正在加载图片...
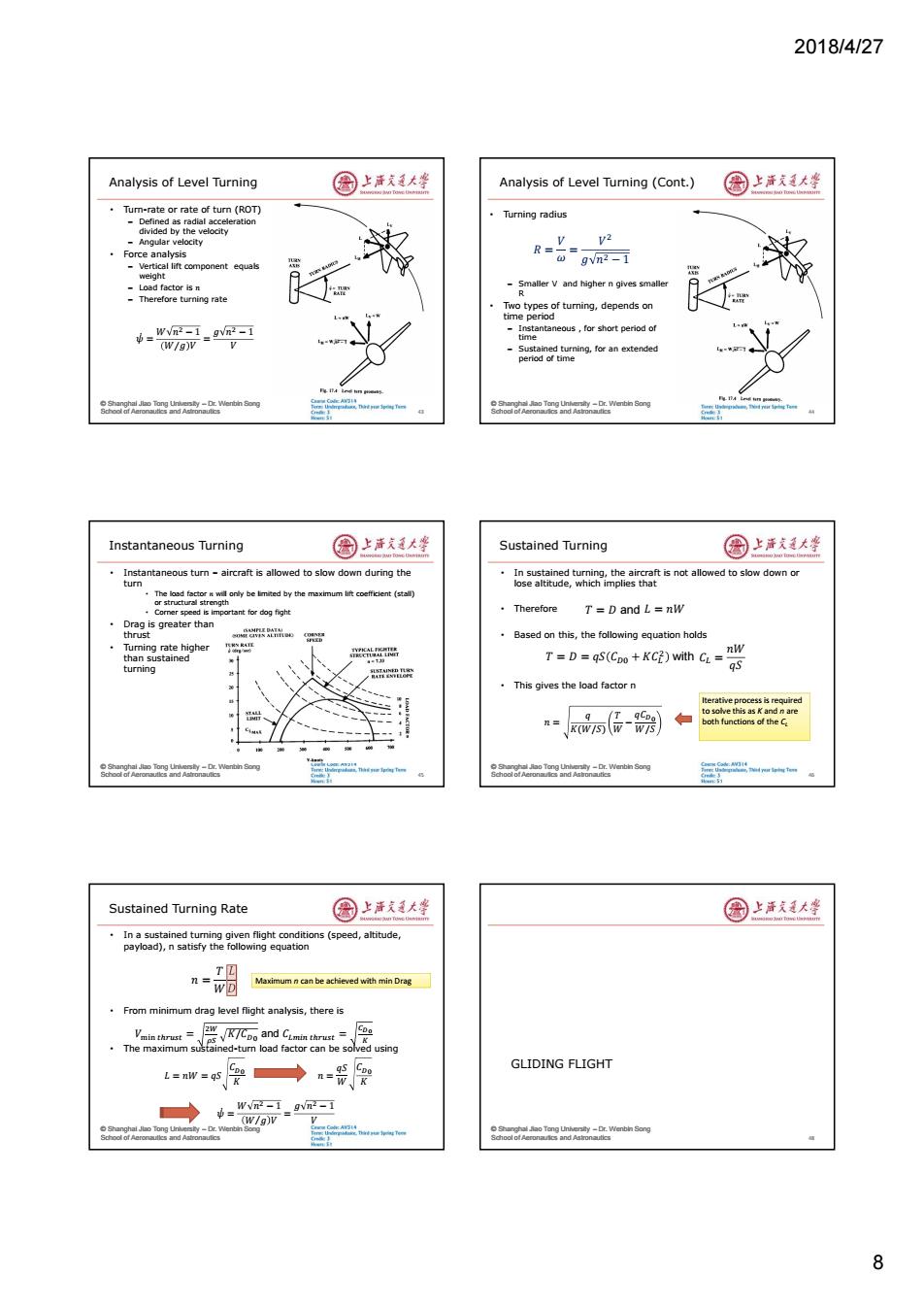
2018/4/27 Analysis of Level Turning 国上活大坐 Analysis of Level Turning (Cont.) 国上清大坐 Tum-rate or rate of turn (ROT) eleration ·Turning radius -Angular velocity Force analysis R= -Vertical lift component equals gvn2i -Smaller V and higher n gives smaller Therefore turning rate Two types of turning,depends on time period h=wn2_9-1 -Instantaneous,for short period of time (W/g)v V Sustained turning,for an extended L-w penod or time : Song Instantaneous Turning 圈上活大坐 Sustained Turning 国上道大坐 Instantaneous turn aircraft is allowed to slow down during the In sustained turning,the aircraft is not allowed to slow down or tum lose altitude,which implies that .Comer speed is important for dog fight Therefore T=D and L=nW 。 Drag is greater than ust OMVIS ALII Based on this,the following equation holds Tuming rate higher T=D qS(Cpo+KC2)with CL nW than sustained n整 qs This gives the load factor n lterative process is reouired to solve this as K and n are n= both functions of the C Sustained Turning Rate 图上洋大峰 园上海发大坐 In a sustained tuming given flight condi(speed,altitude, a9oai2nsaisryheol6geqaion T四 n= wD Maximum n can be achieved with min Drag From minimum drag level flight analysis,there is Vmin thrust= 、√KTCpo and CLmin thrust=, .The maximum sined-tun load factor can be solved using GLIDING FLIGHT L=nW =qs =WR-1_gVm-1 -(wg)v 82018/4/27 8 © Shanghai Jiao Tong University – Dr. Wenbin Song School of Aeronautics and Astronautics Analysis of Level Turning • Turn-rate or rate of turn (ROT) – Defined as radial acceleration divided by the velocity – Angular velocity • Force analysis – Vertical lift component equals weight – Load factor is 𝑛 – Therefore turning rate 43 𝜓̇ = 𝑊 𝑛ଶ − 1 𝑊 𝑔⁄ 𝑉 = 𝑔 𝑛ଶ − 1 𝑉 © Shanghai Jiao Tong