正在加载图片...
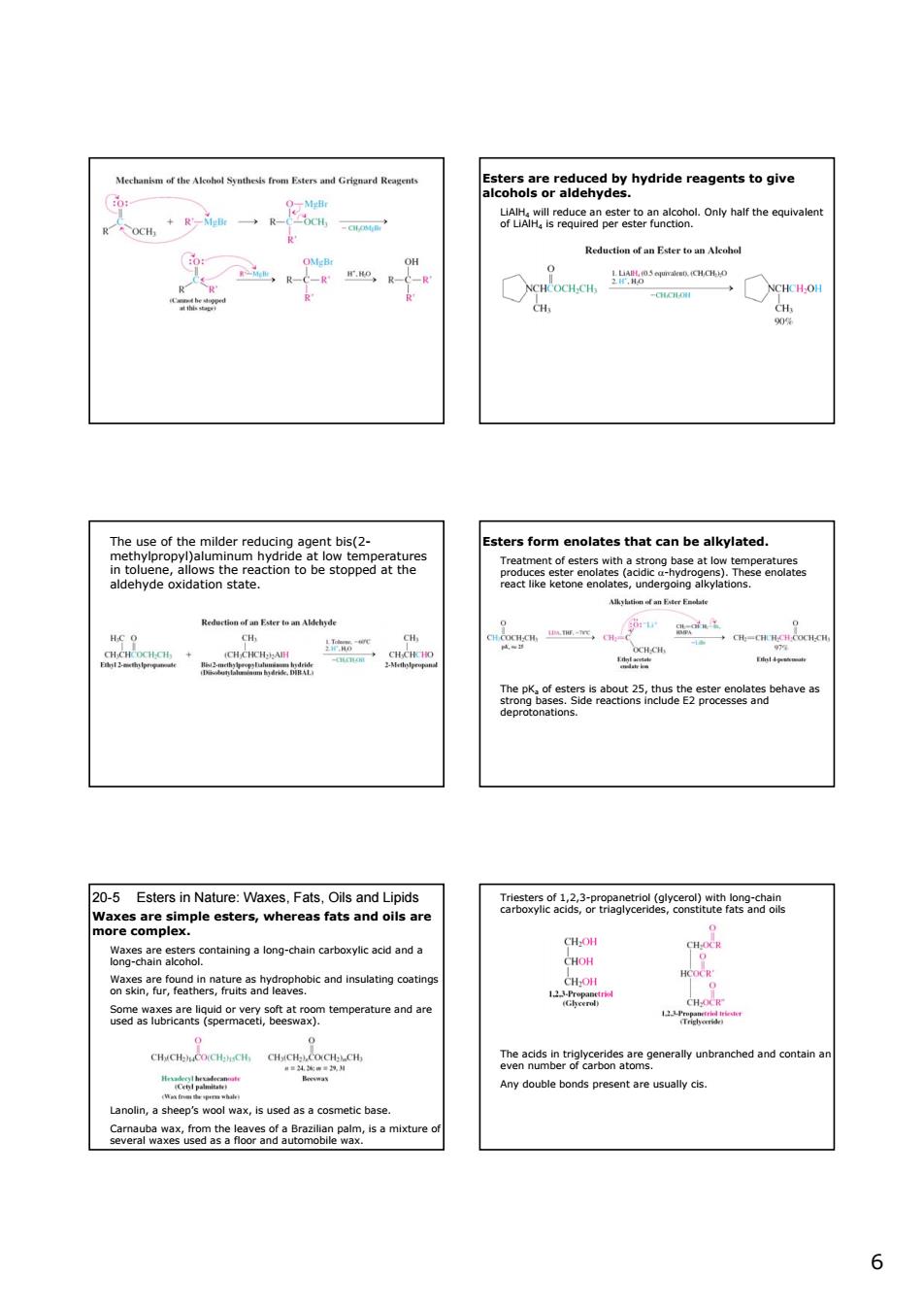
5itonagr8rgsngbyydridereagentstogve On halt the lr CH rs form enolates that can be alkylated alliows the aldehyde oxidation state. 5告e 20-5 Esters in Nature:Waxes.Fats.Oils and Lipids aaPgreoc28a more complex sa山 gnareyoeadhenatesgthoicandtnsuetncoetngg tempertre nd re ouble bonds present are usually c ax,is use d as a cosmetic base vmmixture of 66 Esters are reduced by hydride reagents to give alcohols or aldehydes. LiAlH4 will reduce an ester to an alcohol. Only half the equivalent of LiAlH4 is required per ester function. The use of the milder reducing agent bis(2- methylpropyl)aluminum hydride at low temperatures in toluene, allows the reaction to be stopped at the aldehyde oxidation state. Esters form enolates that can be alkylated. Treatment of esters with a strong base at low temperatures produces ester enolates (acidic α-hydrogens). These enolates react like ketone enolates, undergoing alkylations. The pKa of esters is about 25, thus the ester enolates behave as strong bases. Side reactions include E2 processes and deprotonations. 20-5 Esters in Nature: Waxes, Fats, Oils and Lipids Lanolin, a sheep’s wool wax, is used as a cosmetic base. Carnauba wax, from the leaves of a Brazilian palm, is a mixture of several waxes used as a floor and automobile wax. Waxes are simple esters, whereas fats and oils are more complex. Waxes are esters containing a long-chain carboxylic acid and a long-chain alcohol. Waxes are found in nature as hydrophobic and insulating coatings on skin, fur, feathers, fruits and leaves. Some waxes are liquid or very soft at room temperature and are used as lubricants (spermaceti, beeswax). Triesters of 1,2,3-propanetriol (glycerol) with long-chain carboxylic acids, or triaglycerides, constitute fats and oils The acids in triglycerides are generally unbranched and contain an even number of carbon atoms. Any double bonds present are usually cis