正在加载图片...
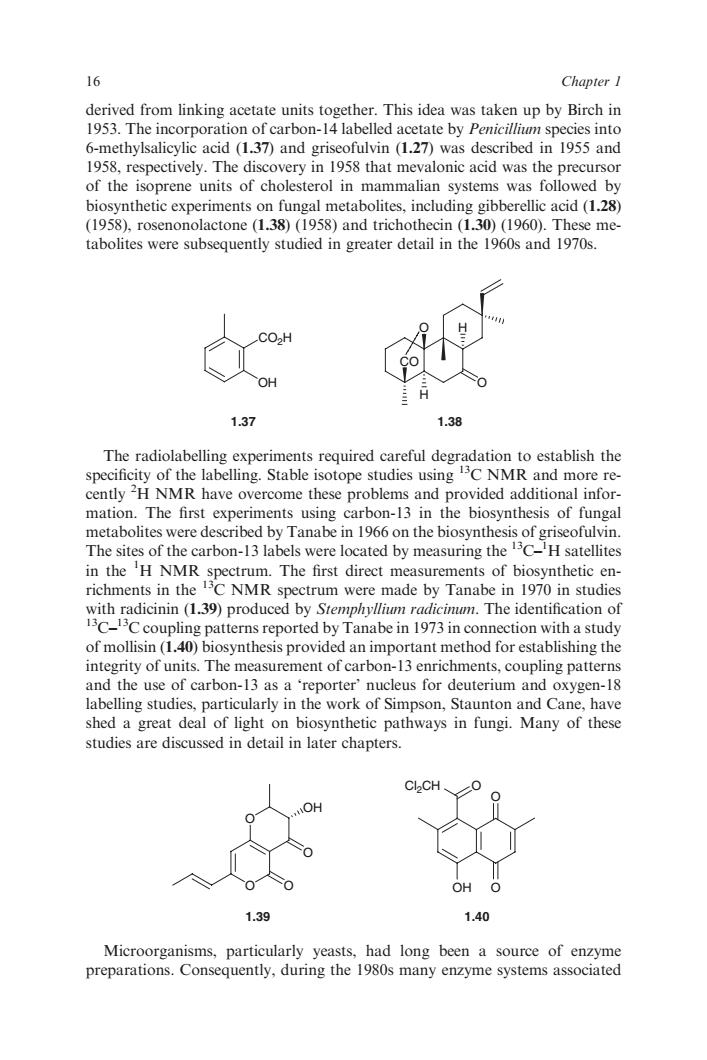
16 derived from linking acetate units together.This idea was taken up by Birch in 1953.The incorporation of carbon-14 labelled acetate by Penicillium species into 6-methylsalicylic acid (1.37)and griseofulvin (1.27)was described in 1955 and 1958,respectively.The discovery in 1958 that mevalonic acid was the precursor of the isoprene units of cholesterol in mammalian systems was followed by biosynthetic experiments on fungal metabolites,including gibberellic acid(1.28) (1958),rosenon olactone (1.38) 1g58 L.301960.The e me tabolites were subsequently studied in greater detail in the 1960s and 1970 CO2H 1.37 1.38 The radiolabelling experiments required careful degradation to establish the specificity of the labelling.Stable isotope studies using C NMR and more re- cently 2H NMR have overcome these problems and provided additional infor mation.The first experiments using carbon-13 in the biosynthesis of funga s were des t the ibed by Tanabe in 1966 on the bi in the H NMR spectrum.The first direct measurements of biosynthetic en richments in the C NMR spectrum were made by Tanabe in 1970 in studies with radicinin (1.39)produced by Stemphyllium radicimm.The identification of C-C coupling patterns reported by Tanabe in 1973 in connection with a study of mollisin(1.40)biosynthesis provided an important method for establishing the integrity of units.The measurement of carbon-13 enrichments,coupling patterns eporternucleus for deuterium and ng stu die rticularly in the wo of Si shed a great studies are discussed in detail in later chapters. OH 1.39 1.40 Microorganisms,particularly yeasts,had long been a source of enzyme preparations.Consequently,during the 1980s many enzyme systems associatedderived from linking acetate units together. This idea was taken up by Birch in 1953. The incorporation of carbon-14 labelled acetate by Penicillium species into 6-methylsalicylic acid (1.37) and griseofulvin (1.27) was described in 1955 and 1958, respectively. The discovery in 1958 that mevalonic acid was the precursor of the isoprene units of cholesterol in mammalian systems was followed by biosynthetic experiments on fungal metabolites, including gibberellic acid (1.28) (1958), rosenonolactone (1.38) (1958) and trichothecin (1.30) (1960). These metabolites were subsequently studied in greater detail in the 1960s and 1970s. CO2H OH 1.37 O CO H H O 1.38 The radiolabelling experiments required careful degradation to establish the specificity of the labelling. Stable isotope studies using 13C NMR and more recently 2 H NMR have overcome these problems and provided additional information. The first experiments using carbon-13 in the biosynthesis of fungal metabolites were described by Tanabe in 1966 on the biosynthesis of griseofulvin. The sites of the carbon-13 labels were located by measuring the 13C–1 H satellites in the 1 H NMR spectrum. The first direct measurements of biosynthetic enrichments in the 13C NMR spectrum were made by Tanabe in 1970 in studies with radicinin (1.39) produced by Stemphyllium radicinum. The identification of 13C–13C coupling patterns reported by Tanabe in 1973 in connection with a study of mollisin (1.40) biosynthesis provided an important method for establishing the integrity of units. The measurement of carbon-13 enrichments, coupling patterns and the use of carbon-13 as a ‘reporter’ nucleus for deuterium and oxygen-18 labelling studies, particularly in the work of Simpson, Staunton and Cane, have shed a great deal of light on biosynthetic pathways in fungi. Many of these studies are discussed in detail in later chapters. O O O O OH 1.39 O OH O Cl2CH O 1.40 Microorganisms, particularly yeasts, had long been a source of enzyme preparations. Consequently, during the 1980s many enzyme systems associated 16 Chapter 1