正在加载图片...
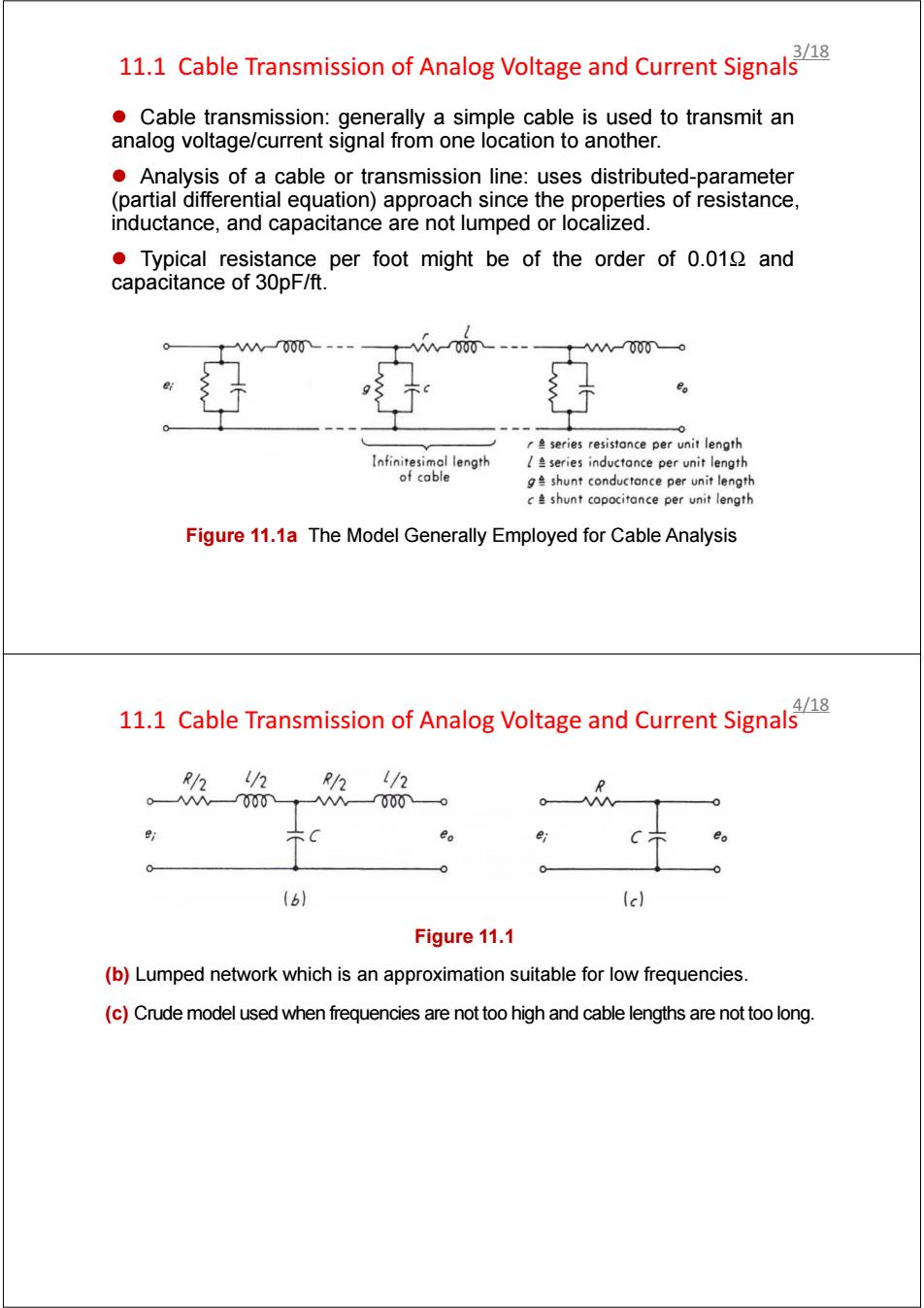
/18 11.1 Cable Transmission of Analog Voltage and Current Signals Cable transmission:generally a simple cable is used to transmit an analog voltage/current signal from one location to another. Analysis of a cable or transmission line:uses distributed-parameter (partial differential equation)approach since the properties of resistance, inductance,and capacitance are not lumped or localized. Typical resistance per foot might be of the order of 0.012 and capacitance of 30pF/ft. 000 000o 8 series resistance per unit length Infinitesimal length series inductonce per unit length of cable ge shunt conductance per unit length c shunt capocitance per unit length Figure 11.1a The Model Generally Employed for Cable Analysis 11.1 Cable Transmission of Analog Voltage and Current Signal R/2 /2 R/2 /2 0000000 eo (6) (e) Figure 11.1 (b)Lumped network which is an approximation suitable for low frequencies. (c)Crude model used when frequencies are not too high and cable lengths are not too long.11.1 Cable Transmission of Analog Voltage and Current Signals z Cable transmission: generally a simple cable is used to transmit an analog voltage/current signal from one location to another. z Analysis of a cable or transmission line: uses distributed-parameter (partial differential equation) approach since the properties of resistance, inductance, and capacitance are not lumped or localized. z Typical resistance per foot might be of the order of 0.01Ω and capacitance of 30pF/ft. Figure 11.1a The Model Generally Employed for Cable Analysis 3/18 11.1 Cable Transmission of Analog Voltage and Current Signals Figure 11.1 (b) Lumped network which is an approximation suitable for low frequencies. (c) Crude model used when frequencies are not too high and cable lengths are not too long. 4/18