正在加载图片...
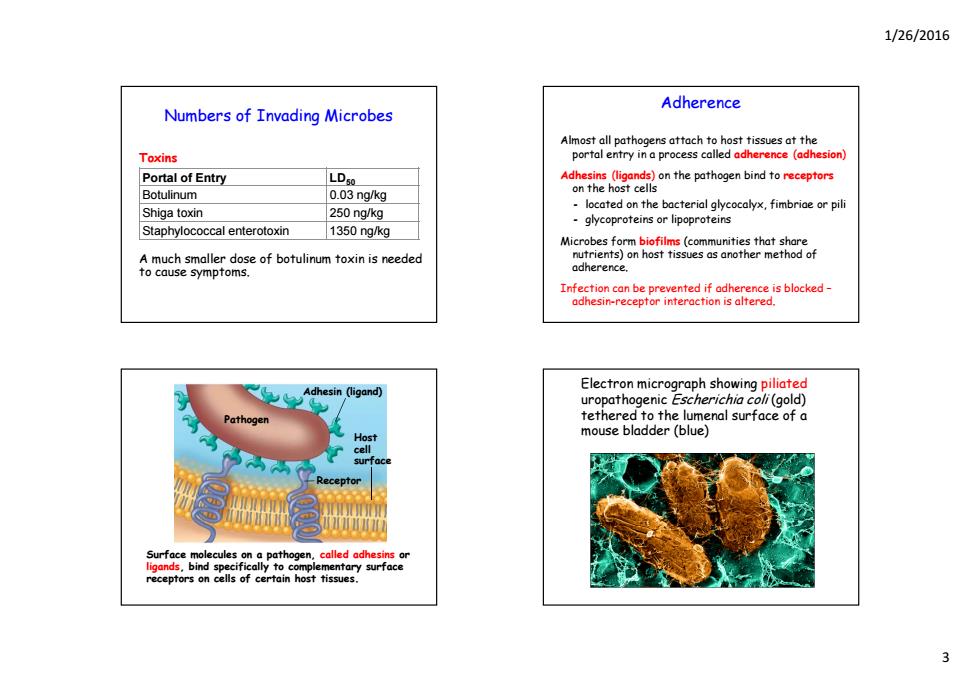
1/26/2016 Adherence Numbers of Invading Microbes Almost all pathogens attach to host tissues at the Toxins portal entry in a process called adherence (adhesion) Portal of Entry LD50 Botulinum 0.03 ng/kg located on the bacterial glycocalyx,fimbriae or pili Shiga toxin 250 ng/kg glycoproteins or lipoproteins Staphylococcal enterotoxin 1350 ng/kg Microbes form biofilms(communities that share much smaller dose of botulinum toxinis neede nutrients)on host tissues as another method of cause symptoms adherence. Infection can be prevented if adherence is blocked- adhesin-receptor interaction is altered. Adhesin (ligand) Electron micrograph showing piliated uropathogenic Escherichia coli(gold) Pathogen tethered to the lumenal surface of a mouse bladder (blue) Surface molecules on a pathogen.called adhesins or ligands.bind specifically to complementary surface receptors on cells of certain host tissues. 1/26/2016 3 Numbers of Invading Microbes Toxins Portal of Entry LD50 Botulinum 0.03 ng/kg Shiga toxin 250 ng/kg Staphylococcal enterotoxin 1350 ng/kg A much smaller dose of botulinum toxin is needed to cause symptoms. Adherence Almost all pathogens attach to host tissues at the portal entry in a process called adherence (adhesion) Adhesins (ligands) on the pathogen bind to receptors on the host cells - located on the bacterial glycocalyx, fimbriae or pili - glycoproteins or lipoproteins Microbes form biofilms (communities that share nutrients) on host tissues as another method of adherence. Infection can be prevented if adherence is blocked – adhesin-receptor interaction is altered. Adhesin (ligand) Pathogen Host cell surface Receptor Surface molecules on a pathogen, called adhesins or ligands, bind specifically to complementary surface receptors on cells of certain host tissues. Electron micrograph showing piliated uropathogenic Escherichia coli (gold) tethered to the lumenal surface of a mouse bladder (blue)