正在加载图片...
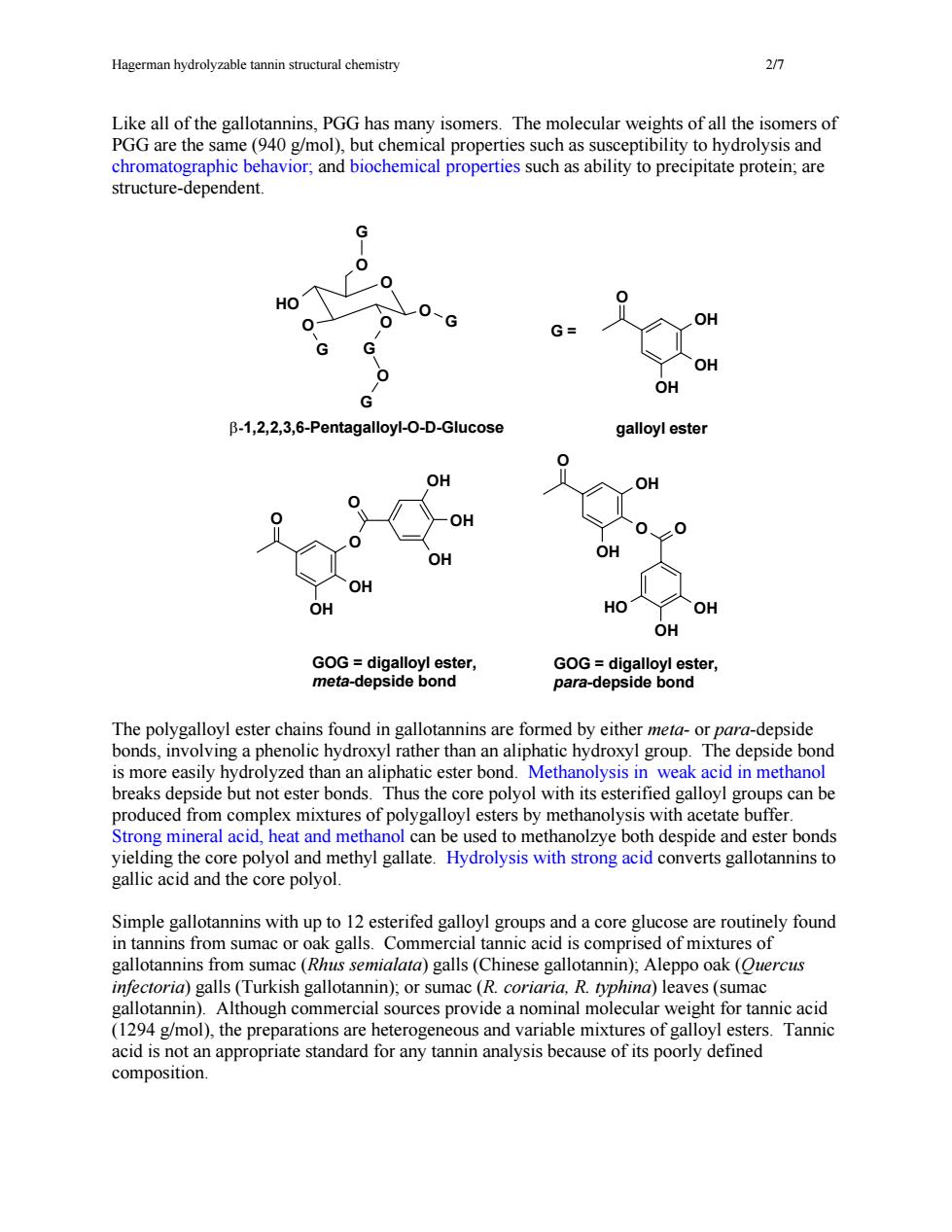
Hagerman hydrolyzable tannin structural chemistry 0 Like all of the gallotannins,PGG has many isomers.The molecular weights of all the isomers of PGG are the same(940 g/mol),but chemical properties such as susceptibility to hydrolysis and chromatographic behavior;and biochemical properties such as ability to precipitate protein;are structure-dependent. G G- OH OH OH B-1,2,2,3,6-PentagalloyI-O-D-GIucose galloyl ester OH OH OH OH GOG=diaallo ester GOG=digalloyl ester meta-depside bond para-depside bond nnins are side bonds,involv ng a phenol hydroxyl rather than an aliphatic hydroxyl group. s more easi hydrolyzed than an aliphatic ester bond Methanolysis in weak acid in methano breaks depside but not ester bonds.Thus the core polyol with its esterified galloyl groups can be produced from complex mixtures of polygalloyl esters by methanolysis with acetate buffer. Strong mineral acid,heat and methanol can be used to methanolzye both despide and ester bonds yielding the core polyol and methyl gallate.Hydrolysis with strong acid converts gallotannins to gallic acid and the core polyol. Simple gallotannins with up to 12 esterifed galloyl groups and a core glucose are routinely found in tannins from sumac or oak galls.Commercial tannic acid is comprised of mixtures of gallotannins from sumac (Rhus semialata)galls (Chinese gallotannin).Aleppo oak(Ouercus infectoria)galls(Turkish gallotannin)or sumac (R.coriaria.R.typhina)le es (sumac in).Although commercial so ide a ominal m eight for tannic acid 1294 /mol).the are het and, Tan acid is at appropr dard for any is he ofits poory omposition. Hagerman hydrolyzable tannin structural chemistry 2/7 Like all of the gallotannins, PGG has many isomers. The molecular weights of all the isomers of PGG are the same (940 g/mol), but chemical properties such as susceptibility to hydrolysis and chromatographic behavior; and biochemical properties such as ability to precipitate protein; are structure-dependent. The polygalloyl ester chains found in gallotannins are formed by either meta- or para-depside bonds, involving a phenolic hydroxyl rather than an aliphatic hydroxyl group. The depside bond is more easily hydrolyzed than an aliphatic ester bond. Methanolysis in weak acid in methanol breaks depside but not ester bonds. Thus the core polyol with its esterified galloyl groups can be produced from complex mixtures of polygalloyl esters by methanolysis with acetate buffer. Strong mineral acid, heat and methanol can be used to methanolzye both despide and ester bonds yielding the core polyol and methyl gallate. Hydrolysis with strong acid converts gallotannins to gallic acid and the core polyol. Simple gallotannins with up to 12 esterifed galloyl groups and a core glucose are routinely found in tannins from sumac or oak galls. Commercial tannic acid is comprised of mixtures of gallotannins from sumac (Rhus semialata) galls (Chinese gallotannin); Aleppo oak (Quercus infectoria) galls (Turkish gallotannin); or sumac (R. coriaria, R. typhina) leaves (sumac gallotannin). Although commercial sources provide a nominal molecular weight for tannic acid (1294 g/mol), the preparations are heterogeneous and variable mixtures of galloyl esters. Tannic acid is not an appropriate standard for any tannin analysis because of its poorly defined composition. OH OH OH O G = galloyl ester O HO OH OH O OH OH O O OH OH OH O OH OH O G O HO O O O O G G G G O β-1,2,2,3,6-Pentagalloyl-O-D-Glucose GOG = digalloyl ester, para-depside bond GOG = digalloyl ester, meta-depside bond