正在加载图片...
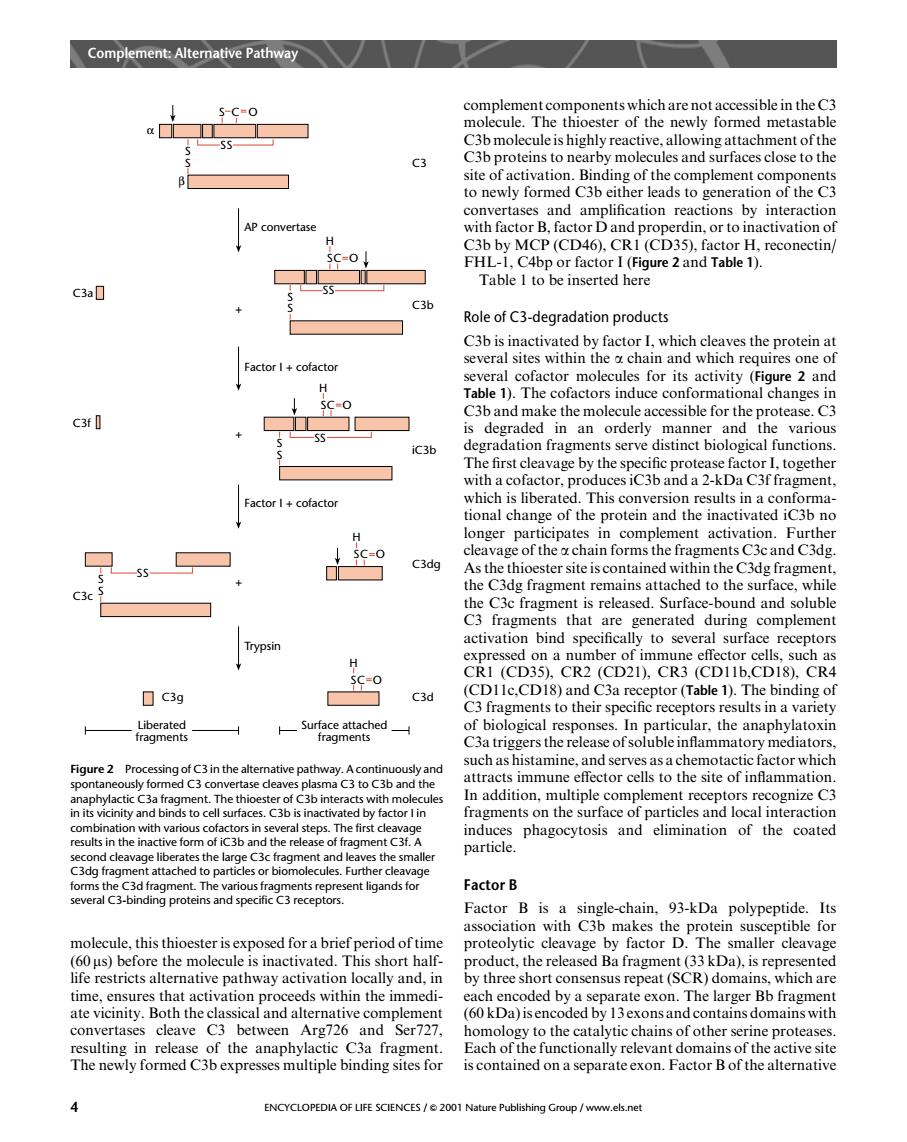
Pathway 5-C-O complement components which are not accessible in the c3 molecule.The thioester of the newly formed metastable C3 site Bind: e0 to newly formed C3b either leads to generation of the C3 convertases and amplification reactions by interaction iacroinactiation FHL-L C4R reconectin Table I to be inserted here C3 Role of c3-degradation products several cofactor molecules for its activity (Figure 2 and Table 1).The cofactors induce conformational changes in and mad in ble for t I+cofactor ns con longer participates in comp nent activation Eurthe C3dg cleavage of the achain forms the fragments C3c and C3dg ragment re C3 fragments that are generated during complement activation bind specifically to several surface receptors The hindi ☐c3g c3d C3 fragments to their specific receptors results in a variety fragments s the rele 3in the In addition,multiple complement receptors rec ognize c3 fragments on the surface of particles and local interaction phagocytosis and elimination of the coated 边恤9n出t6a Factor B molecule this thioester is with Cb makes the proten (60 us)before the molecule is inactivated.This short hal the rele ed Ba fr ment (33kDa)is r life restricts alternative pathway activation locally and,in by three short consensus repeat (SCR)domains.which are ds within the immedi 60k )iser an C?h resulting in release of the anaphylactic C3a fragn Each of the fun nally relevant domains of the active sit The newly formed C3b expresses multiple binding sites for is contained on a separateexon.factor bof the alternative ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES/2001Namolecule, this thioester is exposed for a brief period of time (60 ms) before the molecule is inactivated. This short halflife restricts alternative pathway activation locally and, in time, ensures that activation proceeds within the immediate vicinity. Both the classical and alternative complement convertases cleave C3 between Arg726 and Ser727, resulting in release of the anaphylactic C3a fragment. The newly formed C3b expresses multiple binding sites for complement components which are not accessible in the C3 molecule. The thioester of the newly formed metastable C3b molecule is highly reactive, allowing attachment of the C3b proteins to nearby molecules and surfaces close to the site of activation. Binding of the complement components to newly formed C3b either leads to generation of the C3 convertases and amplification reactions by interaction with factor B, factor D and properdin, or to inactivation of C3b by MCP (CD46), CR1 (CD35), factor H, reconectin/ FHL-1, C4bp or factor I (Figure 2 and Table 1). Table 1 to be inserted here Role of C3-degradation products C3b is inactivated by factor I, which cleaves the protein at several sites within the a chain and which requires one of several cofactor molecules for its activity (Figure 2 and Table 1). The cofactors induce conformational changes in C3b and make the molecule accessible for