正在加载图片...
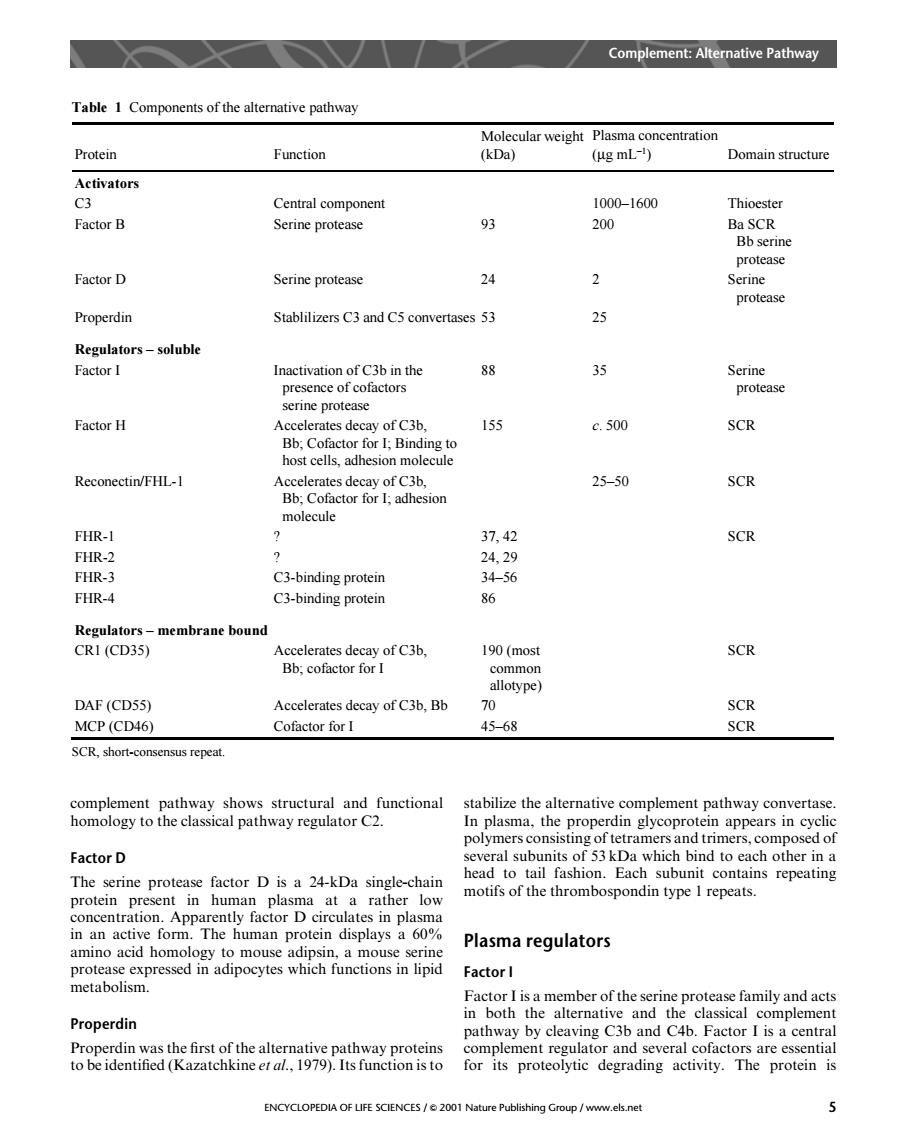
Complement:Alternative Pathway Table 1 Components of the alternative pathway Molecular weight Plasma concentration Protein Function (kDa) (ug mL) Domain structure Activators C3 Central component 1000-1600 Thioester Factor B Serine protease 93 200 Ba SCR Bb serin Factor D Serine protease 24 2 Serin proteas Properdin Stablilizers C3 and C5 convertases 53 25 Regulators-soluble Factor I Inactivation of C3b in the 88 35 Serine presence of cofactors protease serine prot Factor H 15 c.500 SCR Reconectin/FHL-1 25-50 Bb:Cofactor for adhesion SCR molecule FHR-1 37,42 SCR FHR2 24.29 FHR-3 C3-binding protein 34-56 FHR-4 C3-binding protein 86 Regulators-membrane bound CRI (CD35) Accelerates decay of C3b, 190(most SCR Bb,cofactor for I lotype DAF(CD55) Accelerates decay of C3b,Bb MCP(CD46) Cofactor for I 4568 SCR.short-consensus repeat stabilize the alternative complement pathway con th al patnway reg olymers consisting of tetramersand trimers.composed of Factor D several subunits of 53kDa which bind to each other in a The rine protease factor D is a 24-kDa single-chair motifs in an active form.The human protein displays a 60% Plasma regulators Factor I 五actolicmmciaeheaiPreaacapndnci Factor i mber of the serir Properdin pathway by cleaving C3b and C4b.Factor I is a central ne eral..19/ ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES/2001 Nature Publishing Group /www.els.net 5 complement pathway shows structural and functional homology to the classical pathway regulator C2. Factor D The serine protease factor D is a 24-kDa single-chain protein present in human plasma at a rather low concentration. Apparently factor D circulates in plasma in an active form. The human protein displays a 60% amino acid homology to mouse adipsin, a mouse serine protease expressed in adipocytes which functions in lipid metabolism. Properdin Properdin was the first of the alternative pathway proteins to be identified (Kazatchkine et al., 1979). Its function is to stabilize the alternative complement pathway convertase. In plasma, the properdin glycoprotein appears in cyclic polymers consisting of tetramers and trimers, composed of several subunits of 53 kDa which bind to each other in a head to tail fashion. Each subunit contains repeating motifs of the thrombospondin type 1 repeats. Plasma regulators Factor I Factor I is a member of the serine protease family and acts in both the alternative and the classical complement pathway by cleaving C3b and C4b. Factor I is a central complement regulator and several cofactors are essential for its proteolytic degrading activity. The protein is Table 1 Components of the alternative pathway SCR, short-consensus repeat. Protein Function Molecular weight (kDa) Plasma concentration (µg mL–1) Domain structure Activators C3 Central component 1000–1600 Thioester Factor B Serine protease 93 200 Ba SCR Bb serine protease Factor D Serine protease 24 2 Serine protease Properdin Stablilizers C3 and C5 convertases 53 25 Regulators – soluble Factor I Inactivation of C3b in the presence of cofactors serine protease 88 35 Serine protease Factor H Accelerates decay of C3b, Bb; Cofactor for I; Binding to host cells, adhesion molecule 155 c. 500 SCR Reconectin/FHL-1 Accelerates decay of C3b, Bb; Cofactor for I; adhesion molecule 25–50 SCR FHR-1 ? 37, 42 SCR FHR-2 ? 24, 29 FHR-3 C3-binding protein 34–56 FHR-4 C3-binding protein 86 Regulators – membrane bound CR1 (CD35) Accelerates decay of C3b, Bb; cofactor for I 190 (most common allotype) SCR DAF (CD55) Accelerates decay of C3b, Bb 70 SCR MCP (CD46) Cofactor for I 45–68 SCR Complement: Alternative Pathway ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www.els.net 5