正在加载图片...
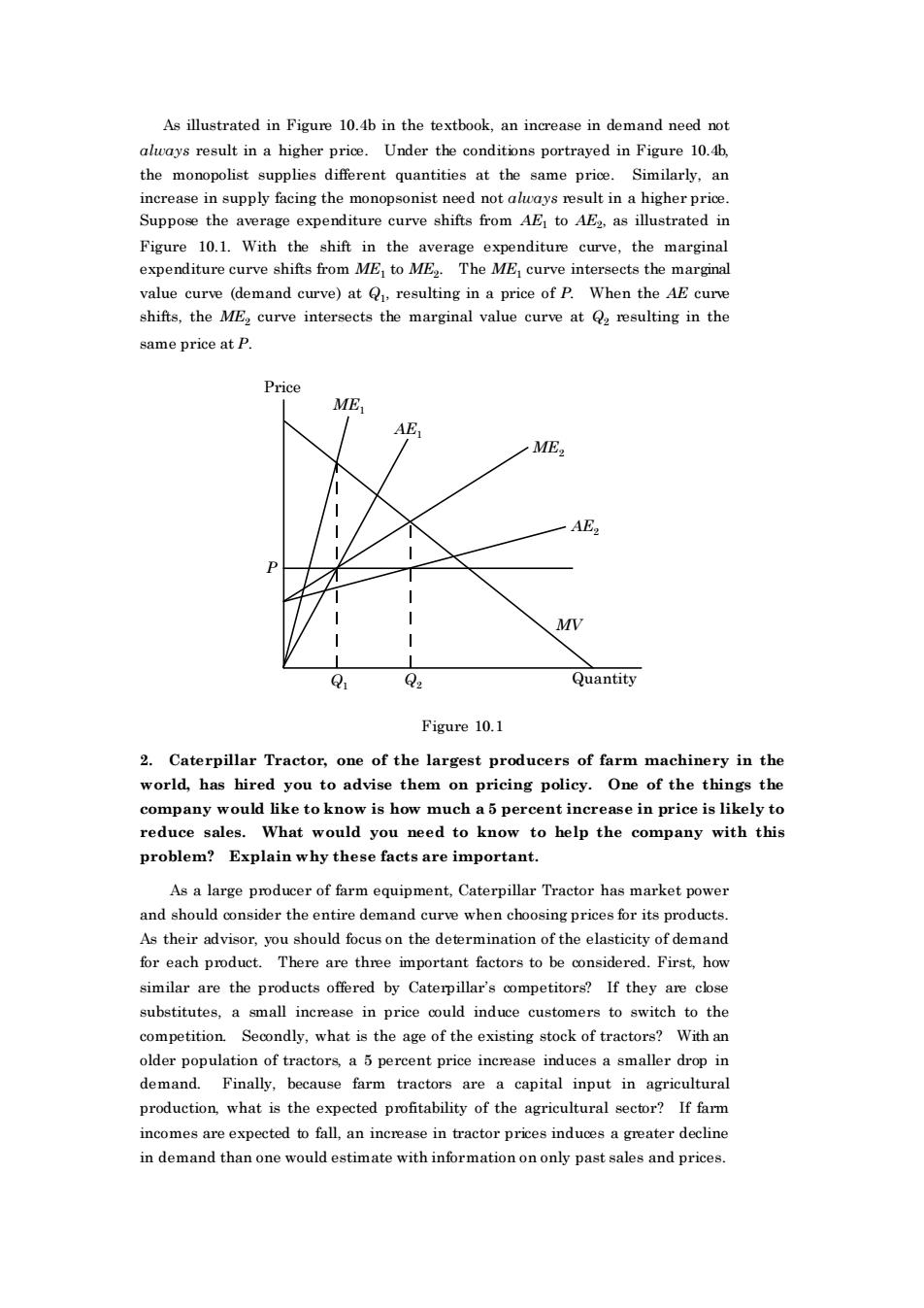
As illustrated in Figure 10.4b in the textbook.an increase in demand need not a higher price.Under the conditions portrayed in Figure 10. the monopolist supplies different quantities at the same price.Similarly,an increase in supply facing the monopsonist need not alays result in a higher price. Suppose the average expenditure curve shifts from AE to Al2,as illustrated in Figure 10.1.With the shift in the average expenditure curve.the marginal expenditure curve shifts from ME to ME.The ME curve intersects the marginal e(demand curve)at resulting in a price of P.When the AE cu shifts,the ME curve intersec the marginal e curve at Q2 rest ulting in th same price at P. Price ME MV Q: Quantity Figure 10.1 2.Caterpillar Tractor,one of the largest producers of farm machinery in the world,has hired you to advise them on pricing policy.One of the things the company would like to know is how much a 5 percent increase in price is likely to reduce sales.What would you need to know to help the company with this problem?Explain why these facts are important. As a large producer of farm equipment.caterpillar tractor has market power and should consider the entire demand curve when choosing As their advisor,you should focuson the determination of the elasticity of demand for each product.There are three important factors to be considered.First,how similar are the products offered by Caterpillar's competitors?If they are close substitutes,a small increase in price could induce customers to switch to the competition.,what is the age of the existingstock of tractors?With an older popu on of tractors,a 5 percent price increase in uces a s aller drop demand.Finally,because farm tractors are a capital input in agricultura production what is the expected profitability of the agricultural sector?If farm incomes are expected to fall,an increase in tractor prices induces a greater decline in demand than one would estimate with informationon only past sales and pricesAs illustrated in Figure 10.4b in the textbook, an increase in demand need not always result in a higher price. Under the conditions portrayed in Figure 10.4b, the monopolist supplies different quantities at the same price. Similarly, an increase in supply facing the monopsonist need not always result in a higher price. Suppose the average expenditure curve shifts from AE1 to AE2 , as illustrated in Figure 10.1. With the shift in the average expenditure curve, the marginal expenditure curve shifts from ME1 to ME2 . The ME1 curve intersects the marginal value curve (demand curve) at Q1 , resulting in a price of P. When the AE curve shifts, the ME2 curve intersects the marginal value curve at Q2 resulting in the same price at P. Price Quantity ME1 AE1 ME2 AE2 P Q1 Q2 MV Figure 10.1 2. Caterpillar Tractor, one of the largest producers of farm machinery in the world, has hired you to advise them on pricing policy. One of the things the company would like to know is how much a 5 percent increase in price is likely to reduce sales. What would you need to know to help the company with this problem? Explain why these facts are important. As a large producer of farm equipment, Caterpillar Tractor has market power and should consider the entire demand curve when choosing prices for its products. As their advisor, you should focus on the determination of the elasticity of demand for each product. There are three important factors to be considered. First, how similar are the products offered by Caterpillar’s competitors? If they are close substitutes, a small increase in price could induce customers to switch to the competition. Secondly, what is the age of the existing stock of tractors? With an older population of tractors, a 5 percent price increase induces a smaller drop in demand. Finally, because farm tractors are a capital input in agricultural production, what is the expected profitability of the agricultural sector? If farm incomes are expected to fall, an increase in tractor prices induces a greater decline in demand than one would estimate with information on only past sales and prices