正在加载图片...
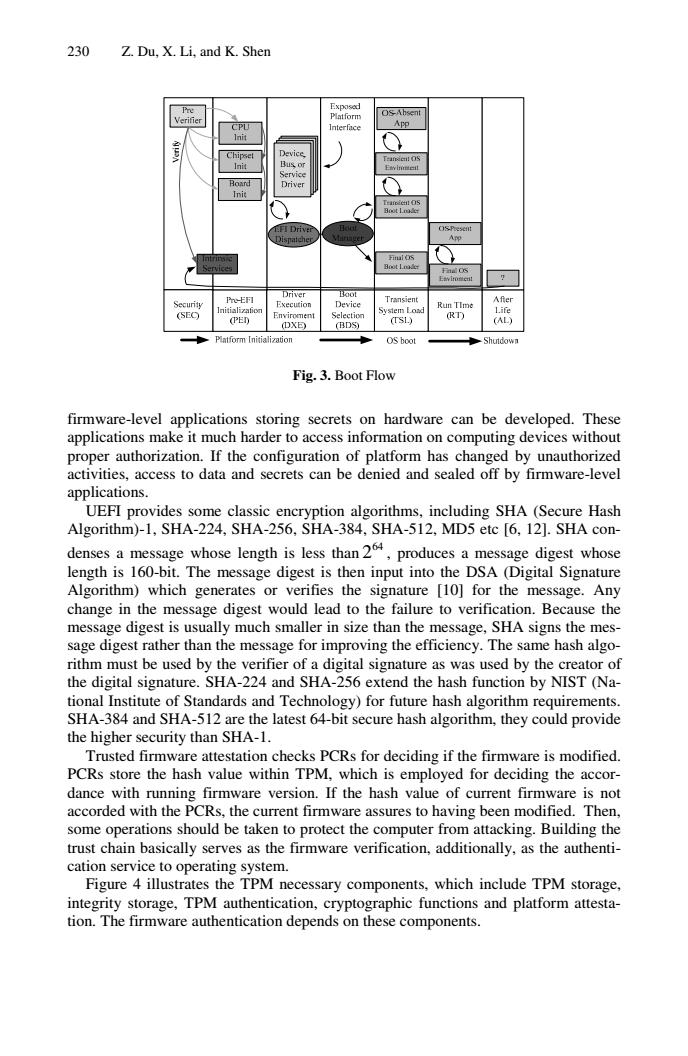
230 Z.Du,X.Li,and K.Shen Exposed Verifier Platform CPU Interface App Init Chipset Device. Tnc O5 Init Bus or Ewimeeil Service Roard Driver Init Tearpiet OS 80t1.a E月DriveP OS-Pesent App Boot Lnode Driver Boot Transient Security he-EF刊 Execution Device After Run TIme (SEO (PED Selectior (TSL) (RT) (DXE) (BDS) Platform Initialization OS boot Fig.3.Boot Flow firmware-level applications storing secrets on hardware can be developed.These applications make it much harder to access information on computing devices without proper authorization.If the configuration of platform has changed by unauthorized activities,access to data and secrets can be denied and sealed off by firmware-level applications. UEFI provides some classic encryption algorithms,including SHA(Secure Hash Algorithm)-1,SHA-224,SHA-256,SHA-384,SHA-512,MD5 etc [6,12].SHA con- denses a message whose length is less than2,produces a message digest whose length is 160-bit.The message digest is then input into the DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm)which generates or verifies the signature [10]for the message.Any change in the message digest would lead to the failure to verification.Because the message digest is usually much smaller in size than the message,SHA signs the mes- sage digest rather than the message for improving the efficiency.The same hash algo- rithm must be used by the verifier of a digital signature as was used by the creator of the digital signature.SHA-224 and SHA-256 extend the hash function by NIST (Na- tional Institute of Standards and Technology)for future hash algorithm requirements. SHA-384 and SHA-512 are the latest 64-bit secure hash algorithm,they could provide the higher security than SHA-1. Trusted firmware attestation checks PCRs for deciding if the firmware is modified. PCRs store the hash value within TPM,which is employed for deciding the accor- dance with running firmware version.If the hash value of current firmware is not accorded with the PCRs,the current firmware assures to having been modified.Then, some operations should be taken to protect the computer from attacking.Building the trust chain basically serves as the firmware verification,additionally,as the authenti- cation service to operating system. Figure 4 illustrates the TPM necessary components,which include TPM storage, integrity storage,TPM authentication,cryptographic functions and platform attesta- tion.The firmware authentication depends on these components.230 Z. Du, X. Li, and K. Shen Verify Fig. 3. Boot Flow firmware-level applications storing secrets on hardware can be developed. These applications make it much harder to access information on computing devices without proper authorization. If the configuration of platform has changed by unauthorized activities, access to data and secrets can be denied and sealed off by firmware-level applications. UEFI provides some classic encryption algorithms, including SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm)-1, SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512, MD5 etc [6, 12]. SHA condenses a message whose length is less than 64 2 , produces a message digest whose length is 160-bit. The message digest is then input into the DSA (Digital Signature Algorithm) which generates or verifies the signature [10] for the message. Any change in the message digest would lead to the failure to verification. Because the message digest is usually much smaller in size than the message, SHA signs the message digest rather than the message for improving the efficiency. The same hash algorithm must be used by the verifier of a digital signature as was used by the creator of the digital signature. SHA-224 and SHA-256 extend the hash function by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) for future hash algorithm requirements. SHA-384 and SHA-512 are the latest 64-bit secure hash algorithm, they could provide the higher security than SHA-1. Trusted firmware attestation checks PCRs for deciding if the firmware is modified. PCRs store the hash value within TPM, which is employed for deciding the accordance with running firmware version. If the hash value of current firmware is not accorded with the PCRs, the current firmware assures to having been modified. Then, some operations should be taken to protect the computer from attacking. Building the trust chain basically serves as the firmware verification, additionally, as the authentication service to operating system. Figure 4 illustrates the TPM necessary components, which include TPM storage, integrity storage, TPM authentication, cryptographic functions and platform attestation. The firmware authentication depends on these components