正在加载图片...
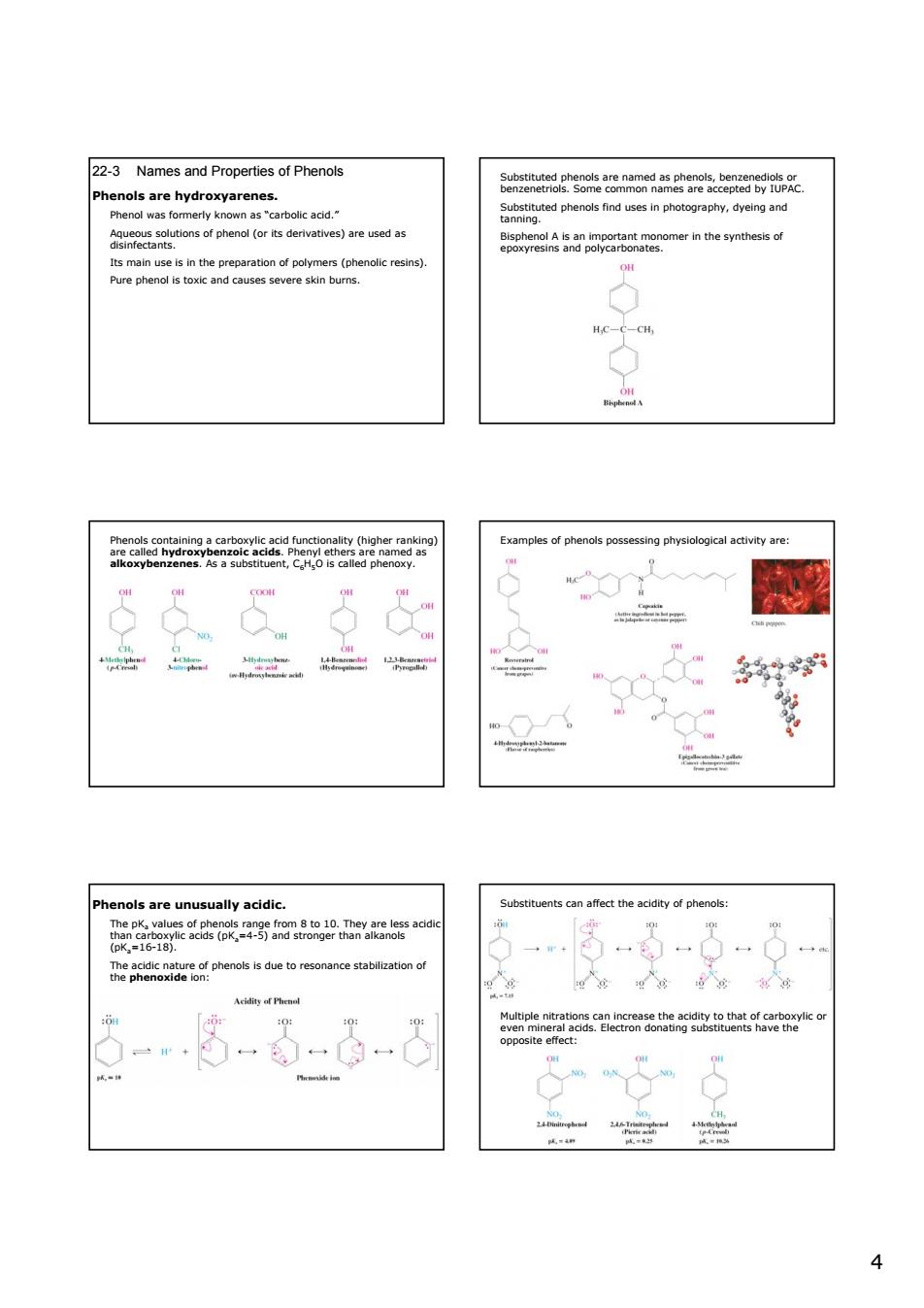
22-3 Names and Properties of Phenols mer in the synthess f HC-6-CH ples of phenols poss 5&. Phenols are unusually acidic Substituents can affect the acidity of phenols: 成gn0e DK. poa8rphenosstaetorsomnceb6aeatone a 4 4 22-3 Names and Properties of Phenols Phenols are hydroxyarenes. Phenol was formerly known as “carbolic acid.” Aqueous solutions of phenol (or its derivatives) are used as disinfectants. Its main use is in the preparation of polymers (phenolic resins). Pure phenol is toxic and causes severe skin burns. Substituted phenols are named as phenols, benzenediols or benzenetriols. Some common names are accepted by IUPAC. Substituted phenols find uses in photography, dyeing and tanning. Bisphenol A is an important monomer in the synthesis of epoxyresins and polycarbonates. Phenols containing a carboxylic acid functionality (higher ranking) are called hydroxybenzoic acids. Phenyl ethers are named as alkoxybenzenes. As a substituent, C6H5O is called phenoxy. Examples of phenols possessing physiological activity are: Phenols are unusually acidic. The pKa values of phenols range from 8 to 10. They are less acidic than carboxylic acids (pKa=4-5) and stronger than alkanols (pKa=16-18). The acidic nature of phenols is due to resonance stabilization of the phenoxide ion: Substituents can affect the acidity of phenols: Multiple nitrations can increase the acidity to that of carboxylic or even mineral acids. Electron donating substituents have the opposite effect: