正在加载图片...
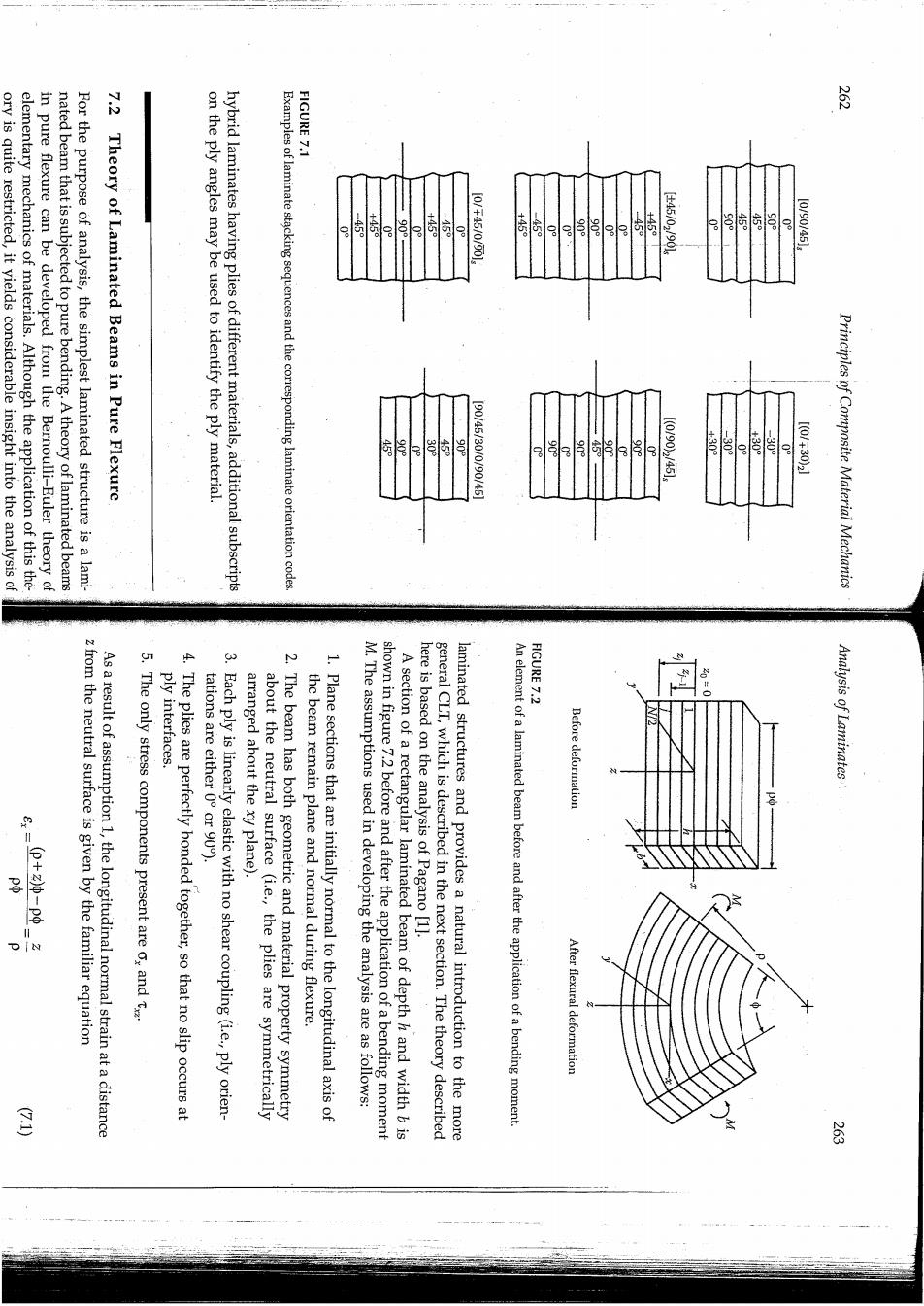
FIGURE 7.1 芦 ory is quite restricted,it yields considerable insight into the analysis of elementary mechanics of materials.Although the application of this the- in pure flexure can be developed from the Bernoulli-Euler theory of nated beam that is subjected to pure bending.A theory of laminated beams For the purpose of analysis,the simplest laminated structure is a lami- Theory of Laminated Beams in Pure Flexure on the ply angles may be used to identify the ply material. hybrid laminates having plies of different materials,additional subscripts Examples of laminate stacking sequences and the corresponding laminate orientation codes +45 115 45 160午44/009o 5。 e 。 446/02090s 10010035l 1(01700945l .300 1001305 Principles of Composite Material Mechanics FIGURE 7.2 z from the neutral surface is given by the familiar equation As a result of assumption 1,the longitudinal normal strain at a distance The only stress components present are o,and t ply interfaces 4.The plies are perfectly bonded together,so that no slip occurs at tations are either 0 or 90). 3.Each ply is linearly elastic with no shear coupling(ie.,ply orien- arranged about the xy plane). about the neutral surface (i.e.,the plies are symmetrically 2.The beam has both geometric and material property symmetry the beam remain plane and normal during flexure. 1.Plane sections that are initially normal to the longitudinal axis of M.The assumptions used in developing the analysis are as follows: shown in figure 7.2 before and after the application of a bending moment A section of a rectangular laminated beam of depth h and width b is here is based on the analysis of Pagano [1]. general CLT,which is described in the next section.The theory described laminated structures and provides a natural introduction to the more An element of a laminated beam before and after the application of a bending moment Before deformation Analysis of Laminates After flexural deformation E