正在加载图片...
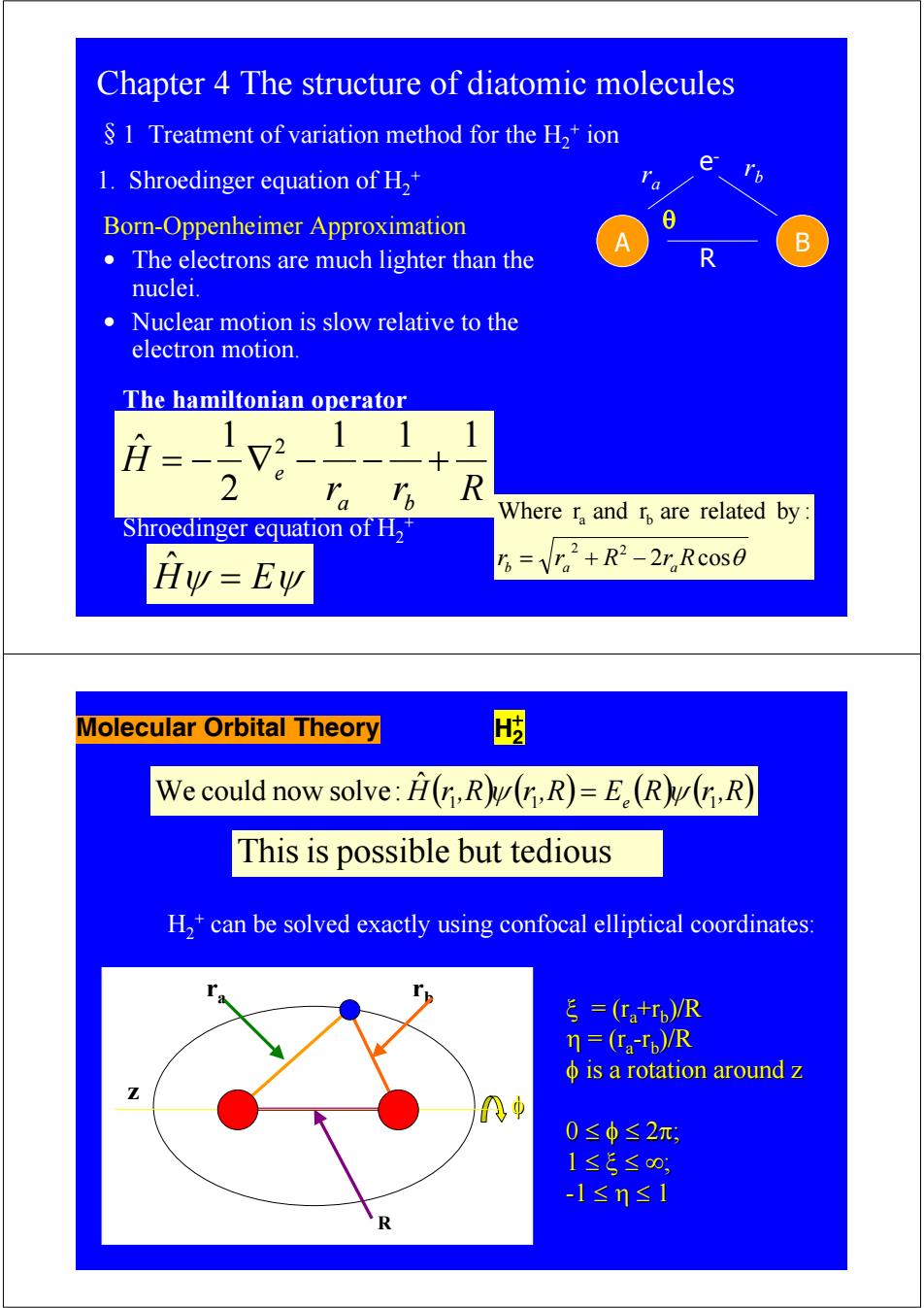
Chapter 4 The structure of diatomic molecules S 1 Treatment of variation method for the H,+ion e 1.Shroedinger equation of H2+ Born-Oppenheimer Approximation 8 B The electrons are much lighter than the nuclei. Nuclear motion is slow relative to the electron motion. The hamiltonian operator 1 1 H 2 、R Where r,and r are related by: Shroedinger equation of H2 Hy=Ew B=V2+R2-2,Rc0s0 Molecular Orbital Theory We could now solve:H(r,R(n,R)=E.(R(r,R) This is possible but tedious H,*can be solved exactly using confocal elliptical coordinates: ξ=(tr,)R n=(ra-Tp)/R φis a rotation around z 0≤φ≤2π, 1≤5≤0, -1≤n≤1 RChapter 4 The structure of diatomic molecules §1 Treatment of variation method for the H2 + ion 1. Shroedinger equation of H2 + A B e- r r b a R Born-Oppenheimer Approximation • The electrons are much lighter than the nuclei. • Nuclear motion is slow relative to the electron motion. r r R H a b e 1 1 1 2 1 ˆ 2 = − ∇ − − + The hamiltonian operator 2 cosθ Where r and r are related by : 2 2 a b rb = ra + R − raR θ Hˆψ = Eψ Shroedinger equation of H2 + Molecular Orbital Theory H2 + We could now solve: Hˆ ( )( ) r 1,R ψ r 1,R = Ee (R)( ) ψ r 1,R Thisis possible but tedious H2 + can be solved exactly using confocal elliptical coordinates: ra rb z ξ = (ra +rb)/R η = (ra-rb)/R φ is a rotation around z is a rotation around z 0 ≤ φ ≤ 2π; 1 ≤ ξ ≤ ∞; -1 ≤ η ≤ 1 R φ