正在加载图片...
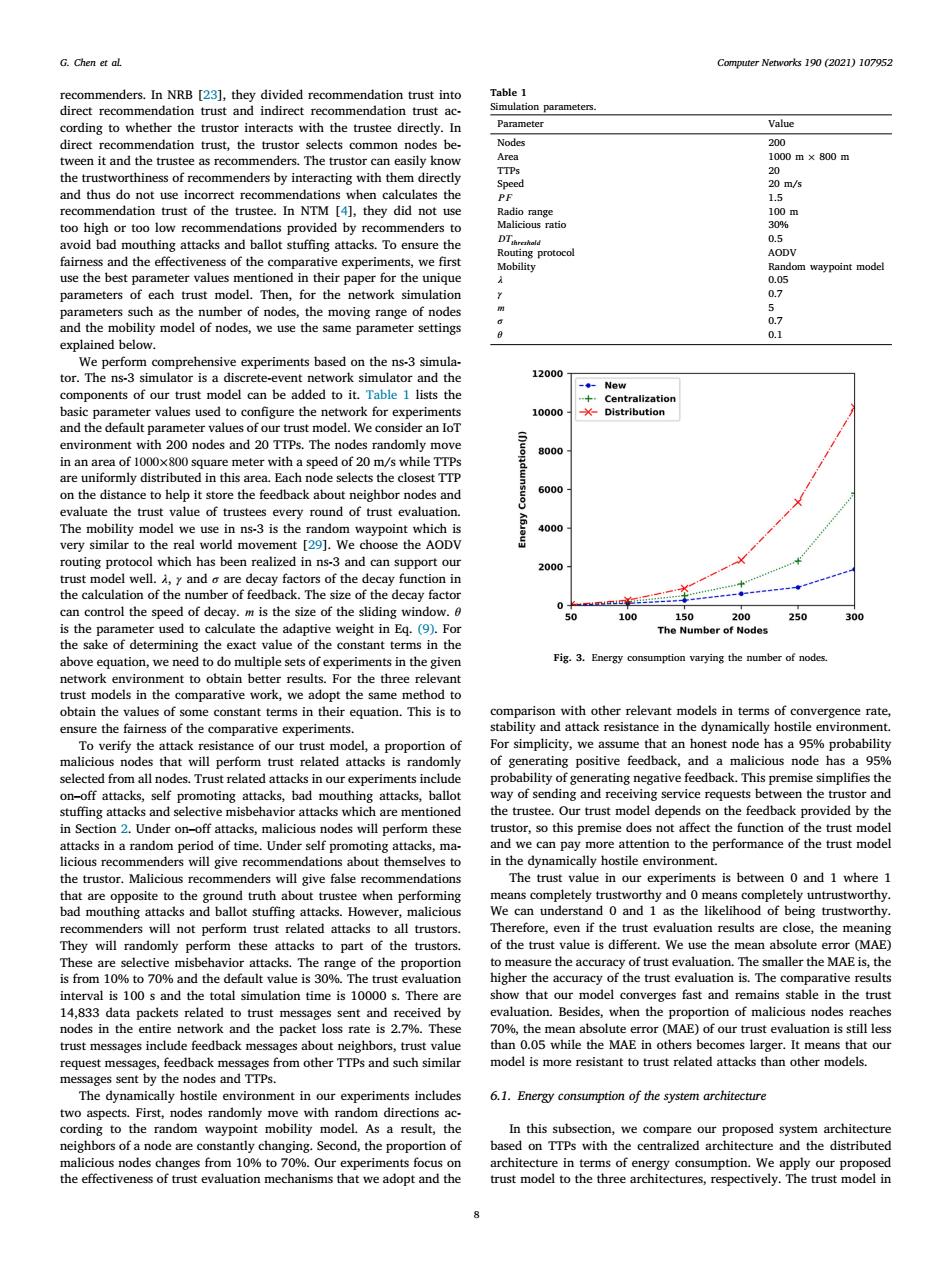
G.Chen et al. Computer Networks 190(2021)107952 recommenders.In NRB [23],they divided recommendation trust into Table 1 direct recommendation trust and indirect recommendation trust ac- Simulation parameters. cording to whether the trustor interacts with the trustee directly.In Parameter Value direct recommendation trust,the trustor selects common nodes be- Nodes 200 tween it and the trustee as recommenders.The trustor can easily know Area 1000m×800m TIPs 20 the trustworthiness of recommenders by interacting with them directly Speed 20m/s and thus do not use incorrect recommendations when calculates the PE 1.5 recommendation trust of the trustee.In NTM [4],they did not use Radio range 100m too high or too low recommendations provided by recommenders to Malicious ratio 30% avoid bad mouthing attacks and ballot stuffing attacks.To ensure the 0.5 Routing protocol AODV fairness and the effectiveness of the comparative experiments,we first Mobility Random waypoint model use the best parameter values mentioned in their paper for the unique 0.05 parameters of each trust model.Then,for the network simulation 0.7 parameters such as the number of nodes,the moving range of nodes 5 and the mobility model of nodes,we use the same parameter settings 0.7 0.1 explained below. We perform comprehensive experiments based on the ns-3 simula- tor.The ns-3 simulator is a discrete-event network simulator and the 12000 -New components of our trust model can be added to it.Table 1 lists the +Centralization basic parameter values used to configure the network for experiments 10000 X-Distribution and the default parameter values of our trust model.We consider an IoT environment with 200 nodes and 20 TTPs.The nodes randomly move 8000 in an area of 1000x800 square meter with a speed of 20 m/s while TTPs are uniformly distributed in this area.Each node selects the closest TTP on the distance to help it store the feedback about neighbor nodes and 6000 9 evaluate the trust value of trustees every round of trust evaluation. The mobility model we use in ns-3 is the random waypoint which is 4000 very similar to the real world movement [29].We choose the AODV routing protocol which has been realized in ns-3 and can support our 2000 trust model well.4,y and o are decay factors of the decay function in the calculation of the number of feedback.The size of the decay factor 0 can control the speed of decay.m is the size of the sliding window.6 50 100 150 200 250 300 is the parameter used to calculate the adaptive weight in Eq.(9).For The Number of Nodes the sake of determining the exact value of the constant terms in the above equation,we need to do multiple sets of experiments in the given Fig.3.Energy consumption varying the number of nodes. network environment to obtain better results.For the three relevant trust models in the comparative work,we adopt the same method to obtain the values of some constant terms in their equation.This is to comparison with other relevant models in terms of convergence rate, ensure the fairness of the comparative experiments. stability and attack resistance in the dynamically hostile environment To verify the attack resistance of our trust model,a proportion of For simplicity,we assume that an honest node has a 95%probability malicious nodes that will perform trust related attacks is randomly of generating positive feedback,and a malicious node has a 95% selected from all nodes.Trust related attacks in our experiments include probability of generating negative feedback.This premise simplifies the on-off attacks,self promoting attacks,bad mouthing attacks,ballot way of sending and receiving service requests between the trustor and stuffing attacks and selective misbehavior attacks which are mentioned the trustee.Our trust model depends on the feedback provided by the in Section 2.Under on-off attacks,malicious nodes will perform these trustor,so this premise does not affect the function of the trust model attacks in a random period of time.Under self promoting attacks,ma- and we can pay more attention to the performance of the trust model licious recommenders will give recommendations about themselves to in the dynamically hostile environment. the trustor.Malicious recommenders will give false recommendations The trust value in our experiments is between 0 and 1 where 1 that are