University – Dr. Wenbin Song School of Aeronautics and Astronautics Analysis of Level Turning (Cont.) • Turning radius – Smaller V and higher n gives smaller R • Two types of turning, depends on time period – Instantaneous , for short period of time – Sustained turning, for an extended period of time 44 𝑅 = 𝑉𝜔 = 𝑉 ଶ 𝑔 𝑛ଶ − 1 © Shanghai Jiao Tong University – Dr. Wenbin Song School of Aeronautics and Astronautics Instantaneous Turning • Instantaneous turn – aircraft is allowed to slow down during the turn • The load factor 𝑛 will only be limited by the maximum lift coefficient (stall) or structural strength • Corner speed is important for dog fight • Drag is greater than thrust • Turning rate higher than sustained turning 45 © Shanghai Jiao Tong University – Dr. Wenbin Song School of Aeronautics and Astronautics Sustained Turning • In sustained turning, the aircraft is not allowed to slow down or lose altitude, which implies that • Therefore • Based on this, the following equation holds • This gives the load factor n 46 𝑇 = 𝐷 and 𝐿 = 𝑛𝑊 𝑇 = 𝐷 = 𝑞𝑆 𝐶 + 𝐾𝐶ଶ with 𝐶 = 𝑛𝑊 𝑞𝑆 𝑛 = 𝑞 𝐾(𝑊/𝑆) 𝑇𝑊 − 𝑞𝐶 𝑊/𝑆 Iterative process is required to solve this as K and n are both functions of the CL © Shanghai Jiao Tong University – Dr. Wenbin Song School of Aeronautics and Astronautics Sustained Turning Rate • In a sustained turning given flight conditions (speed, altitude, payload), n satisfy the following equation • From minimum drag level flight analysis, there is • The maximum sustained-turn load factor can be solved using 𝑛 = 𝑇 𝑊 𝐿 𝐷 𝐿 = 𝑛𝑊 = 𝑞𝑆 𝐶 𝐾 𝑉୫୧୬ ௧௨௦௧ = ଶௐ ఘௌ 𝐾/𝐶 and 𝐶 ௧௨௦௧ = ವబ 𝑛 = 𝑞𝑆𝑊 𝐶 𝐾 𝜓̇ = 𝑊 𝑛ଶ − 1 𝑊 𝑔⁄ 𝑉 = 𝑔 𝑛ଶ − 1 𝑉 Maximum n can be achieved with min Drag © Shanghai Jiao Tong University – Dr. Wenbin Song School of Aeronautics and Astronautics GLIDING FLIGHT 48