正在加载图片...
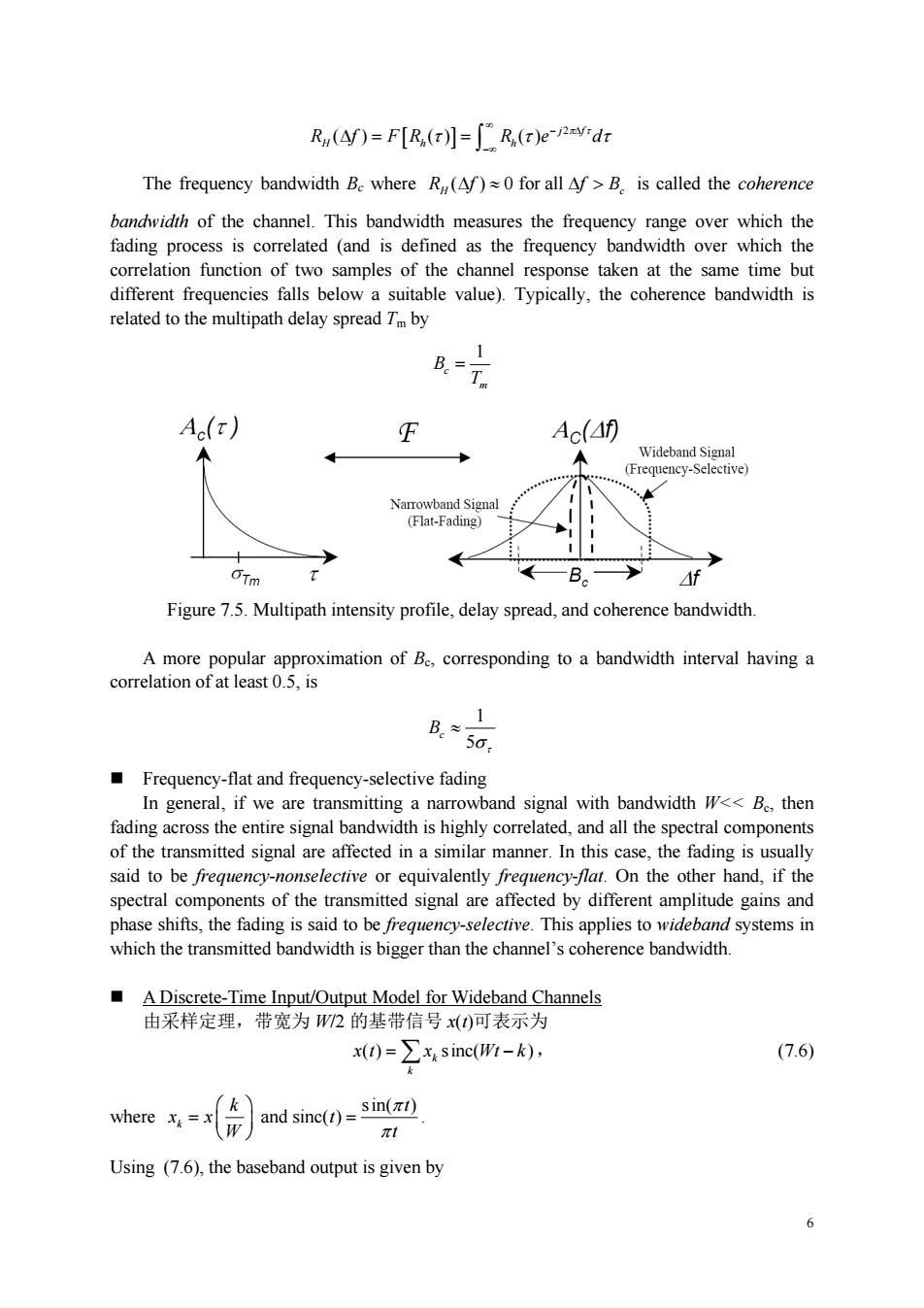
R(f)=F[R,()]=[R(r)e-vidr The frequency bandwidth B.where R(f)0 for all f>B.is called the coherence bandwidth of the channel.This bandwidth measures the frequency range over which the fading process is correlated (and is defined as the frequency bandwidth over which the correlation function of two samples of the channel resp onse taken at the same time but different frequencies falls below a suitable value).Typically,the coherence bandwidth is related to the multipath delay spread 7m by B.= T Ac() Ac(40 A N (Flat-Fading) ← B。1 Figure 7.5.Multipath intensity profile,delay spread,and coherence bandwidth. B50, Frequency-flat and frequency-selective fading In gene eral,if we are a na rowband signal with bandwidth W<<B.then of the transmitted signal are affected in a similar manner.In this case,the fading is usually said to be frequency-nonselective or equivalently frequency-flat.On the other hand,if the spectral components of the transmitted signal are affected by different amplitude gains and hase shifts,the fading is said to be freque ncy-selective.This applies to wideband systems in which the transmitted bandwidth is bigger than the channel's coherence bandwidth A Discrete-Time Input/Output Model for Wideband Channels 由采样定理,带宽为W2的基带信号x()可表示为 x()=∑x4sinc(W所-k), (7.6) where)and sine()i) Using (7.6),the baseband output is given by a6 2 ( ) () () j f RH hh f FR R e d The frequency bandwidth Bc where ( ) 0 for all RH c f fB is called the coherence bandwidth of the channel. This bandwidth measures the frequency range over which the fading process is correlated (and is defined as the frequency bandwidth over which the correlation function of two samples of the channel response taken at the same time but different frequencies falls below a suitable value). Typically, the coherence bandwidth is related to the multipath delay spread Tm by 1 c m B T Figure 7.5. Multipath intensity profile, delay spread, and coherence bandwidth. A more popular approximation of Bc, corresponding to a bandwidth interval having a correlation of at least 0.5, is 1 5 Bc Frequency-flat and frequency-selective fading In general, if we are transmitting a narrowband signal with bandwidth W<< Bc, then fading across the entire signal bandwidth is highly correlated, and all the spectral components of the transmitted signal are affected in a similar manner. In this case, the fading is usually said to be frequency-nonselective or equivalently frequency-flat. On the other hand, if the spectral components of the transmitted signal are affected by different amplitude gains and phase shifts, the fading is said to be frequency-selective. This applies to wideband systems in which the transmitted bandwidth is bigger than the channel’s coherence bandwidth. A Discrete-Time Input/Output Model for Wideband Channels 由采样定理,带宽为 W/2 的基带信号 x(t)可表示为 ( ) sinc( ) k k x t x Wt k , (7.6) where sin( ) and sinc( ) k k t xx t W t . Using (7.6), the baseband output is given by