opposite to the ground truth about trustee when performing means completely trustworthy and 0 means completely untrustworthy. bad mouthing attacks and ballot stuffing attacks.However,malicious We can understand 0 and 1 as the likelihood of being trustworthy. recommenders will not perform trust related attacks to all trustors. Therefore,even if the trust evaluation results are close,the meaning They will randomly perform these attacks to part of the trustors. of the trust value is different.We use the mean absolute error (MAE) These are selective misbehavior attacks.The range of the proportion to measure the accuracy of trust evaluation.The smaller the MAE is,the is from 10%to 70%and the default value is 30%.The trust evaluation higher the accuracy of the trust evaluation is.The comparative results interval is 100 s and the total simulation time is 10000 s.There are show that our model converges fast and remains stable in the trust 14,833 data packets related to trust messages sent and received by evaluation.Besides,when the proportion of malicious nodes reaches nodes in the entire network and the packet loss rate is 2.7%.These 70%,the mean absolute error (MAE)of our trust evaluation is still less trust messages include feedback messages about neighbors,trust value than 0.05 while the MAE in others becomes larger.It means that our request messages,feedback messages from other TTPs and such similar model is more resistant to trust related attacks than other models. messages sent by the nodes and TTPs. The dynamically hostile environment in our experiments includes 6.1.Energy consumption of the system architecture two aspects.First,nodes randomly move with random directions ac- cording to the random waypoint mobility model.As a result,the In this subsection,we compare our proposed system architecture neighbors of a node are constantly changing.Second,the proportion of based on TTPs with the centralized architecture and the distributed malicious nodes changes from 10%to 70%.Our experiments focus on architecture in terms of energy consumption.We apply our proposed the effectiveness of trust evaluation mechanisms that we adopt and the trust model to the three architectures,respectively.The trust model in 8Computer Networks 190 (2021) 107952 8 G. Chen et al. recommenders. In NRB [23], they divided recommendation trust into direct recommendation trust and indirect recommendation trust according to whether the trustor interacts with the trustee directly. In direct recommendation trust, the trustor selects common nodes between it and the trustee as recommenders. The trustor can easily know the trustworthiness of recommenders by interacting with them directly and thus do not use incorrect recommendations when calculates the recommendation trust of the trustee. In NTM [4], they did not use too high or too low recommendations provided by recommenders to avoid bad mouthing attacks and ballot stuffing attacks. To ensure the fairness and the effectiveness of the comparative experiments, we first use the best parameter values mentioned in their paper for the unique parameters of each trust model. Then, for the network simulation parameters such as the number of nodes, the moving range of nodes and the mobility model of nodes, we use the same parameter settings explained below. We perform comprehensive experiments based on the ns-3 simulator. The ns-3 simulator is a discrete-event network simulator and the components of our trust model can be added to it. Table 1 lists the basic parameter values used to configure the network for experiments and the default parameter values of our trust model. We consider an IoT environment with 200 nodes and 20 TTPs. The nodes randomly move in an area of 1000×800 square meter with a speed of 20 m/s while TTPs are uniformly distributed in this area. Each node selects the closest TTP on the distance to help it store the feedback about neighbor nodes and evaluate the trust value of trustees every round of trust evaluation. The mobility model we use in ns-3 is the random waypoint which is very similar to the real world movement [29]. We choose the AODV routing protocol which has been realized in ns-3 and can support our trust model well. 𝜆, 𝛾 and 𝜎 are decay factors of the decay function in the calculation of the number of feedback. The size of the decay factor can control the speed of decay. 𝑚 is the size of the sliding window. 