正在加载图片...
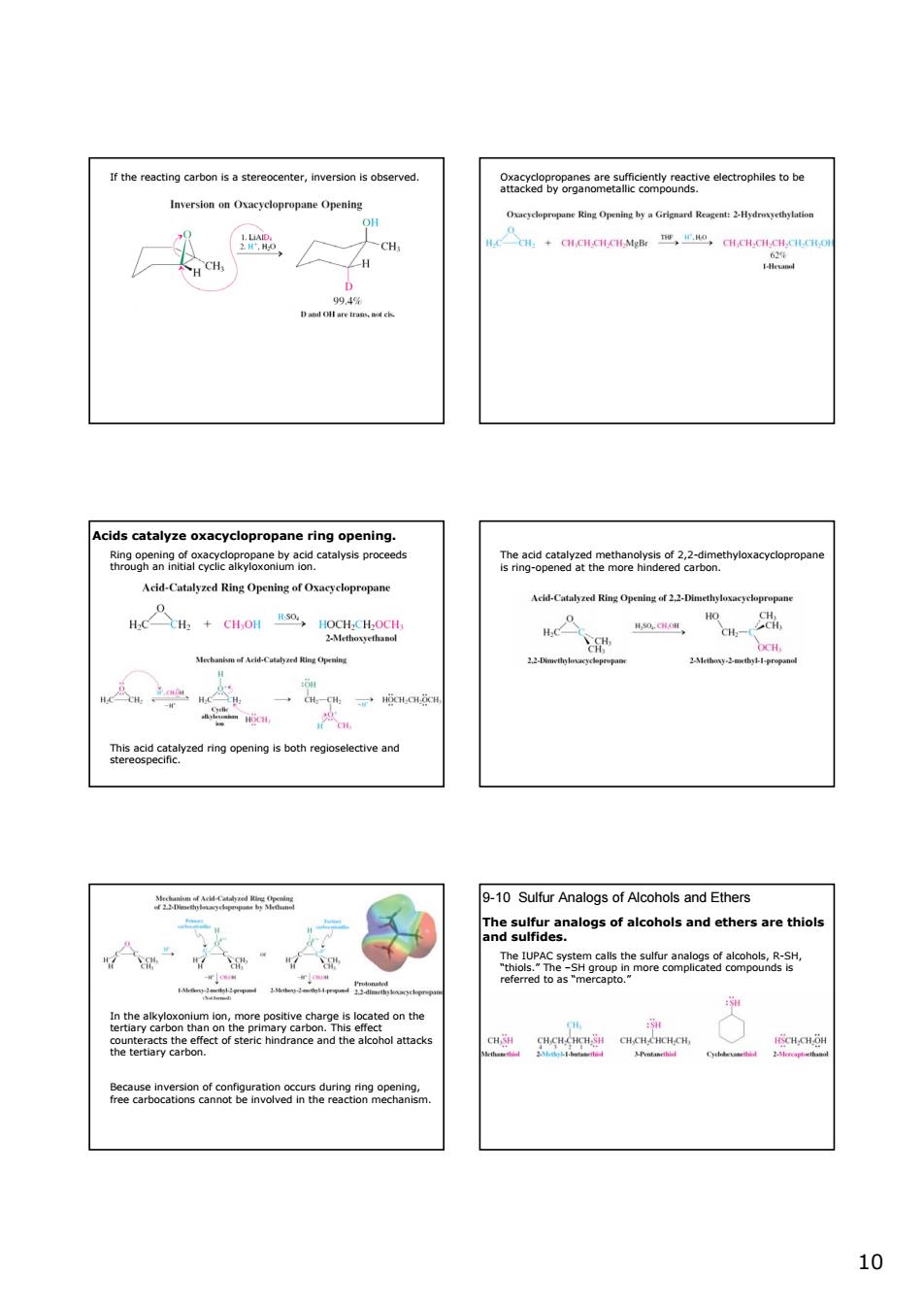
r therciner,inversion served. 9nacxeg8weaeiomeaeeamgoeseuecrophlsotbe -CH Acids catalyze oxacyclopr onane ring on eds ggataaeta0k.2rtahyhoxaqycopropan Acd-Catalyzed Ring Opening ofxayclopropane cd-Cal Ring Opmleg f Hc+CH.OH,a4C 0. 9-10 Sulfur Analogs of Alcohols and Ethers hgumeanalogsofalcoholsandethersarethiols 1010 If the reacting carbon is a stereocenter, inversion is observed. Oxacyclopropanes are sufficiently reactive electrophiles to be attacked by organometallic compounds. Acids catalyze oxacyclopropane ring opening. Ring opening of oxacyclopropane by acid catalysis proceeds through an initial cyclic alkyloxonium ion. This acid catalyzed ring opening is both regioselective and stereospecific. The acid catalyzed methanolysis of 2,2-dimethyloxacyclopropane is ring-opened at the more hindered carbon. In the alkyloxonium ion, more positive charge is located on the tertiary carbon than on the primary carbon. This effect counteracts the effect of steric hindrance and the alcohol attacks the tertiary carbon. Because inversion of configuration occurs during ring opening, free carbocations cannot be involved in the reaction mechanism. 9-10 Sulfur Analogs of Alcohols and Ethers The sulfur analogs of alcohols and ethers are thiols and sulfides. The IUPAC system calls the sulfur analogs of alcohols, R-SH, “thiols.” The –SH group in more complicated compounds is referred to as “mercapto