正在加载图片...
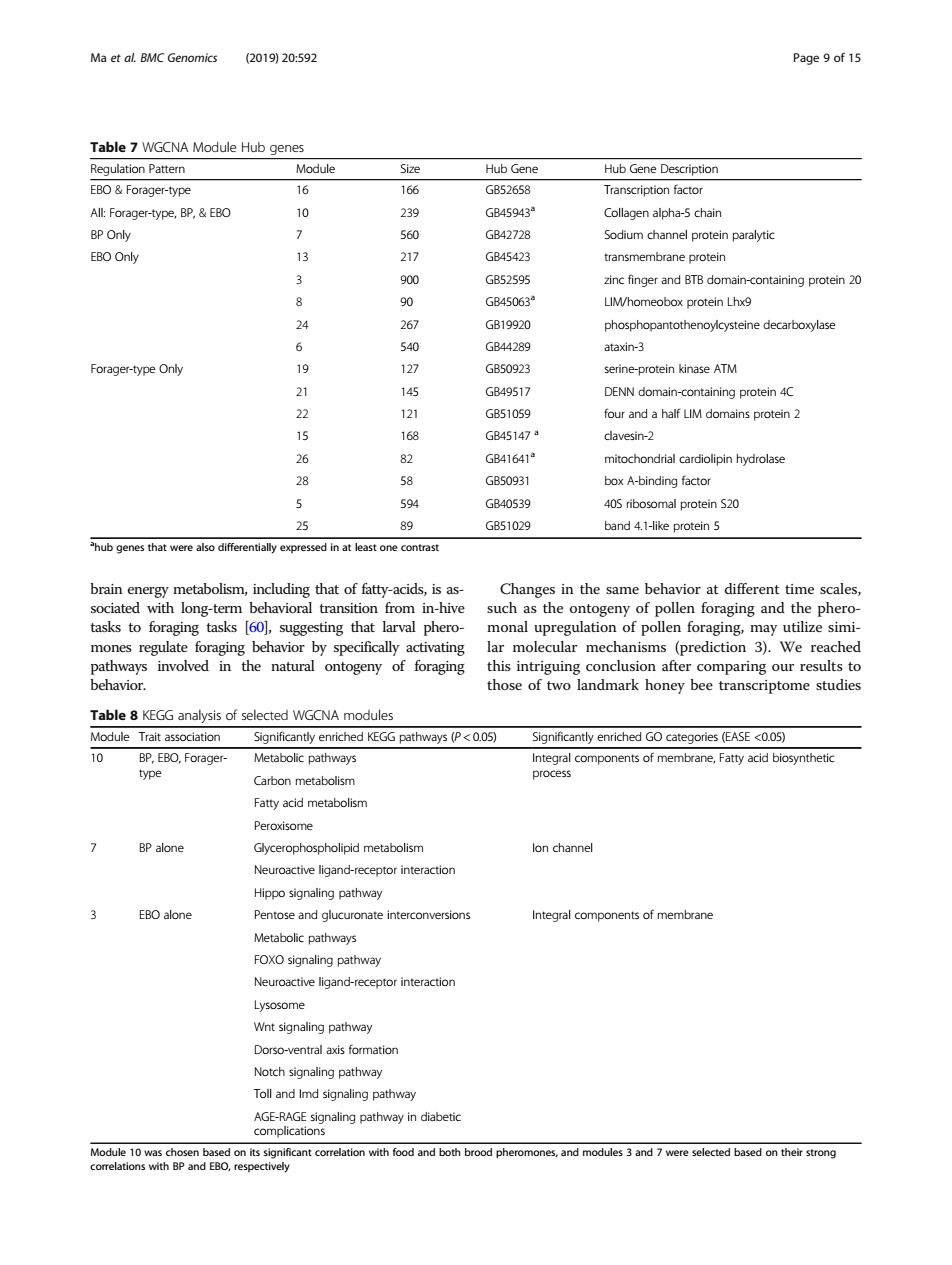
Ma et aL BMC Genomics (2019)20:592 Page 9 of 15 Table7 WGCNA Module Hub genes Hub Gene Description A Forager-type.BP& B45943 BP Onhy GB42728 Sodium channel protein paralytic EBO Only 13 217 G4542 transmembrane protein 900 GB52595 zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 20 GB45063 LIMhomeobox protein Lhx9 24 267 GB19920 phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase 540 GB44289 ataxin3 Forager-type Only 19 127 GB50823 rotein kinase ATM 21 CB49517 DENN G851059 omains pro 1 GB45147 18 inding factor GB40539 405 ribosomal protein S20 25 89 GB51029 band 4.1-ike protein 5 that were o iffe ntially expressed in at least one contrast .that of fatty-acids s as e scale tasks to foragin asks 601.sugg sting that larval pherd nonal mones regulate for ging behavior by specifically activating this intriguing after hose of two andmark honey bee transcriptome stuc Table 8 KEGG analysis of selected WGCNA modules y5P<00 (EASE <005) on meta Fatty acid metabolisn BP alone Glycerophospholipid metabolism lon channel Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction Hipoo signaling pathway EBO alone Pentose and clucuronate interconversion Intearal components of membrane Metabolic pathwavs FOXO signaling pathway Neuroactive ligand-rec Notch signaling pathway Toll and Imd signaling pathway Modle 10oncant corelation h ood and bo brood pheromones and modesandere selected aed on ther strong brain energy metabolism, including that of fatty-acids, is associated with long-term behavioral transition from in-hive tasks to foraging tasks [60], suggesting that larval pheromones regulate foraging behavior by specifically activating pathways involved in the natural ontogeny of foraging behavior. Changes in the same behavior at different time scales, such as the ontogeny of pollen foraging and the pheromonal upregulation of pollen foraging, may utilize similar molecular mechanisms (prediction 3). We reached this intriguing conclusion after comparing our results to those of two landmark