正在加载图片...
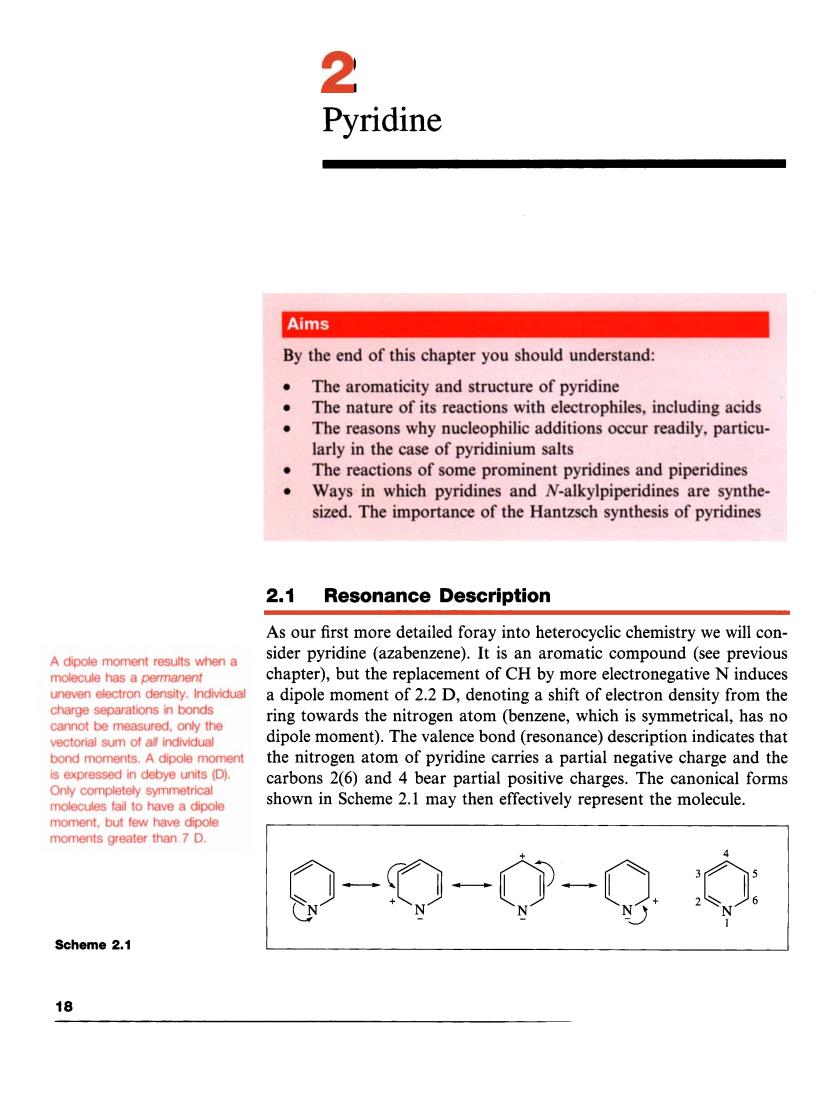
2 Pyridine Aims By the end of this chapter you should understand: The aromaticity and structure of pyridine The nature of its reactions with electrophiles,including acids The reasons why nucleophilic additions occur readily,particu larly in the case of pyridinium salts The reactions of some prominent pyridines and piperidines Ways in which pyridines and Naikylpiperidines are syth sized.The importance of the Hantzsch synthesis of pyridines 2.1 Resonance Description As our first more detailed foray into heterocyclic chemistry we will con- A dipole moment results when a sider pyridine (azabenzene).It is an aromatic compound(see previous chapter).but the replacement of ch by more electronegative n induces a dipole moment of 2.2 D,denoting a shift of electron den sity from the ring towards the nitrogen atom(benzene,which is symmetrical,has no dipole moment).The valence bond (resonance)description indicates that bond m the nitrogen atom of pyridine carries a partial negative charge and the is expressed in debye units (D). carbons 2(6)and 4 bear partial positive charges. The nonical forms shown in Scheme 2.1 may then effectively represent the molecule. moment.but few have dip moments greater than.7 D. ②-p-中- Scheme 2.1 18 Pyridine A dipole moment results when a molecule has a permanent uneven electron density. Individual charge separations in bonds cannot be measured, only the vectorial sum of all individual bond moments. A dipole moment is expressed in debye units (D). Only completely symmetrical molecules fail to have a dipole moment, but few have dipole moments greater than 7 D. 2.1 Resonance Description As our first more detailed foray into heterocyclic chemistry we will consider pyridine (azabenzene). It is an aromatic compound (see previous chapter), but the replacement of CH by more electronegative N induces a dipole moment of 2.2 D, denoting a shift of electron density from the ring towards the nitrogen atom (benzene, which is symmetrical, has no dipole moment). The valence bond (resonance) description indicates that the nitrogen atom of pyridine carries a partial negative charge and the carbons 2(6) and 4 bear partial positive charges. The canonical forms shown in Scheme 2.1 may then effectively represent the molecule. 4 Scheme 2.1 18