正在加载图片...
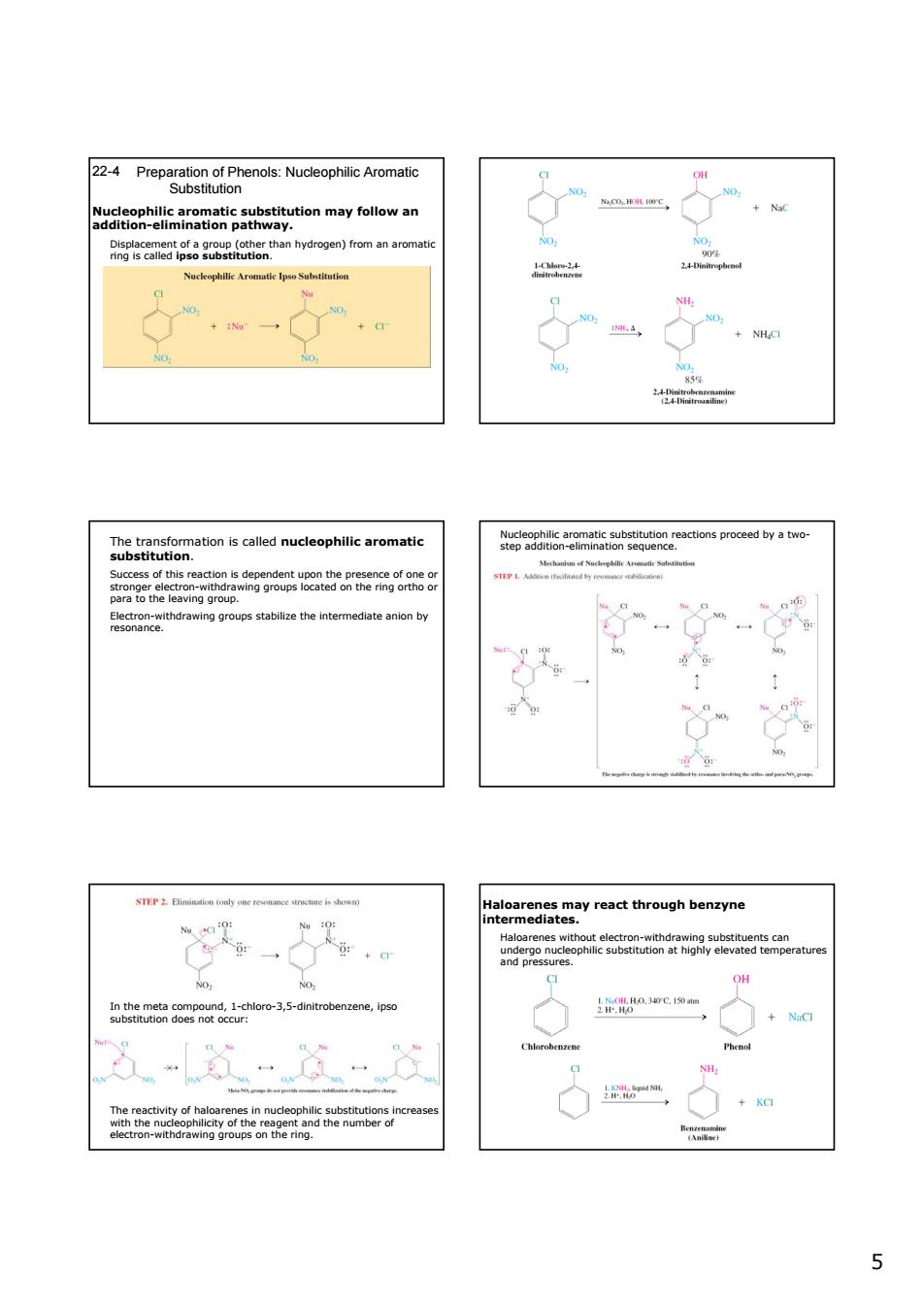
ay followan Na tn ydrge)from NO. tee3lSnamaaeaiutaeeacioasprocedbyatmwo TEP L A ara to the leaving group 8 hameasie2yreathroughbenane OH neme8edehioro-35-dntroenzene,psa 55 Preparation of Phenols: Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution 22-4 Nucleophilic aromatic substitution may follow an addition-elimination pathway. Displacement of a group (other than hydrogen) from an aromatic ring is called ipso substitution. The transformation is called nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Success of this reaction is dependent upon the presence of one or stronger electron-withdrawing groups located on the ring ortho or para to the leaving group. Electron-withdrawing groups stabilize the intermediate anion by resonance. Nucleophilic aromatic substitution reactions proceed by a twostep addition-elimination sequence. In the meta compound, 1-chloro-3,5-dinitrobenzene, ipso substitution does not occur: The reactivity of haloarenes in nucleophilic substitutions increases with the nucleophilicity of the reagent and the number of electron-withdrawing groups on the ring. Haloarenes may react through benzyne intermediates. Haloarenes without electron-withdrawing substituents can undergo nucleophilic substitution at highly elevated temperatures and pressures