正在加载图片...
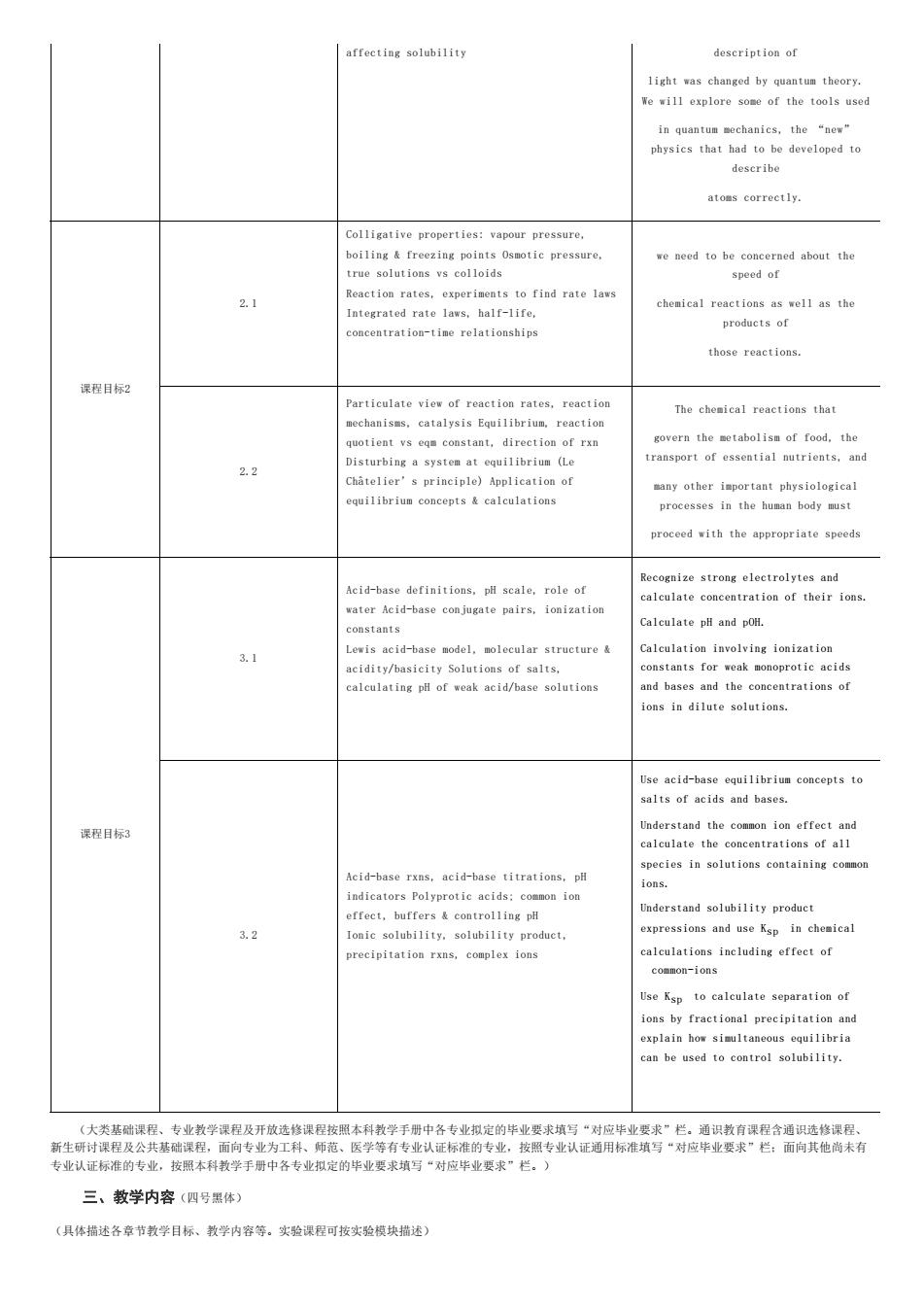
affecting solubility description of light was changed by quantun theory. eexplore some of the tools used describe atoms correctly. Colligative properties:vapour pressure. we need to he c 2.1 to find rate avs Integrated rate lavs,half-life. chenical reactions as well as the products of oncentration-tine relationships those reactions. 课程目标2 Particulate vies of reaction rates.reaction The chesical reactions that quotieat vse constant.direction of ran overs the tabolism of food,the transport of essestial mutrients,and 2.2 equilibriun concepts calculations proe proceed with the appropriate speeds Recognize strong electrolytes and Acid-hase definitions.pl scale.role of alculate concentration of their ioms ater Acid-base conjugate pairs,ionization alculate p日andp0H. 3.1 alculation inrolving ionization calculating pl of weak acid/base solutions nd bases and the concentrations of in dilute solutions Use acid-base equilibrium concepts to salts of acids and bases. 课程目标3 Understand the comron ion effect and calculate the concestrations of all Acid-base rxns.acid-base titrations, species in solutions contaiming coamo 32 onic solubilit solubility product, se ksp in chemica precipitation rxns,complex ions Use Ksp to calculate separation of ons by fraction lprecioitatioand can be used to comtrol solubility 条款物金 三、教学内容(四号黑体) (具体描述各章节教学目标、教学内容等。实验课程可按实验模块描透)affecting solubility description of light was changed by quantum theory. We will explore some of the tools used in quantum mechanics, the “new” physics that had to be developed to describe atoms correctly. 课程目标2 2.1 Colligative properties: vapour pressure, boiling & freezing points Osmotic pressure, true solutions vs colloids Reaction rates, experiments to find rate laws Integrated rate laws, half-life, concentration-time relationships we need to be concerned about the speed of chemical reactions as well as the products of those reactions. 2.2 Particulate view of reaction rates, reaction mechanisms, catalysis Equilibrium, reaction quotient vs eqm constant, direction of rxn Disturbing a system at equilibrium (Le Châtelier’s principle) Application of equilibrium concepts & calculations The chemical reactions that govern the metabolism of food, the transport of essential nutrients, and many other important physiological processes in the human body must proceed with the appropriate speeds 课程目标3 3.1 Acid-base definitions, pH scale, role of water Acid-base conjugate pairs, ionization constants Lewis acid-base model, molecular structure & acidity/basicity Solutions of salts, calculating pH of weak acid/base solutions Recognize strong electrolytes and calculate concentration of their ions. Calculate pH and pOH. Calculation involving ionization constants for weak monoprotic acids and bases and the concentrations of ions in dilute solutions. 3.2 Acid-base rxns, acid-base titrations, pH indicators Polyprotic acids; common ion effect, buffers & controlling pH Ionic solubility, solubility product, precipitation rxns, complex ions Use acid-base equilibrium concepts to salts of acids and bases. Understand the common ion effect and calculate the concentrations of all species in solutions containing common ions. Understand solubility product expressions and use Ksp in chemical calculations including effect of common-ions Use Ksp to calculate separation of ions by fractional precipitation and explain how simultaneous equilibria can be used to control solubility. (大类基础课程、专业教学课程及开放选修课程按照本科教学手册中各专业拟定的毕业要求填写“对应毕业要求”栏。通识教育课程含通识选修课程、 新生研讨课程及公共基础课程,面向专业为工科、师范、医学等有专业认证标准的专业,按照专业认证通用标准填写“对应毕业要求”栏;面向其他尚未有 专业认证标准的专业,按照本科教学手册中各专业拟定的毕业要求填写“对应毕业要求”栏。) 三、教学内容(四号黑体) (具体描述各章节教学目标、教学内容等。实验课程可按实验模块描述)