正在加载图片...
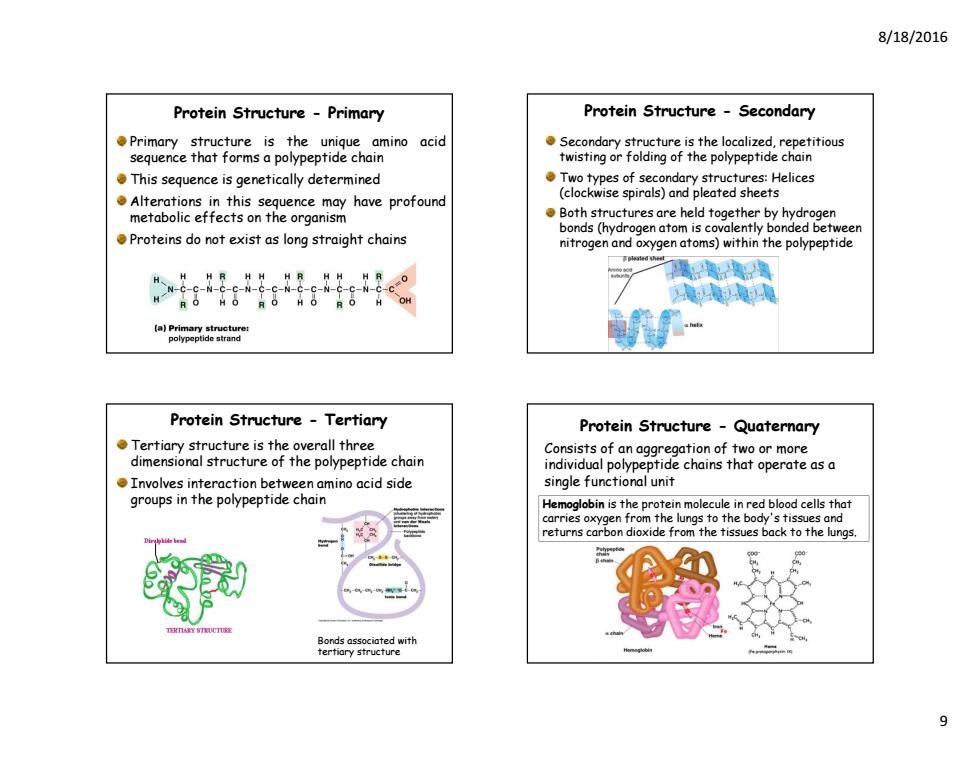
8/18/2016 Protein Structure-Primary Protein Structure -Secondary Primary structure is the unique amino acid Secondary structure is the localized,repetitious sequence that forms a polypeptide chain twisting or folding of the polypeptide chain This sequence is genetically determined Two types of secondary structures:Helices Alterations in this sequence may have profound (clockwise spirals)and pleated sheets metabolic effects on the organism Both structures are held together by hydrogen bonds(hydrogen atom is covalently bonded between Proteins do not exist as long straight chains nitrogen and oxygen atoms)within the polypeptide Protein Structure Tertiary Protein Structure-Quaternary Tertiary structure is the overall three Consists of an aggregation of two or more dimensional structure of the polypeptide chain individual polypeptide chains that operate asa Involves interaction between amino acid side single functional unit groups in the polypeptide chain Hemoglobin is the protein molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen the ungs to the body's tissue and returns carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs. 8/18/2016 9 Protein Structure - Primary Primary structure is the unique amino acid sequence that forms a polypeptide chain This sequence is genetically determined Alterations in this sequence may have profound metabolic effects on the organism Proteins do not exist as long straight chains Protein Structure - Secondary Secondary structure is the localized, repetitious twisting or folding of the polypeptide chain Two types of secondary structures: Helices (clockwise spirals) and pleated sheets Both structures are held together by hydrogen bonds (hydrogen atom is covalently bonded between nitrogen and oxygen atoms) within the polypeptide Protein Structure - Tertiary Tertiary structure is the overall three dimensional structure of the polypeptide chain Involves interaction between amino acid side groups in the polypeptide chain Bonds associated with tertiary structure Protein Structure - Quaternary Consists of an aggregation of two or more individual polypeptide chains that operate as a single functional unit Hemoglobin is the protein molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the body's tissues and returns carbon dioxide from the tissues back to the lungs