正在加载图片...
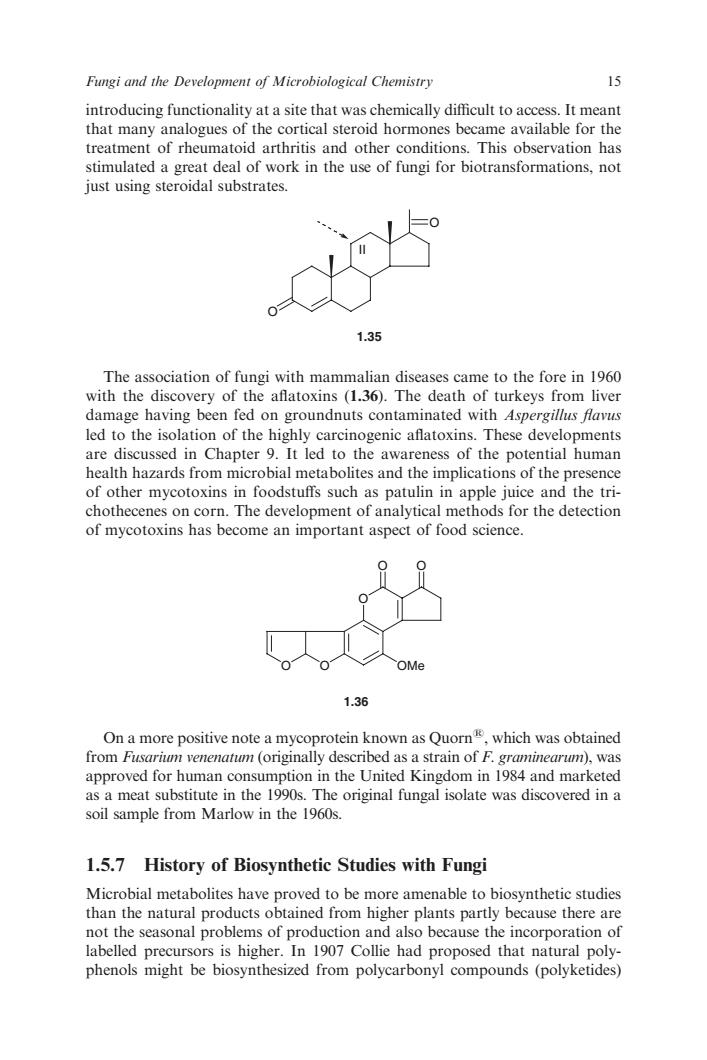
Fungi and the Development of Microbiological Chemistry 15 introducing functionality at a site that was chemically difficult to access.It meant that many analogues of the cortical steroid hormones became available for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and other conditions.This observation has stimulated a geat deal of work in the s of fungi for just using stero idal substrates 1.35 The association of fungi with mammalian diseases came to the fore in 1960 with the discovery of the aflatoxins (1.36).The death of turkeys from liver damage having been fed on groundnuts contaminated with Aspergillus flavus led to the isolation of the highly carcinogenic aflatoxins.These developments are discussed in Chapter 9.It led to the awareness of the potential human health hazards from microbial metabolites and the implications of the presence of other mycotoxins in foodstufs such as patulin in chothec orn.The development of analytical me of mycotoxins has come an important aspect of food science 1.36 On a more positive note a mycoprotein known as Quor which was obtaine from Fusarium venenatum (originally described as a strain of F.graminearum),was approved for human consumption in the United Kingdom in 1984 and marketed as a meat substitute in the 1990s.The original fungal isolate was discovered in a soil sample from Marlow in the 1960s. 1.5.7 History of Biosynthetic Studies with Fungi Microbial metabolites have proved to be more amenable to biosynthetic studies than the natural products obtained from higher plants partly because there are not the seasonal problems of production and also because the incorporation of labelled precursors is higher.In 1907 Collie had proposed that natural poly- phenols might be biosynthesized from polycarbonyl compounds (polyketides) introducing functionality at a site that was chemically difficult to access. It meant that many analogues of the cortical steroid hormones became available for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and other conditions. This observation has stimulated a great deal of work in the use of fungi for biotransformations, not just using steroidal substrates. O 1.35 O II The association of fungi with mammalian diseases came to the fore in 1960 with the discovery of the aflatoxins (1.36). The death of turkeys from liver damage having been fed on groundnuts contaminated with Aspergillus flavus led to the isolation of the highly carcinogenic aflatoxins. These developments are discussed in Chapter 9. It led to the awareness of the potential human health hazards from microbial metabolites and the implications of the presence of other mycotoxins in foodstuffs such as patulin in apple juice and the trichothecenes on corn. The development of analytical methods for the detection of mycotoxins has become an important aspect of food science. O O O O O OMe 1.36 On a more positive note a mycoprotein known as Quorns, which was obtained from Fusarium venenatum (originally described as a strain of F. graminearum), was approved for human consumption in the United Kingdom in 1984 and marketed as a meat substitute in the 1990s. The original fungal isolate was discovered in a soil sample from Marlow in the 1960s. 1.5.7 History of Biosynthetic Studies with Fungi Microbial metabolites have proved to be more amenable to biosynthetic studies than the natural products obtained from higher plants partly because there are not the seasonal problems of production and also because the incorporation of labelled precursors is higher. In 1907 Collie had proposed that natural polyphenols might be biosynthesized from polycarbonyl compounds (polyketides) Fungi and the Development of Microbiological Chemistry 15