honey bee transcriptome studies Table 7 WGCNA Module Hub genes Regulation Pattern Module Size Hub Gene Hub Gene Description EBO & Forager-type 16 166 GB52658 Transcription factor All: Forager-type, BP, & EBO 10 239 GB45943a Collagen alpha-5 chain BP Only 7 560 GB42728 Sodium channel protein paralytic EBO Only 13 217 GB45423 transmembrane protein 3 900 GB52595 zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 20 8 90 GB45063a LIM/homeobox protein Lhx9 24 267 GB19920 phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase 6 540 GB44289 ataxin-3 Forager-type Only 19 127 GB50923 serine-protein kinase ATM 21 145 GB49517 DENN domain-containing protein 4C 22 121 GB51059 four and a half LIM domains protein 2 15 168 GB45147 a clavesin-2 26 82 GB41641a mitochondrial cardiolipin hydrolase 28 58 GB50931 box A-binding factor 5 594 GB40539 40S ribosomal protein S20 25 89 GB51029 band 4.1-like protein 5 a hub genes that were also differentially expressed in at least one contrast Table 8 KEGG analysis of selected WGCNA modules Module Trait association Significantly enriched KEGG pathways (P < 0.05) Significantly enriched GO categories (EASE <0.05) 10 BP, EBO, Foragertype Metabolic pathways Integral components of membrane, Fatty acid biosynthetic process Carbon metabolism Fatty acid metabolism Peroxisome 7 BP alone Glycerophospholipid metabolism Ion channel Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction Hippo signaling pathway 3 EBO alone Pentose and glucuronate interconversions Integral components of membrane Metabolic pathways FOXO signaling pathway Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction Lysosome Wnt signaling pathway Dorso-ventral axis formation Notch signaling pathway Toll and Imd signaling pathway AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications Module 10 was chosen based on its significant correlation with food and both brood pheromones, and modules 3 and 7 were selected based on their strong correlations with BP and EBO, respectively Ma et al. BMC Genomics (2019) 20:592 Page 9 of 15