正在加载图片...
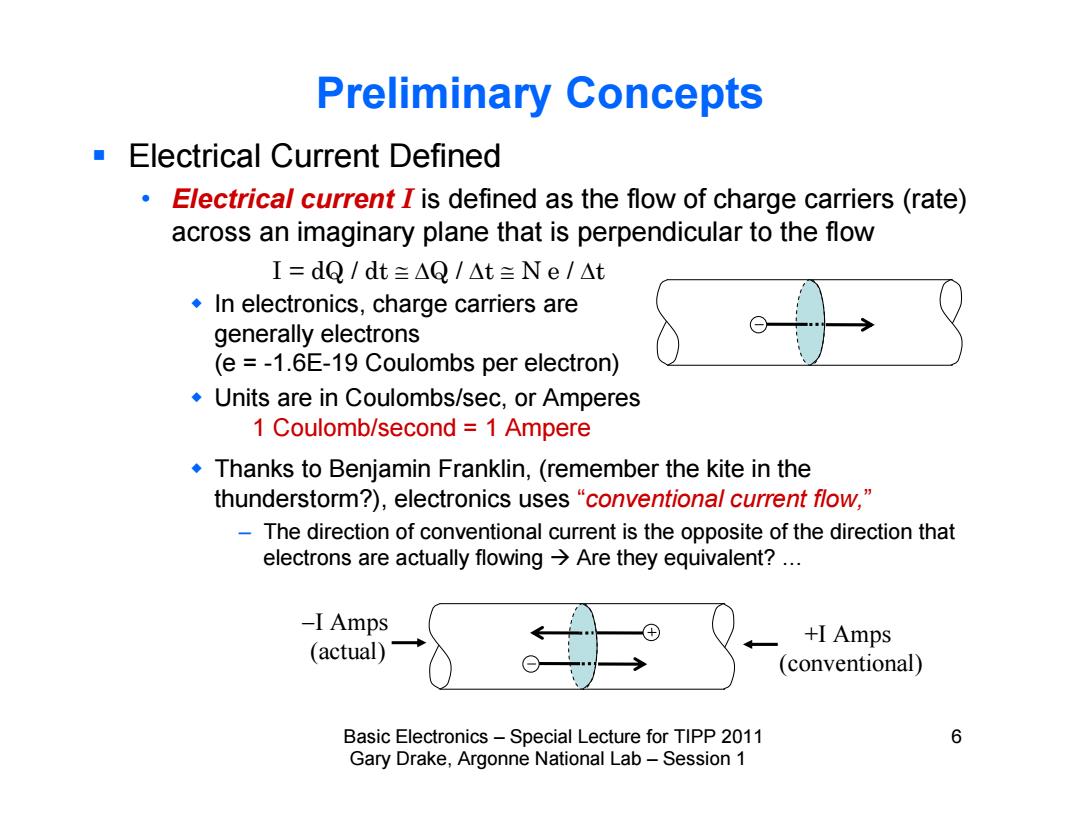
Preliminary Concepts Electrical Current Defined Electrical current I is defined as the flow of charge carriers (rate) across an imaginary plane that is perpendicular to the flow I=dQ/dt=△Q/△t三Ne/△t In electronics,charge carriers are generally electrons (e =-1.6E-19 Coulombs per electron) Units are in Coulombs/sec,or Amperes 1 Coulomb/second =1 Ampere Thanks to Benjamin Franklin,(remember the kite in the thunderstorm?),electronics uses "conventional current flow," The direction of conventional current is the opposite of the direction that electrons are actually flowing Are they equivalent?... -I Amps +I Amps (actual) (conventional) Basic Electronics-Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 6 Gary Drake,Argonne National Lab-Session 1Basic Electronics – Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 6 Gary Drake, Argonne National Lab – Session 1 Preliminary Concepts Electrical Current Defined • Electrical current I is defined as the flow of charge carriers (rate) across an imaginary plane that is perpendicular to the flow In electronics, charge carriers are generally electrons (e = -1.6E-19 Coulombs per electron) Units are in Coulombs/sec, or Amperes Thanks to Benjamin Franklin, (remember the kite in the thunderstorm?), electronics uses “conventional current flow,” – The direction of conventional current is the opposite of the direction that electrons are actually flowing Are they equivalent? … 1 Coulomb/second = 1 Ampere +I Amps (conventional) I Amps (actual) I = dQ / dt Q / t N e / t