正在加载图片...
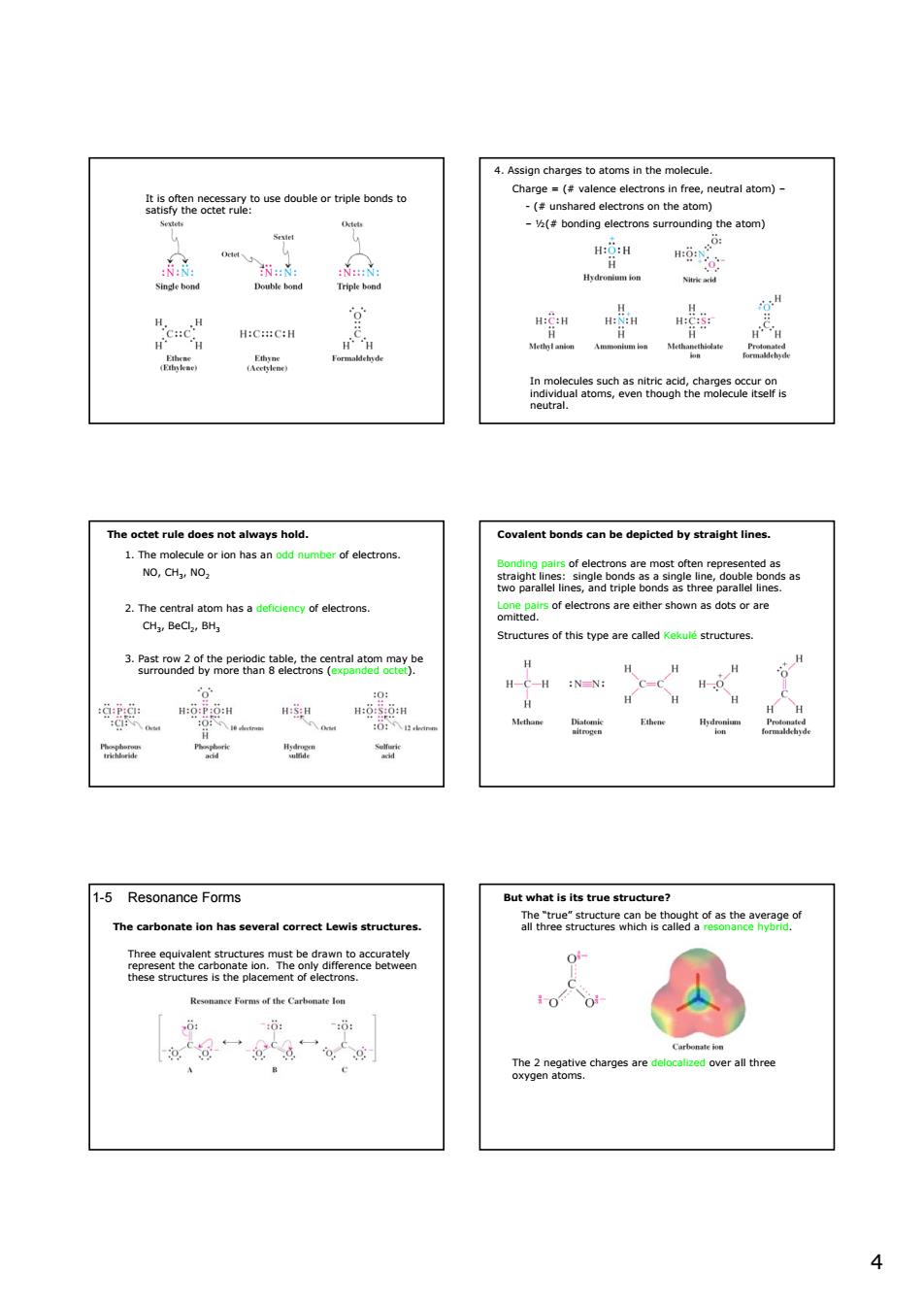
4.Assign charges to atoms in the molecule. obl orponds Charge(valence electrons in free,neutral atom) “ e。 The octet rule does not always hold. Covalent bondscan be depicted by straight lines. 1.ho: Structures of this type are called. 3atea3nwmopehe8tb2rtnlatomyc =-” 1-5 Resonance Forms at is its true structure? The carbonate ion has rrect Lewis stru of s the vereo caled over all three4 It is often necessary to use double or triple bonds to satisfy the octet rule: 4. Assign charges to atoms in the molecule. Charge = (# valence electrons in free, neutral atom) – - (# unshared electrons on the atom) – ½(# bonding electrons surrounding the atom) In molecules such as nitric acid, charges occur on individual atoms, even though the molecule itself is neutral. The octet rule does not always hold. 1. The molecule or ion has an odd number of electrons. NO, CH3, NO2 2. The central atom has a deficiency of electrons. CH3, BeCl2, BH3 3. Past row 2 of the periodic table, the central atom may be surrounded by more than 8 electrons (expanded octet). Covalent bonds can be depicted by straight lines. Bonding pairs of electrons are most often represented as straight lines: single bonds as a single line, double bonds as two parallel lines, and triple bonds as three parallel lines. Lone pairs of electrons are either shown as dots or are omitted. Structures of this type are called Kekulé structures. 1-5 Resonance Forms The carbonate ion has several correct Lewis structures. Three equivalent structures must be drawn to accurately represent the carbonate ion. The only difference between these structures is the placement of electrons. But what is its true structure? The “true” structure can be thought of as the average of all three structures which is called a resonance hybrid. The 2 negative charges are delocalized over all three oxygen atoms