正在加载图片...
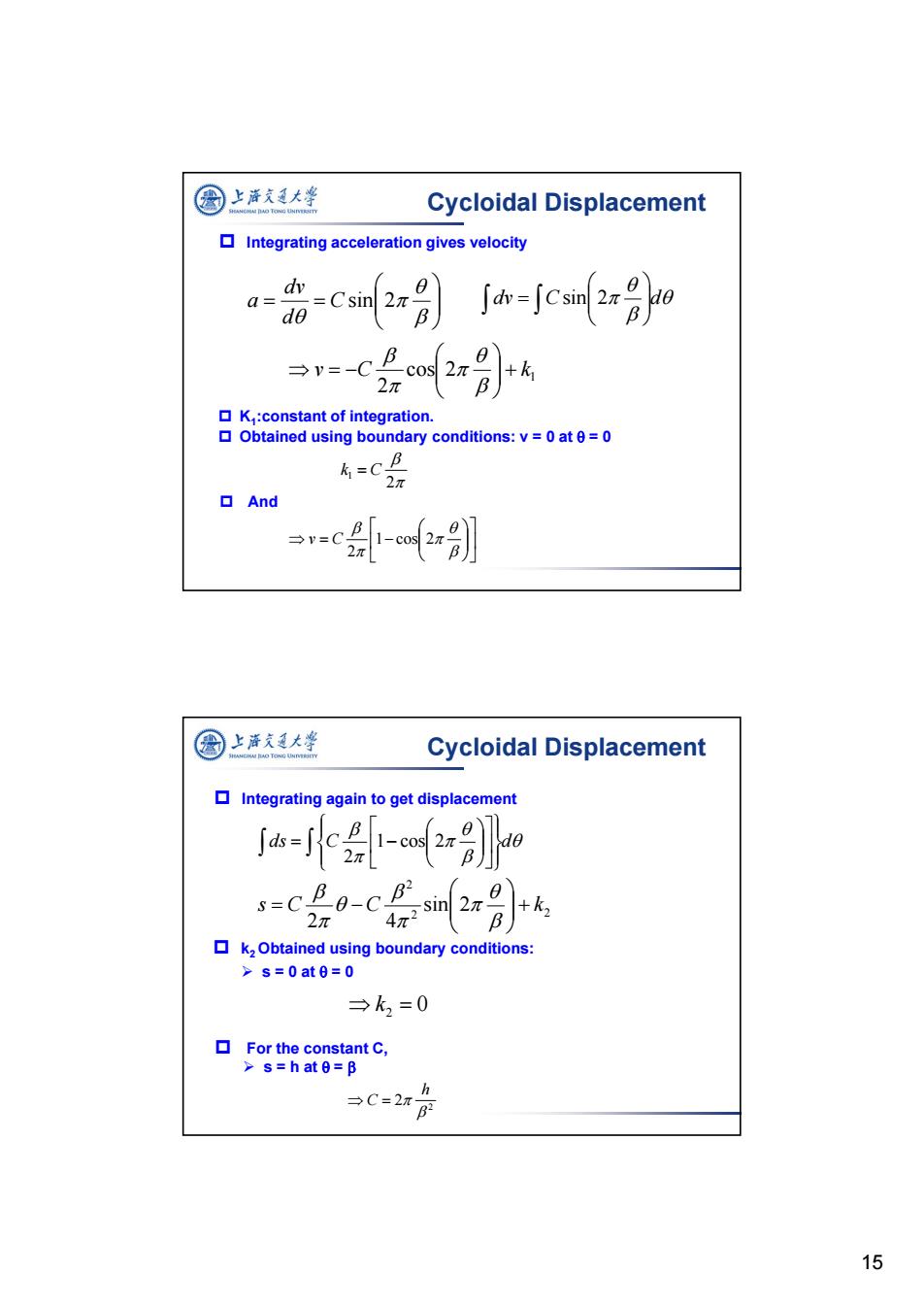
圈上泽充大峰 Cycloidal Displacement Integrating acceleration gives velocity d Q= _=Csin d jh-jcs2r →v=-C cos 2π B +k 2π K:constant of integration Obtained using boundary conditions:v=0 at 0=0 k=CB 2π And 圆上清支大华 Cycloidal Displacement Integrating again to get displacement Ja-p s-CB0-cB +k2 2π B k2 Obtained using boundary conditions: >s=0at0=0 →k2=0 ▣For the constant C, >s=hate=B →C=2π- 1515 Integrating acceleration gives velocity Csin 2 d dv a K1:constant of integration. Obtained using boundary conditions: v = 0 at = 0 dv C d sin 2 1 cos 2 2 v C k Cycloidal Displacement 2 k1 C 1 cos 2 2 v C And Integrating again to get displacement 2 2 2 sin 2 2 4 s C C k ds C d 1 cos 2 2 Cycloidal Displacement k2 Obtained using boundary conditions: s = 0 at = 0 0 k2 For the constant C, s = h at = 2 2 h C