𝜃 is the parameter used to calculate the adaptive weight in Eq. (9). For the sake of determining the exact value of the constant terms in the above equation, we need to do multiple sets of experiments in the given network environment to obtain better results. For the three relevant trust models in the comparative work, we adopt the same method to obtain the values of some constant terms in their equation. This is to ensure the fairness of the comparative experiments. To verify the attack resistance of our trust model, a proportion of malicious nodes that will perform trust related attacks is randomly selected from all nodes. Trust related attacks in our experiments include on–off attacks, self promoting attacks, bad mouthing attacks, ballot stuffing attacks and selective misbehavior attacks which are mentioned in Section 2. Under on–off attacks, malicious nodes will perform these attacks in a random period of time. Under self promoting attacks, malicious recommenders will give recommendations about themselves to the trustor. Malicious recommenders will give false recommendations that are opposite to the ground truth about trustee when performing bad mouthing attacks and ballot stuffing attacks. However, malicious recommenders will not perform trust related attacks to all trustors. They will randomly perform these attacks to part of the trustors. These are selective misbehavior attacks. The range of the proportion is from 10% to 70% and the default value is 30%. The trust evaluation interval is 100 s and the total simulation time is 10000 s. There are 14,833 data packets related to trust messages sent and received by nodes in the entire network and the packet loss rate is 2.7%. These trust messages include feedback messages about neighbors, trust value request messages, feedback messages from other TTPs and such similar messages sent by the nodes and TTPs. The dynamically hostile environment in our experiments includes two aspects. First, nodes randomly move with random directions according to the random waypoint mobility model. As a result, the neighbors of a node are constantly changing. Second, the proportion of malicious nodes changes from 10% to 70%. Our experiments focus on the effectiveness of trust evaluation mechanisms that we adopt and the Table 1 Simulation parameters. Parameter Value Nodes 200 Area 1000 m × 800 m TTPs 20 Speed 20 m/s 𝑃 𝐹 1.5 Radio range 100 m Malicious ratio 30% 𝐷𝑇𝑡ℎ𝑟𝑒𝑠ℎ𝑜𝑙𝑑 0.5 Routing protocol AODV Mobility Random waypoint model 𝜆 0.05 𝛾 0.7 𝑚 5 𝜎 0.7 𝜃 0.1 Fig. 3. Energy consumption varying the number of nodes. comparison with other relevant models in terms of convergence rate, stability and attack resistance in the dynamically hostile environment. For simplicity, we assume that an honest node has a 95% probability of generating positive feedback, and a malicious node has a 95% probability of generating negative feedback. This premise simplifies the way of sending and receiving service requests between the trustor and the trustee. Our trust model depends on the feedback provided by the trustor, so this premise does not affect the function of the trust model and we can pay more attention to the performance of the trust model in the dynamically hostile environment. The trust value in our experiments is between 0 and 1 where 1 means completely trustworthy and 0 means completely untrustworthy. We can understand 0 and 1 as the likelihood of being trustworthy. Therefore, even if the trust evaluation results are close, the meaning of the trust value is different. We use the mean absolute error (MAE) to measure the accuracy of trust evaluation. The smaller the MAE is, the higher the accuracy of the trust evaluation is. The comparative results show that our model converges fast and remains stable in the trust evaluation. Besides, when the proportion of malicious nodes reaches 70%, the mean absolute error (MAE) of our trust evaluation is still less than 0.05 while the MAE in others becomes larger. It means that our model is more resistant to trust related attacks than other models. 6.1. Energy consumption of the system architecture In this subsection, we compare our proposed system architecture based on TTPs with the centralized architecture and the distributed architecture in terms of energy consumption. We apply our proposed trust model to the three architectures, respectively. The trust model in