正在加载图片...
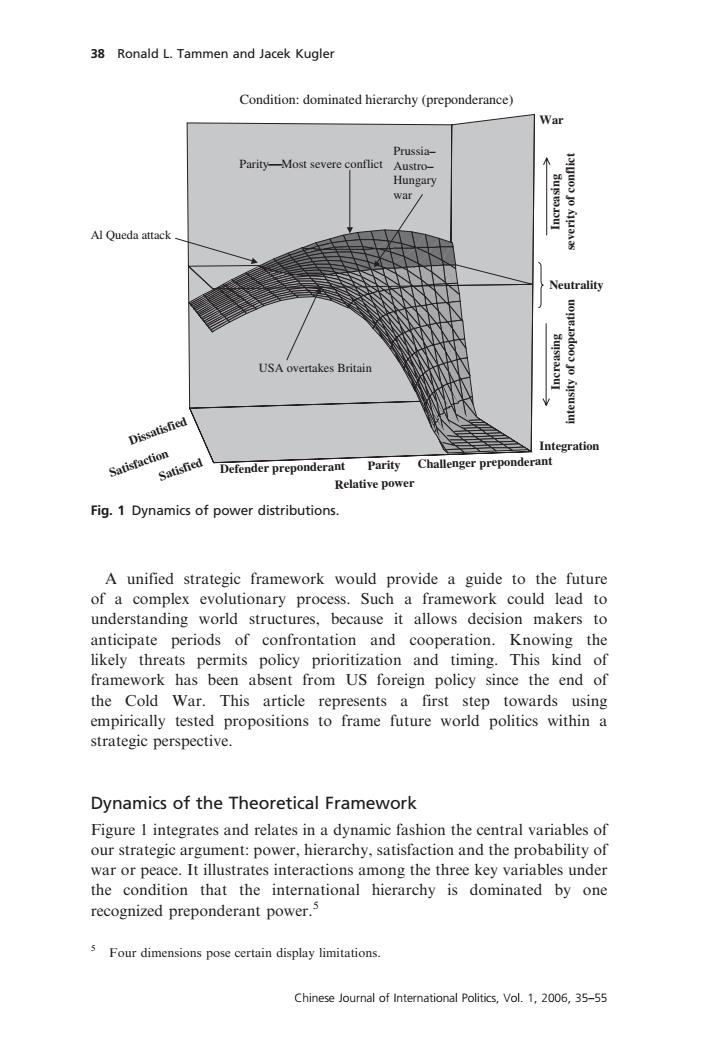
38 Ronald L.Tammen and Jacek Kugler Condition:dominated hierarchy(preponderance) War Prussia- Parity-Most severe conflict Austro- Hungary war/ Al Queda attack Neutrality USA overtakes Britain Dissatisfied Integration Satisfaction Satisfied Defender preponderant Parity Challenger preponderant Relative power Fig.1 Dynamics of power distributions. A unified strategic framework would provide a guide to the future of a complex evolutionary process.Such a framework could lead to understanding world structures,because it allows decision makers to anticipate periods of confrontation and cooperation.Knowing the likely threats permits policy prioritization and timing.This kind of framework has been absent from US foreign policy since the end of the Cold War.This article represents a first step towards using empirically tested propositions to frame future world politics within a strategic perspective. Dynamics of the Theoretical Framework Figure I integrates and relates in a dynamic fashion the central variables of our strategic argument:power,hierarchy,satisfaction and the probability of war or peace.It illustrates interactions among the three key variables under the condition that the international hierarchy is dominated by one recognized preponderant power.5 5 Four dimensions pose certain display limitations. Chinese Journal of International Politics,Vol.1,2006,35-55A unified strategic framework would provide a guide to the future of a complex evolutionary process. Such a framework could lead to understanding world structures, because it allows decision makers to anticipate periods of confrontation and cooperation. Knowing the likely threats permits policy prioritization and timing. This kind of framework has been absent from US foreign policy since the end of the Cold War. This article represents a first step towards using empirically tested propositions to frame future world politics within a strategic perspective. Dynamics of the Theoretical Framework Figure 1 integrates and relates in a dynamic fashion the central variables of our strategic argument: power, hierarchy, satisfaction and the probability of war or peace. It illustrates interactions among the three key variables under the condition that the international hierarchy is dominated by one recognized preponderant power.5 Relative power Defender preponderant Parity Challenger preponderant Satisfaction Dissatisfied Satisfied Condition: dominated hierarchy (preponderance) Neutrality War Integration Increasing severity of conflict Increasing intensity of cooperation ParityMost severe conflict Prussia– Austro– Hungary war Al Queda attack USA overtakes Britain Fig. 1 Dynamics of power distributions. 5 Four dimensions pose certain display limitations. 38 Ronald L. Tammen and Jacek Kugler Chinese Journal of International Politics, Vol. 1, 2006, 35–55