正在加载图片...
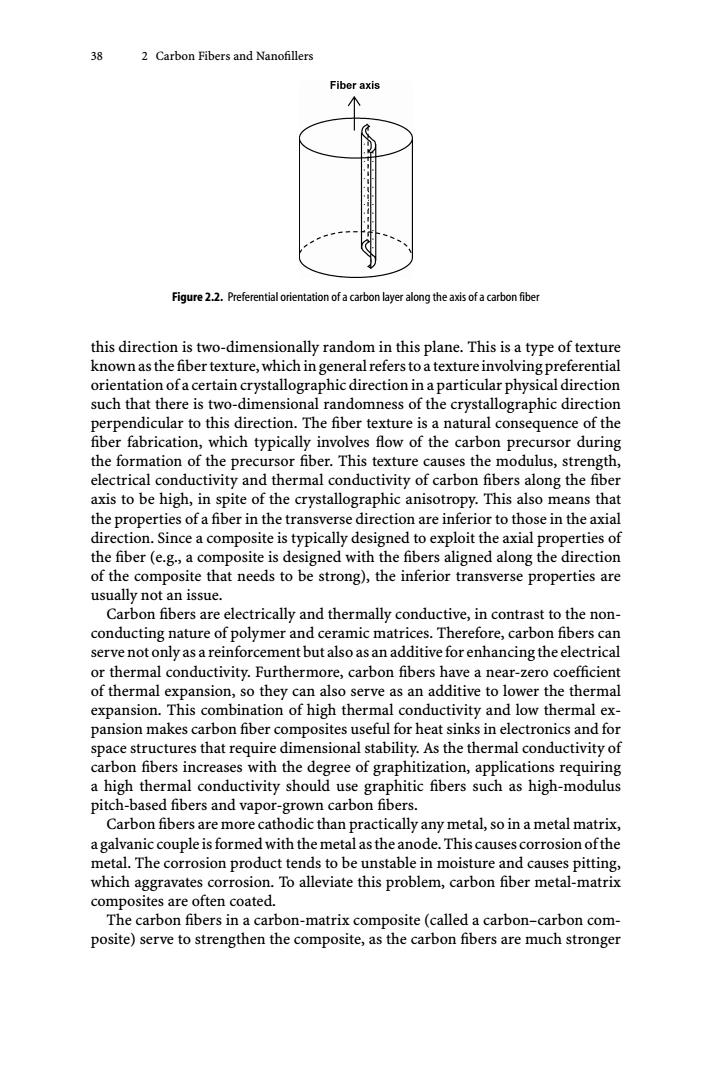
38 2 Carbon Fibers and Nanofillers Fiber axis Figure 2.2.Preferential orientation of a carbon layer along the axis of a carbon fiber this direction is two-dimensionally random in this plane.This is a type of texture known as the fiber texture,which in general refers to a texture involving preferential orientation ofa certain crystallographic direction in a particular physical direction such that there is two-dimensional randomness of the crystallographic direction perpendicular to this direction.The fiber texture is a natural consequence of the fiber fabrication,which typically involves flow of the carbon precursor during the formation of the precursor fiber.This texture causes the modulus,strength, electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity of carbon fibers along the fiber axis to be high,in spite of the crystallographic anisotropy.This also means that the properties of a fiber in the transverse direction are inferior to those in the axial direction.Since a composite is typically designed to exploit the axial properties of the fiber (e.g.,a composite is designed with the fibers aligned along the direction of the composite that needs to be strong),the inferior transverse properties are usually not an issue. Carbon fibers are electrically and thermally conductive,in contrast to the non- conducting nature of polymer and ceramic matrices.Therefore,carbon fibers can serve not only as a reinforcement but also as an additive for enhancing the electrical or thermal conductivity.Furthermore,carbon fibers have a near-zero coefficient of thermal expansion,so they can also serve as an additive to lower the thermal expansion.This combination of high thermal conductivity and low thermal ex- pansion makes carbon fiber composites useful for heat sinks in electronics and for space structures that require dimensional stability.As the thermal conductivity of carbon fibers increases with the degree of graphitization,applications requiring a high thermal conductivity should use graphitic fibers such as high-modulus pitch-based fibers and vapor-grown carbon fibers. Carbon fibers are more cathodic than practically any metal,so in a metal matrix, a galvanic couple is formed with the metal as the anode.This causes corrosion ofthe metal.The corrosion product tends to be unstable in moisture and causes pitting, which aggravates corrosion.To alleviate this problem,carbon fiber metal-matrix composites are often coated. The carbon fibers in a carbon-matrix composite(called a carbon-carbon com- posite)serve to strengthen the composite,as the carbon fibers are much stronger38 2 Carbon Fibers and Nanofillers Figure 2.2. Preferential orientation of a carbon layer along the axis of a carbon fiber this direction is two-dimensionally random in this plane. This is a type of texture knownasthefibertexture,whichingeneralreferstoatextureinvolvingpreferential orientation of a certain crystallographic direction in a particular physical direction such that there is two-dimensional randomness of the crystallographic direction perpendicular to this direction. The fiber texture is a natural consequence of the fiber fabrication, which typically involves flow of the carbon precursor during the formation of the precursor fiber. This texture causes the modulus, strength, electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity of carbon fibers along the fiber axis to be high, in spite of the crystallographic anisotropy. This also means that the properties of a fiber in the transverse direction are inferior to those in the axial direction. Since a composite is typically designed to exploit the axial properties of the fiber (e.g., a composite is designed with the fibers aligned along the direction of the composite that needs to be strong), the inferior transverse properties are usually not an issue. Carbon fibers are electrically and thermally conductive, in contrast to the nonconducting nature of polymer and ceramic matrices. Therefore, carbon fibers can serve not only as a reinforcement but also as an additive for enhancing the electrical or thermal conductivity. Furthermore, carbon fibers have a near-zero coefficient of thermal expansion, so they can also serve as an additive to lower the thermal expansion. This combination of high thermal conductivity and low thermal expansion makes carbon fiber composites useful for heat sinks in electronics and for space structures that require dimensional stability. As the thermal conductivity of carbon fibers increases with the degree of graphitization, applications requiring a high thermal conductivity should use graphitic fibers such as high-modulus pitch-based fibers and vapor-grown carbon fibers. Carbon fibers are more cathodic than practically any metal, so in a metal matrix, agalvanic coupleisformedwith themetalastheanode.Thiscausescorrosionofthe metal. The corrosion product tends to be unstable in moisture and causes pitting, which aggravates corrosion. To alleviate this problem, carbon fiber metal-matrix composites are often coated. The carbon fibers in a carbon-matrix composite (called a carbon–carbon composite) serve to strengthen the composite, as the carbon fibers are much stronger