正在加载图片...
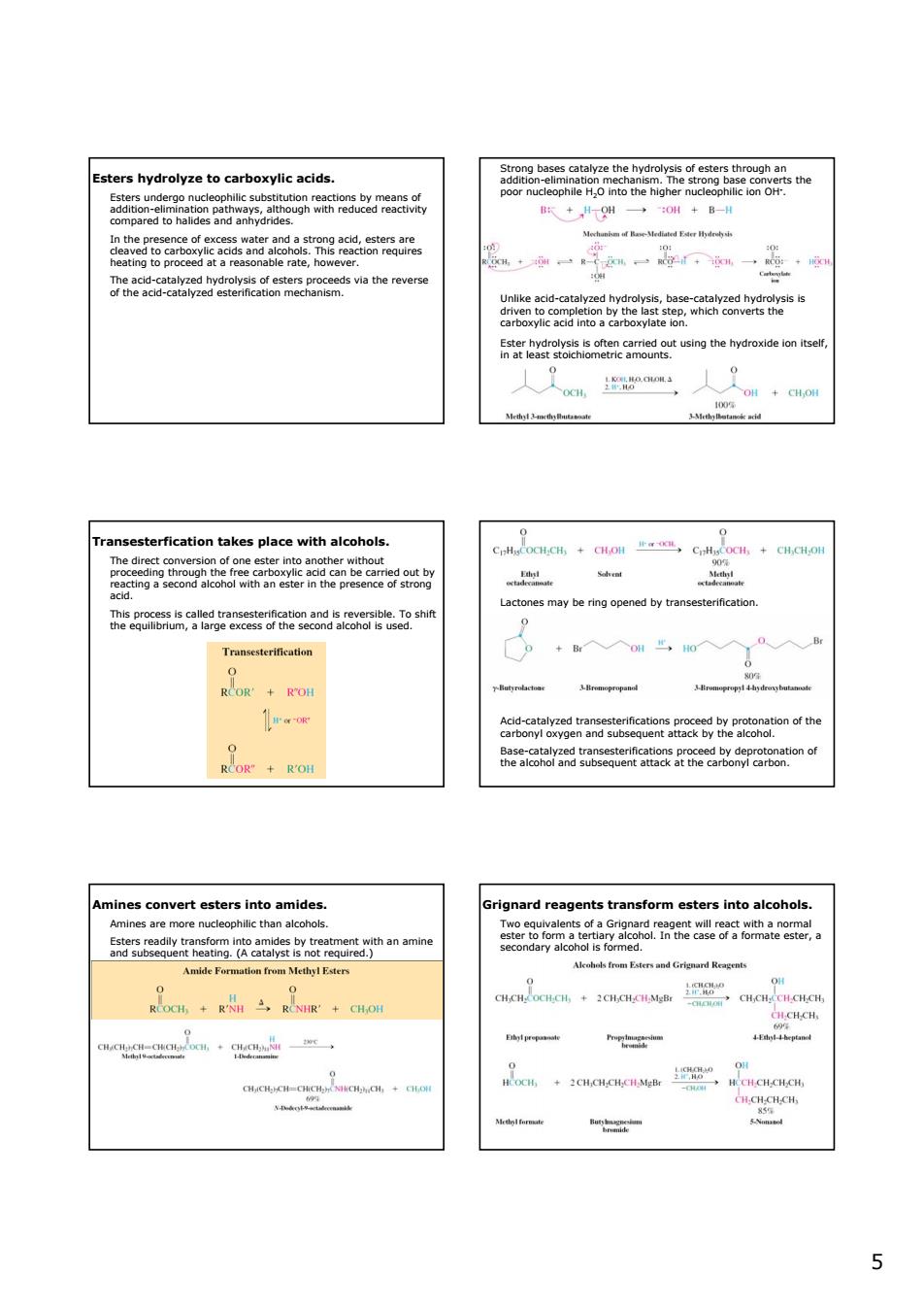
Esters hydrolyze to carboxylic acids. sophile Ho into the hiah 253oa 跃+用一0啡+B- Em尚n动中 lvreacton hm df Bne-M 一一一· thecm via the revers fteagco55snoeeRameactusngthehydroxideontee .m a erfication ta kes place with alcohols Lactones may be ring opened by transesterification esterineadon RCOR'KOH 事w取 ard reagents transform esters into alcohols 5 5 Esters hydrolyze to carboxylic acids. Esters undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions by means of addition-elimination pathways, although with reduced reactivity compared to halides and anhydrides. In the presence of excess water and a strong acid, esters are cleaved to carboxylic acids and alcohols. This reaction requires heating to proceed at a reasonable rate, however. The acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of esters proceeds via the reverse of the acid-catalyzed esterification mechanism. Strong bases catalyze the hydrolysis of esters through an addition-elimination mechanism. The strong base converts the poor nucleophile H2O into the higher nucleophilic ion OH- . Unlike acid-catalyzed hydrolysis, base-catalyzed hydrolysis is driven to completion by the last step, which converts the carboxylic acid into a carboxylate ion. Ester hydrolysis is often carried out using the hydroxide ion itself, in at least stoichiometric amounts. Transesterfication takes place with alcohols. The direct conversion of one ester into another without proceeding through the free carboxylic acid can be carried out by reacting a second alcohol with an ester in the presence of strong acid. This process is called transesterification and is reversible. To shift the equilibrium, a large excess of the second alcohol is used. Lactones may be ring opened by transesterification. Acid-catalyzed transesterifications proceed by protonation of the carbonyl oxygen and subsequent attack by the alcohol. Base-catalyzed transesterifications proceed by deprotonation of the alcohol and subsequent attack at the carbonyl carbon. Amines convert esters into amides. Amines are more nucleophilic than alcohols. Esters readily transform into amides by treatment with an amine and subsequent heating. (A catalyst is not required.) Grignard reagents transform esters into alcohols. Two equivalents of a Grignard reagent will react with a normal ester to form a tertiary alcohol. In the case of a formate ester, a secondary alcohol is formed