the protease. C3 is degraded in an orderly manner and the various degradation fragments serve distinct biological functions. The first cleavage by the specific protease factor I, together with a cofactor, produces iC3b and a 2-kDa C3f fragment, which is liberated. This conversion results in a conformational change of the protein and the inactivated iC3b no longer participates in complement activation. Further cleavage of the a chain forms the fragments C3c and C3dg. As the thioester site is contained within the C3dg fragment, the C3dg fragment remains attached to the surface, while the C3c fragment is released. Surface-bound and soluble C3 fragments that are generated during complement activation bind specifically to several surface receptors expressed on a number of immune effector cells, such as CR1 (CD35), CR2 (CD21), CR3 (CD11b,CD18), CR4 (CD11c,CD18) and C3a receptor (Table 1). The binding of C3 fragments to their specific receptors results in a variety of biological responses. In particular, the anaphylatoxin C3a triggers the release of soluble inflammatory mediators, such as histamine, and serves as a chemotactic factor which attracts immune effector cells to the site of inflammation. In addition, multiple complement receptors recognize C3 fragments on the surface of particles and local interaction induces phagocytosis and elimination of the coated particle. Factor B Factor B is a single-chain, 93-kDa polypeptide. Its association with C3b makes the protein susceptible for proteolytic cleavage by factor D. The smaller cleavage product, the released Ba fragment (33 kDa), is represented by three short consensus repeat (SCR) domains, which are each encoded by a separate exon. The larger Bb fragment (60 kDa) is encoded by 13 exons and contains domains with homology to the catalytic chains of other serine proteases. Each of the functionally relevant domains of the active site is contained on a separate exon. Factor B of the alternative SC O S S SS + + + AP convertase S S H SC O SS Factor I + cofactor Factor I + cofactor H SC O SS S S S S SS Trypsin H SC O H SC O C3a C3f C3c C3d C3dg iC3b C3b C3 Surface attached fragments Liberated fragments α β C3g Figure 2 Processing of C3 in the alternative pathway. A continuously and spontaneously formed C3 convertase cleaves plasma C3 to C3b and the anaphylactic C3a fragment. The thioester of C3b interacts with molecules in its vicinity and binds to cell surfaces. C3b is inactivated by factor I in combination with various cofactors in several steps. The first cleavage results in the inactive form of iC3b and the release of fragment C3f. A second cleavage liberates the large C3c fragment and leaves the smaller C3dg fragment attached to particles or biomolecules. Further cleavage forms the C3d fragment. The various fragments represent ligands for several C3-binding proteins and specific C3 receptors. Complement: Alternative Pathway 4 ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES / & 2001 Nature Publishing Group / www.els.net