正在加载图片...
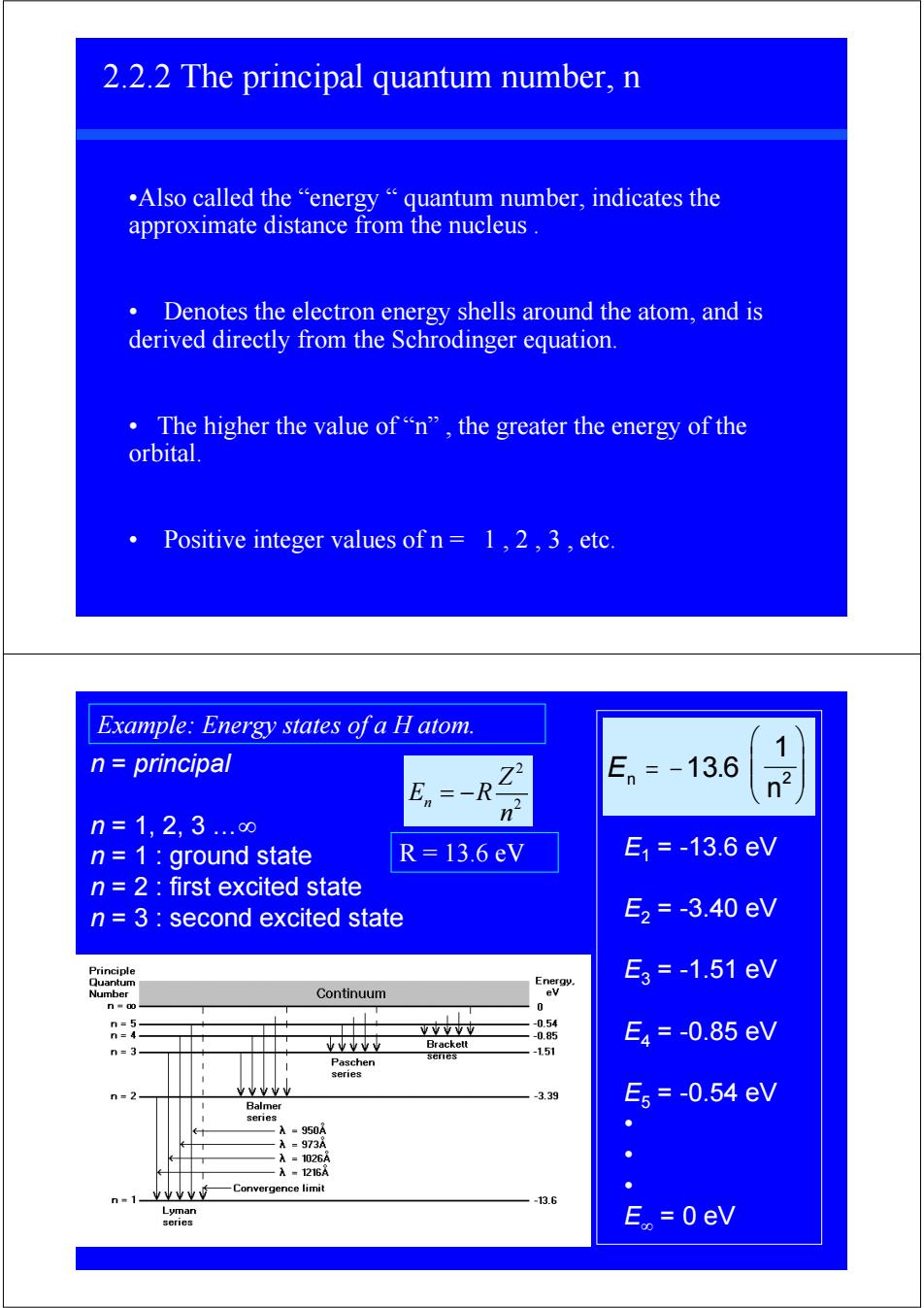
2.2.2 The principal quantum number,n .Also called the"energy"quantum number,indicates the approximate distance from the nucleus. Denotes the electron energy shells around the atom,and is derived directly from the Schrodinger equation. 。The higher the value of“n”,the greater the energy of the orbital. Positive integer values of n=1,2,3,etc. Example:Energy states of a H atom. 1 n principal En=-13.6 En -R n=1,2,3..∞ n n=1 ground state R=13.6eV E1=-13.6eV n 2 first excited state n 3 second excited state E2=-3.40eV Principle Quantum Energy. E3=-1.51eV Numher Continuum ev 0 n=5 -0.54 n=4 VVYV业 -0.85 E4=-0.85eV n=3- tvvve Brackett Paschen series -1.51 series n=2 YY业业 -3.39 E5=-0.54eV Balmer senes A=950A A=973A A=1026A A-1216A 业业业业" Convergence limit n"1 -13.6 Lyman series E。=0eV2.2.2 The principal quantum number, n •Also called the “energy “ quantum number, indicates the approximate distance from the nucleus . • Denotes the electron energy shells around the atom, and is derived directly from the Schrodinger equation. • The higher the value of “n” , the greater the energy of the orbital. • Positive integer values of n = 1 , 2 , 3 , etc. n = principal n = 1, 2, 3 …∞ n = 1 : ground state n = 2 : first excited state n = 3 : second excited state En n = − ⎛ ⎝ ⎜ ⎜ ⎞ ⎠ ⎟ ⎟ 13 6 1 2 . E1 = -13.6 eV E2 = -3.40 eV E3 = -1.51 eV E4 = -0.85 eV E5 = -0.54 eV • • • E∞ = 0 eV Example: Energy states of a H atom. 2 n 2 Z E R n = − R = 13.6 eV