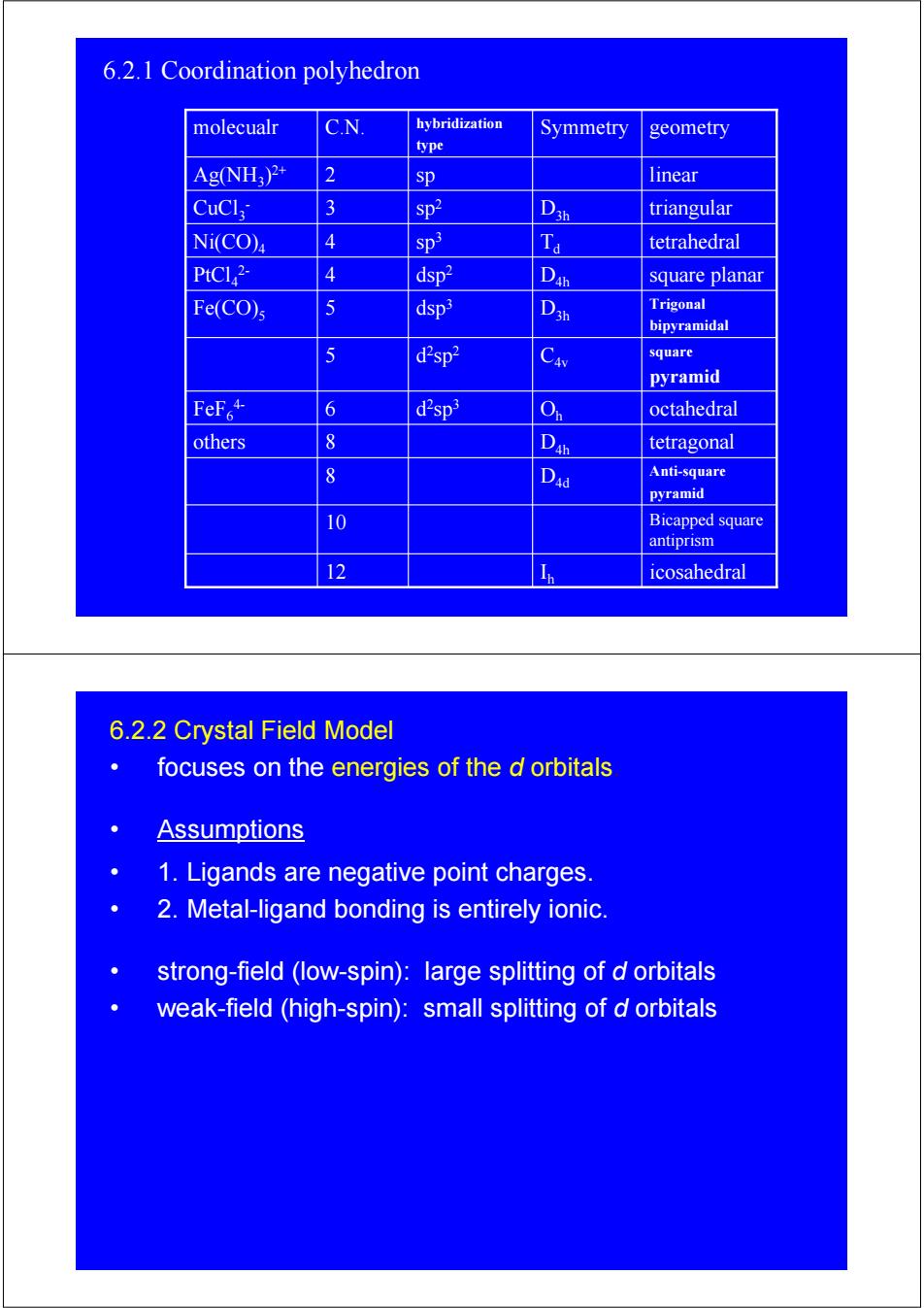
6.2.1 Coordination polyhedron molecualr C.N. hybridization Symmetry geometry type Ag(NH:)2+ 2 sp linear CuCl 3 sp2 triangular Ni(CO)4 4 Sp3 tetrahedral PtCl2- 4 dsp2 D square planar Fe(CO)s 5 dsp3 Trigonal bipyramidal 5 d2sp2 Cav square pyramid FeF+ 6 d2sp3 octahedral others 8 D tetragonal 8 Dad Anti-square pyramid 10 Bicapped square antiprism 12 Icosahedral 6.2.2 Crystal Field Model focuses on the energies of the d orbitals Assumptions 1.Ligands are negative point charges. 2.Metal-ligand bonding is entirely ionic. strong-field (low-spin):large splitting of d orbitals weak-field (high-spin):small splitting of d orbitals
I icosahedral 12 h Bicapped square antiprism 10 Anti-square pyramid 8 D4d D tetragonal others 8 4h O octahedral d h 2sp3 FeF6 6 4- square pyramid d C4v 2sp2 5 Trigonal bipyramidal dsp D3h 3 Fe(CO)5 5 D square planar dsp 4h 2 PtCl4 4 2- T tetrahedral d sp3 Ni(CO)4 4 D triangular 3h sp2 CuCl3 3 - Ag(NH 2 sp linear 3)2+ Symmetry geometry hybridization type molecualr C.N. 6.2.1 Coordination polyhedron 6.2.2 Crystal Field Model • focuses on the energies of the d orbitals. • Assumptions • 1. Ligands are negative point charges. • 2. Metal-ligand bonding is entirely ionic. • strong-field (low-spin): large splitting of d orbitals • weak-field (high-spin): small splitting of d orbitals