正在加载图片...
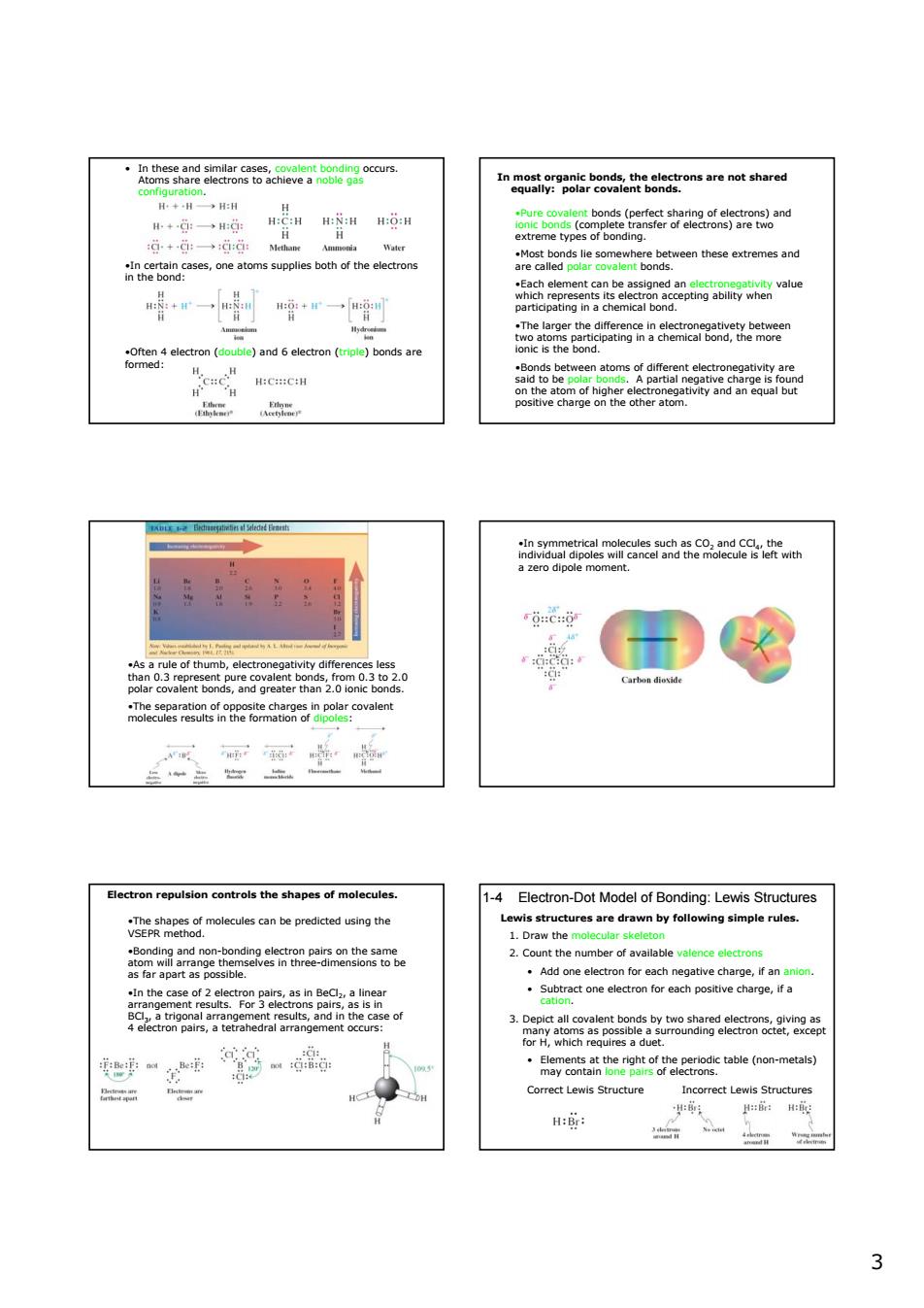
0+g一0g: W are2c8sermemegeemheseearemsand fecin pol cova oulsion co the shapes of molec Electron-Dot Model of Bonding:Lewis Structures .rawn by fol ing simple rule 2 2.Count the mtable (non-metal Correct Lewis Structure correct Lewis Struct H:: 4山 3 3 • In these and similar cases, covalent bonding occurs. Atoms share electrons to achieve a noble gas configuration. •In certain cases, one atoms supplies both of the electrons in the bond: •Often 4 electron (double) and 6 electron (triple) bonds are formed: In most organic bonds, the electrons are not shared equally: polar covalent bonds. •Pure covalent bonds (perfect sharing of electrons) and ionic bonds (complete transfer of electrons) are two extreme types of bonding. •Most bonds lie somewhere between these extremes and are called polar covalent bonds. •Each element can be assigned an electronegativity value which represents its electron accepting ability when participating in a chemical bond. •The larger the difference in electronegativety between two atoms participating in a chemical bond, the more ionic is the bond. •Bonds between atoms of different electronegativity are said to be polar bonds. A partial negative charge is found on the atom of higher electronegativity and an equal but positive charge on the other atom. •As a rule of thumb, electronegativity differences less than 0.3 represent pure covalent bonds, from 0.3 to 2.0 polar covalent bonds, and greater than 2.0 ionic bonds. •The separation of opposite charges in polar covalent molecules results in the formation of dipoles: •In symmetrical molecules such as CO2 and CCl4, the individual dipoles will cancel and the molecule is left with a zero dipole moment. Electron repulsion controls the shapes of molecules. •The shapes of molecules can be predicted using the VSEPR method. •Bonding and non-bonding electron pairs on the same atom will arrange themselves in three-dimensions to be as far apart as possible. •In the case of 2 electron pairs, as in BeCl2, a linear arrangement results. For 3 electrons pairs, as is in BCl3, a trigonal arrangement results, and in the case of 4 electron pairs, a tetrahedral arrangement occurs: 1-4 Electron-Dot Model of Bonding: Lewis Structures Lewis structures are drawn by following simple rules. 1. Draw the molecular skeleton 2. Count the number of available valence electrons • Add one electron for each negative charge, if an anion. • Subtract one electron for each positive charge, if a cation. 3. Depict all covalent bonds by two shared electrons, giving as many atoms as possible a surrounding electron octet, except for H, which requires a duet. • Elements at the right of the periodic table (non-metals) may contain lone pairs of electrons. Correct Lewis Structure Incorrect Lewis Structures