正在加载图片...
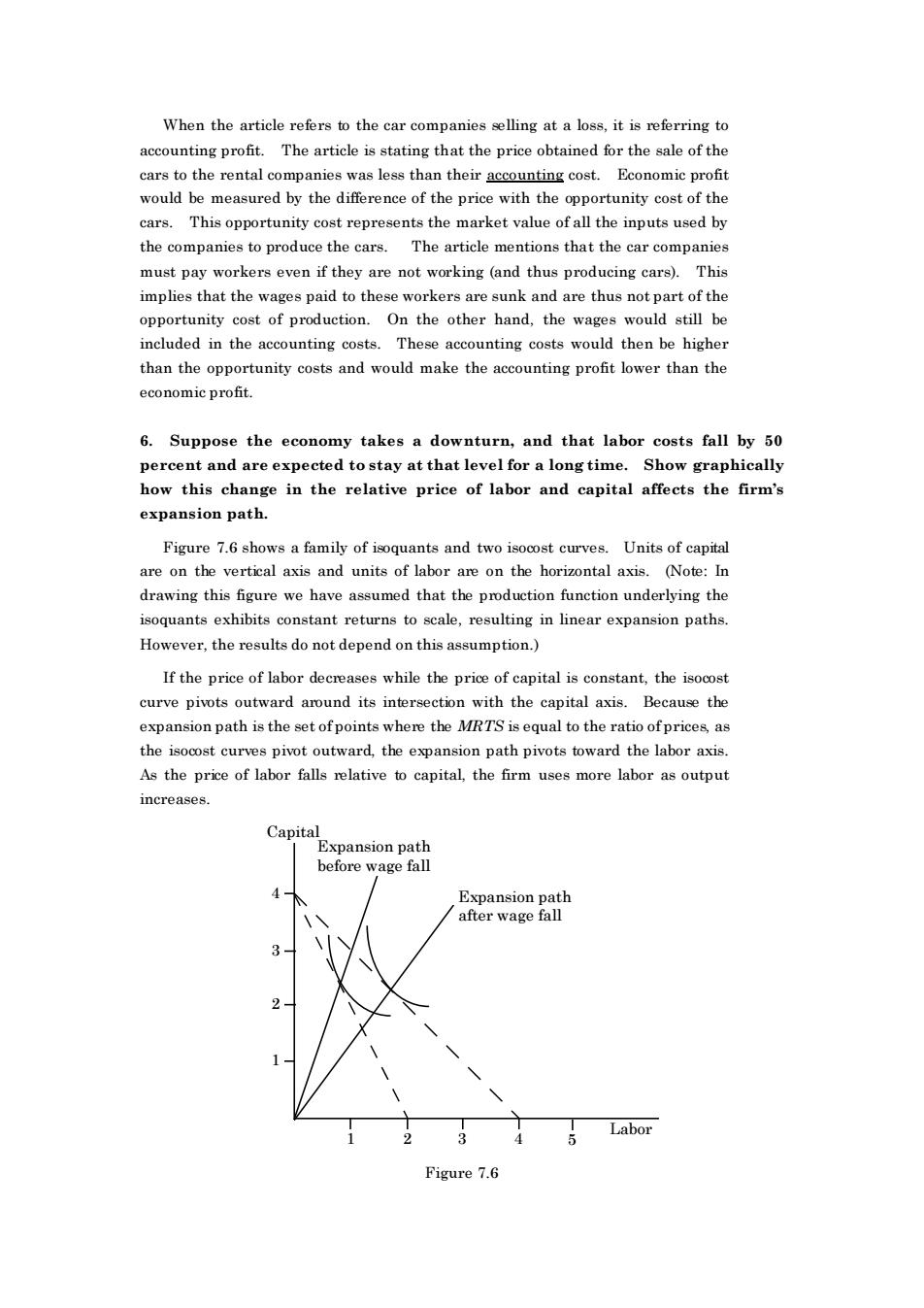
When the article refers to the car companies selling at a loss,it is referring to accounting profit.The article is stating that the price obtained for the sale of the cars to the rental companies was less than theirac inting cost. Economie prof would be measured by the difference of the price with the opportunity cost of th cars.This opportunity cost represents the market value of all the inputs used by the companies to produce the cars.The article mentions that the car companies must pay workers even if they are not working(and thus producing cars). This implies that the to these workerre dare thus notpart opportnitotO the atherd.the included in the accounting costs.These accounting costs would then be higher than the opportunity costs and would make the accounting profit lower than the economic profit. 6.Suppose the economy takes a downturn,and that labor costs fall by 50 percent and are expected to stay at that level for a long time.Show graphically how this change in the relative price of labor and capital affects the firm's expansion path. Figure 7.6 shows a family of isoquants and two isocost curves.Units of capital function underlying th isoquants exhibits constant returns to scale,resulting in linear expansion paths However.the results do not depend on this assumption.) If the price of labor decreases while the price of capital is constant.the isocost curve pivots outward around its intersection with the capital axis.Because the expansion path is the set of points where the ratio of pricesas es pivo outward,the expanion path pivots toward the labor axis As the price of labor falls relative to capital,the firm uses more labor as output increases. Capital Expansion path before wage fall Labo Figure 7.6 When the article refers to the car companies selling at a loss, it is referring to accounting profit. The article is stating that the price obtained for the sale of the cars to the rental companies was less than their accounting cost. Economic profit would be measured by the difference of the price with the opportunity cost of the cars. This opportunity cost represents the market value of all the inputs used by the companies to produce the cars. The article mentions that the car companies must pay workers even if they are not working (and thus producing cars). This implies that the wages paid to these workers are sunk and are thus not part of the opportunity cost of production. On the other hand, the wages would still be included in the accounting costs. These accounting costs would then be higher than the opportunity costs and would make the accounting profit lower than the economic profit. 6. Suppose the economy takes a downturn, and that labor costs fall by 50 percent and are expected to stay at that level for a long time. Show graphically how this change in the relative price of labor and capital affects the firm’s expansion path. Figure 7.6 shows a family of isoquants and two isocost curves. Units of capital are on the vertical axis and units of labor are on the horizontal axis. (Note: In drawing this figure we have assumed that the production function underlying the isoquants exhibits constant returns to scale, resulting in linear expansion paths. However, the results do not depend on this assumption.) If the price of labor decreases while the price of capital is constant, the isocost curve pivots outward around its intersection with the capital axis. Because the expansion path is the set of points where the MRTS is equal to the ratio of prices, as the isocost curves pivot outward, the expansion path pivots toward the labor axis. As the price of labor falls relative to capital, the firm uses more labor as output increases. Capital Labor 2 1 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 Expansion path before wage fall Expansion path after wage fall Figure 7.6