正在加载图片...
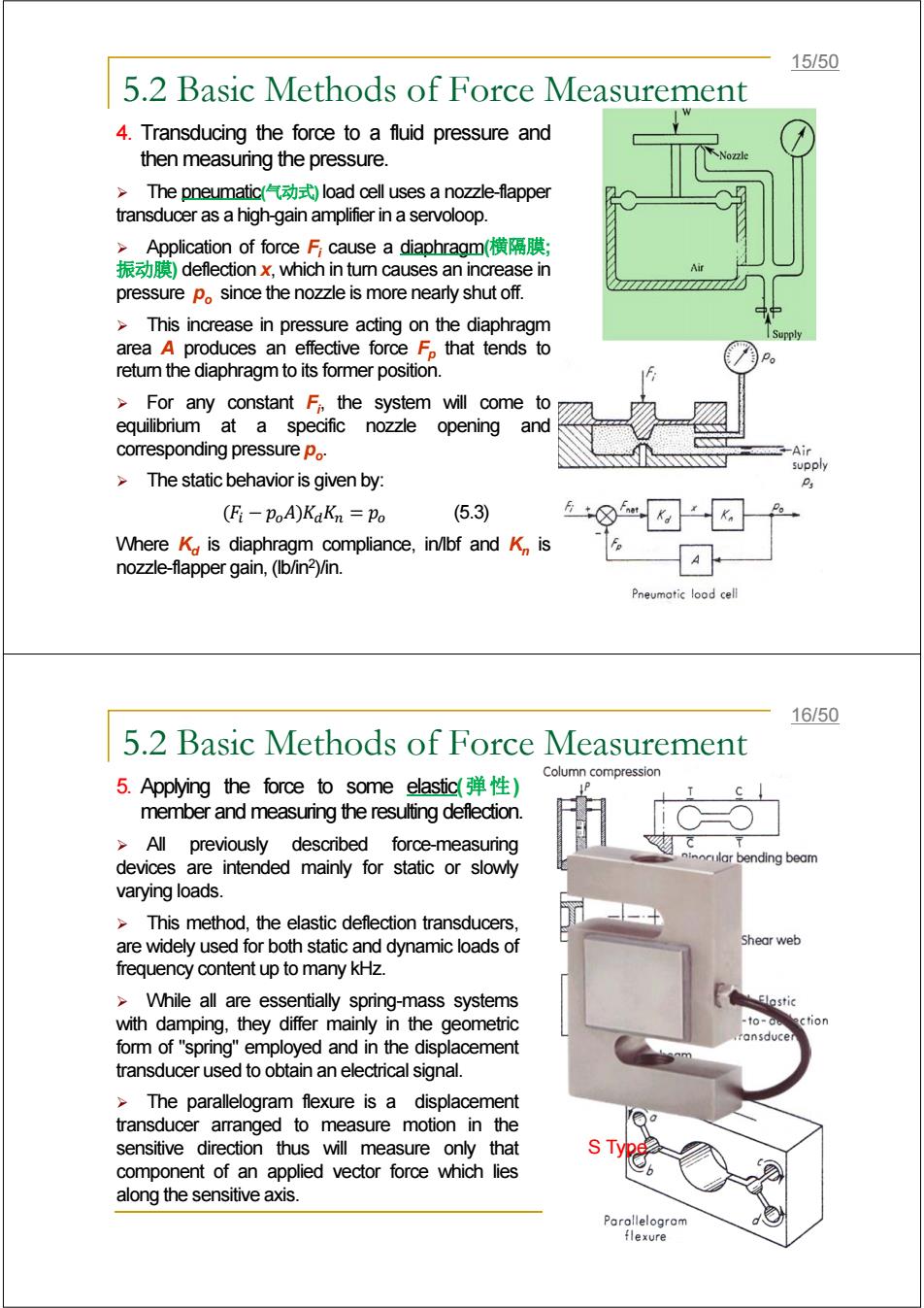
15/50 5.2 Basic Methods of Force Measurement 4.Transducing the force to a fluid pressure and then measuring the pressure. >The pneumatic(气动式load cell uses a nozzle-flapper transducer as a high-gain amplifier in a servoloop. >Application of force F cause a diaphragm(横隔膜; 振动膜)deflection x,which in tum causes an increase in pressure po since the nozzle is more nearly shut off. This increase in pressure acting on the diaphragm area A produces an effective force F that tends to retum the diaphragm to its former position. >For any constant F,the system will come to equilibrium at a specific nozzle opening and corresponding pressure po. -Air supply >The static behavior is given by: (Fi-PoA)KaKn Po (5.3) 8☑ Where K is diaphragm compliance,in/lbf and K,is nozzle-flapper gain,(Ib/in2)/in. Pneumotic lood cell 16/50 5.2 Basic Methods of Force Measurement Column compression 5.Applying the force to some elastic(弹性) member and measuring the resulting deflection. All previously described force-measuring incular bending beam devices are intended mainly for static or slowly varying loads. >This method,the elastic deflection transducers, are widely used for both static and dynamic loads of Shear web frequency content up to many kHz. While all are essentially spring-mass systems Elostic with damping,they differ mainly in the geometric -to-do ection .ransducer form of "spring"employed and in the displacement transducer used to obtain an electrical signal. The parallelogram flexure is a displacement transducer arranged to measure motion in the a sensitive direction thus will measure only that component of an applied vector force which lies sT along the sensitive axis. Parollelogram flexure5.2 Basic Methods of Force Measurement 4. Transducing the force to a fluid pressure and then measuring the pressure. ¾ The pneumatic(气动式)load cell uses a nozzle-flapper transducer as a high-gain amplifier in a servoloop. ¾ Application of force Fi cause a diaphragm(横隔膜; 振动膜) deflection x, which in turn causes an increase in pressure po since the nozzle is more nearly shut off. ¾ This increase in pressure acting on the diaphragm area A produces an effective force Fp that tends to return the diaphragm to its former position. ¾ For any constant Fi , the system will come to equilibrium at a specific nozzle opening and corresponding pressure po. ¾ The static behavior is given by: (3.5 ( = ܭௗܭ(ܣ − ܨ) Where Kd is diaphragm compliance, in/lbf and Kn is nozzle-flapper gain, (lb/in2)/in. 15/50 5.2 Basic Methods of Force Measurement 5. Applying the force to some elastic(弹性) member and measuring the resulting deflection. ¾ All previously described force-measuring devices are intended mainly for static or slowly varying loads. ¾ This method, the elastic deflection transducers, are widely used for both static and dynamic loads of frequency content up to many kHz. ¾ While all are essentially spring-mass systems with damping, they differ mainly in the geometric form of "spring" employed and in the displacement transducer used to obtain an electrical signal. ¾ The parallelogram flexure is a displacement transducer arranged to measure motion in the sensitive direction thus will measure only that component of an applied vector force which lies along the sensitive axis. S Type 16/50